{beta}-Arrestin-2 Mediates Anti-apoptotic Signaling through Regulation of BAD Phosphorylation
- PMID: 19171933
- PMCID: PMC2659243
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M808463200
{beta}-Arrestin-2 Mediates Anti-apoptotic Signaling through Regulation of BAD Phosphorylation
Abstract
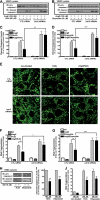
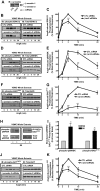
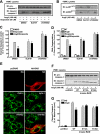
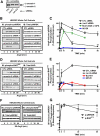
beta-Arrestins, originally discovered as terminators of G protein-coupled receptor signaling, have more recently been appreciated to also function as signal transducers in their own right, although the consequences for cellular physiology have not been well understood. Here we demonstrate that beta-arrestin-2 mediates anti-apoptotic cytoprotective signaling stimulated by a typical 7-transmembrane receptor the angiotensin ATII 1A receptor, expressed endogenously in rat vascular smooth muscle cells or by transfection in HEK-293 cells. Receptor stimulation leads to concerted activation of two pathways, ERK/p90RSK and PI3K/AKT, which converge to phosphorylate and inactivate the pro-apoptotic protein BAD. Anti-apoptotic effects as well as pathway activities can be stimulated by an angiotensin analog (SII), which has been previously shown to activate beta-arrestin but not G protein-dependent signaling, and are abrogated by beta-arrestin-2 small interfering RNA. These findings establish a key role for beta-arrestin-2 in mediating cellular cytoprotective functions by a 7-transmembrane receptor and define the biochemical pathways involved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Independent beta-arrestin2 and Gq/protein kinase Czeta pathways for ERK stimulated by angiotensin type 1A receptors in vascular smooth muscle cells converge on transactivation of the epidermal growth factor receptor.J Biol Chem. 2009 May 1;284(18):11953-62. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M808176200. Epub 2009 Mar 2. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19254952 Free PMC article.
-
Arrestin-dependent angiotensin AT1 receptor signaling regulates Akt and mTor-mediated protein synthesis.J Biol Chem. 2014 Sep 19;289(38):26155-26166. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.595728. Epub 2014 Jul 31. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 25081544 Free PMC article.
-
Stable interaction between beta-arrestin 2 and angiotensin type 1A receptor is required for beta-arrestin 2-mediated activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1 and 2.J Biol Chem. 2004 Nov 12;279(46):48255-61. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M406205200. Epub 2004 Sep 7. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15355986
-
Emerging paradigms of β-arrestin-dependent seven transmembrane receptor signaling.Trends Biochem Sci. 2011 Sep;36(9):457-69. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2011.06.003. Epub 2011 Jul 20. Trends Biochem Sci. 2011. PMID: 21764321 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Beta-arrestin-mediated signaling in the heart.Circ J. 2008 Nov;72(11):1725-9. doi: 10.1253/circj.cj-08-0734. Epub 2008 Oct 7. Circ J. 2008. PMID: 18838825 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
GRK2 and β-arrestins in cardiovascular disease: Something old, something new.Am J Cardiovasc Dis. 2011;1(2):126-37. Epub 2011 Jun 28. Am J Cardiovasc Dis. 2011. PMID: 22254193 Free PMC article.
-
Arrestin orchestrates crosstalk between G protein-coupled receptors to modulate the spatiotemporal activation of ERK MAPK.Circ Res. 2010 Jan 8;106(1):79-88. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.109.198580. Epub 2009 Nov 19. Circ Res. 2010. PMID: 19926878 Free PMC article.
-
G-protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 and endothelial dysfunction: molecular insights and pathophysiological mechanisms.J Smooth Muscle Res. 2015;51:37-49. doi: 10.1540/jsmr.51.37. J Smooth Muscle Res. 2015. PMID: 26447102 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Diverse Roles of Arrestin Scaffolds in G Protein-Coupled Receptor Signaling.Pharmacol Rev. 2017 Jul;69(3):256-297. doi: 10.1124/pr.116.013367. Pharmacol Rev. 2017. PMID: 28626043 Free PMC article. Review.
-
G protein-coupled receptor signaling: transducers and effectors.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2022 Sep 1;323(3):C731-C748. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00210.2022. Epub 2022 Jul 11. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35816644 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- DeWire, S. M., Ahn, S., Lefkowitz, R. J., and Shenoy, S. K. (2007) Annu. Rev. Physiol. 69 483-510 - PubMed
-
- Shi, Y., Feng, Y., Kang, J., Liu, C., Li, Z., Li, D., Cao, W., Qiu, J., Guo, Z., Bi, E., Zang, L., Lu, C., Zhang, J. Z., and Pei, G. (2007) Nat. Immunol. 8 817-824 - PubMed
-
- Zhao, M., Wimmer, A., Trieu, K., Discipio, R. G., and Schraufstatter, I. U. (2004) J. Biol. Chem. 279 49259-49267 - PubMed
-
- Revankar, C. M., Vines, C. M., Cimino, D. F., and Prossnitz, E. R. (2004) J. Biol. Chem. 279 24578-24584 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

