Epigenetic regulation of stress responses in plants
- PMID: 19179104
- PMCID: PMC3139470
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pbi.2008.12.006
Epigenetic regulation of stress responses in plants
Abstract
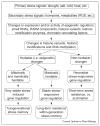
Gene expression driven by developmental and stress cues often depends on nucleosome histone post-translational modifications and sometimes on DNA methylation. A number of studies have shown that these DNA and histone modifications play a key role in gene expression and plant development under stress. Most of these stress-induced modifications are reset to the basal level once the stress is relieved, while some of the modifications may be stable, that is, may be carried forward as 'stress memory' and may be inherited across mitotic or even meiotic cell divisions. Epigenetic stress memory may help plants more effectively cope with subsequent stresses. Comparative studies on stress-responsive epigenomes and transcriptomes will enhance our understanding of stress adaptation of plants.
Conflict of interest statement
There is no conflict of interest relating to this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Epigenomics in stress tolerance of plants under the climate change.Mol Biol Rep. 2023 Jul;50(7):6201-6216. doi: 10.1007/s11033-023-08539-6. Epub 2023 Jun 9. Mol Biol Rep. 2023. PMID: 37294468 Review.
-
Epigenetic memory and priming in plants.Genetica. 2020 Apr;148(2):47-54. doi: 10.1007/s10709-020-00093-4. Epub 2020 Apr 30. Genetica. 2020. PMID: 32356021 Review.
-
A review of the potential involvement of small RNAs in transgenerational abiotic stress memory in plants.Funct Integr Genomics. 2024 Apr 11;24(2):74. doi: 10.1007/s10142-024-01354-7. Funct Integr Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38600306 Review.
-
Plants' Epigenetic Mechanisms and Abiotic Stress.Genes (Basel). 2021 Jul 21;12(8):1106. doi: 10.3390/genes12081106. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34440280 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic memory for stress response and adaptation in plants.Plant Cell Physiol. 2014 Nov;55(11):1859-63. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcu125. Epub 2014 Oct 8. Plant Cell Physiol. 2014. PMID: 25298421 Review.
Cited by
-
Performance and Genetic Parameters of Poplar Hybrids and Clones in a Field Trial Are Modified by Contrasting Environmental Conditions during the Vegetative Propagation Phase.Plants (Basel). 2022 Sep 15;11(18):2401. doi: 10.3390/plants11182401. Plants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36145802 Free PMC article.
-
m6A RNA Methylation in Marine Plants: First Insights and Relevance for Biological Rhythms.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Oct 12;21(20):7508. doi: 10.3390/ijms21207508. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33053767 Free PMC article.
-
CRISPR for accelerating genetic gains in under-utilized crops of the drylands: Progress and prospects.Front Genet. 2022 Oct 6;13:999207. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.999207. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 36276961 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic Diversity of Clonal White Poplar (Populus alba L.) Populations: Could Methylation Support the Success of Vegetative Reproduction Strategy?PLoS One. 2015 Jul 6;10(7):e0131480. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0131480. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26147352 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide identification of regulatory DNA elements and protein-binding footprints using signatures of open chromatin in Arabidopsis.Plant Cell. 2012 Jul;24(7):2719-31. doi: 10.1105/tpc.112.098061. Epub 2012 Jul 5. Plant Cell. 2012. PMID: 22773751 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Thomashow MF. Plant cold acclimation: freezing tolerance genes and regulatory mechanisms. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol. 1999;50:571–599. - PubMed
-
- Iba K. Acclimative response to temperature stress in higher plants: approaches of gene engineering for temperature tolerance. Annu Rev Plant Biol. 2002;53:225–245. - PubMed
-
- Sridhar VV, Kapoor A, Zhang K, Zhu J, Zhou T, Hasegawa PM, Bressan RA, Zhu JK. Control of DNA methylation and heterochromatic silencing by histone H2B deubiquitination. Nature. 2007;447:735–738. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

