Large-scale structural analysis of the classical human protein tyrosine phosphatome
- PMID: 19167335
- PMCID: PMC2638020
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.11.038
Large-scale structural analysis of the classical human protein tyrosine phosphatome
Abstract
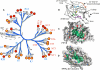
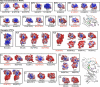
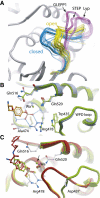
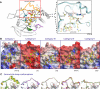
Protein tyrosine phosphatases (PTPs) play a critical role in regulating cellular functions by selectively dephosphorylating their substrates. Here we present 22 human PTP crystal structures that, together with prior structural knowledge, enable a comprehensive analysis of the classical PTP family. Despite their largely conserved fold, surface properties of PTPs are strikingly diverse. A potential secondary substrate-binding pocket is frequently found in phosphatases, and this has implications for both substrate recognition and development of selective inhibitors. Structural comparison identified four diverse catalytic loop (WPD) conformations and suggested a mechanism for loop closure. Enzymatic assays revealed vast differences in PTP catalytic activity and identified PTPD1, PTPD2, and HDPTP as catalytically inert protein phosphatases. We propose a "head-to-toe" dimerization model for RPTPgamma/zeta that is distinct from the "inhibitory wedge" model and that provides a molecular basis for inhibitory regulation. This phosphatome resource gives an expanded insight into intrafamily PTP diversity, catalytic activity, substrate recognition, and autoregulatory self-association.
Figures

Comment in
-
The PTP family photo album.Cell. 2009 Jan 23;136(2):213-4. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.01.006. Cell. 2009. PMID: 19167325
Similar articles
-
Crystal structure of PTP-SL/PTPBR7 catalytic domain: implications for MAP kinase regulation.J Mol Biol. 2001 Aug 17;311(3):557-68. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.2001.4890. J Mol Biol. 2001. PMID: 11493009
-
Crystal structures and inhibitor identification for PTPN5, PTPRR and PTPN7: a family of human MAPK-specific protein tyrosine phosphatases.Biochem J. 2006 May 1;395(3):483-91. doi: 10.1042/BJ20051931. Biochem J. 2006. PMID: 16441242 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structure of the catalytic domain of protein-tyrosine phosphatase SHP-1.J Biol Chem. 1998 Oct 23;273(43):28199-207. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.43.28199. J Biol Chem. 1998. PMID: 9774441
-
Mechanistic studies on protein tyrosine phosphatases.Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 2003;73:171-220. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(03)01006-7. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 2003. PMID: 12882518 Review.
-
An overview of the protein tyrosine phosphatase superfamily.Curr Top Med Chem. 2003;3(7):739-48. doi: 10.2174/1568026033452302. Curr Top Med Chem. 2003. PMID: 12678841 Review.
Cited by
-
Receptor-type protein-tyrosine phosphatase ζ is a functional receptor for interleukin-34.J Biol Chem. 2013 Jul 26;288(30):21972-86. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.442731. Epub 2013 Jun 6. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23744080 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of BET bromodomains as a therapeutic strategy for cancer drug discovery.Oncotarget. 2015 Mar 20;6(8):5501-16. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3551. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 25849938 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structure and function of the intracellular region of the plexin-b1 transmembrane receptor.J Biol Chem. 2009 Dec 18;284(51):35962-72. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.056275. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19843518 Free PMC article.
-
High-resolution crystal structures of the D1 and D2 domains of protein tyrosine phosphatase epsilon for structure-based drug design.Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol. 2018 Oct 1;74(Pt 10):1015-1026. doi: 10.1107/S2059798318011919. Epub 2018 Oct 2. Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol. 2018. PMID: 30289412 Free PMC article.
-
Computational Strategy for Bound State Structure Prediction in Structure-Based Virtual Screening: A Case Study of Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase Receptor Type O Inhibitors.J Chem Inf Model. 2018 Nov 26;58(11):2331-2342. doi: 10.1021/acs.jcim.8b00548. Epub 2018 Oct 19. J Chem Inf Model. 2018. PMID: 30299094 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alonso A., Sasin J., Bottini N., Friedberg I., Friedberg I., Osterman A., Godzik A., Hunter T., Dixon J., Mustelin T. Protein tyrosine phosphatases in the human genome. Cell. 2004;117:699–711. - PubMed
-
- Aricescu A.R., Siebold C., Choudhuri K., Chang V.T., Lu W., Davis S.J., van der Merwe P.A., Jones E.Y. Structure of a tyrosine phosphatase adhesive interaction reveals a spacer-clamp mechanism. Science. 2007;317:1217–1220. - PubMed
-
- Barford D., Das A.K., Egloff M.P. The structure and mechanism of protein phosphatases: insights into catalysis and regulation. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 1998;27:133–164. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

