Medium- and high-throughput screening of neurotoxicants using C. elegans
- PMID: 19166924
- PMCID: PMC2819467
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ntt.2008.12.004
Medium- and high-throughput screening of neurotoxicants using C. elegans
Abstract
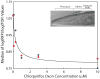
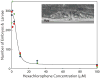
The U.S. National Toxicology Program, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, and other national and international agencies are committing significant resources towards the development of alternative species to be used as replacements for mammalian models in toxicological studies. Caenorhabditis elegans is a well-characterized soil nematode that is becoming a useful model in the assessment of neurotoxicants. To determine the effects of potential neurotoxicants on C. elegans, four medium-throughput (feeding, growth, reproduction and locomotion) and two high-throughput (growth and reproduction) assays have been developed. Three of these assays use the COPAS Biosort, a flow cytometer capable of rapidly measuring thousands of nematodes in minutes. Medium-throughput feeding, growth, and reproduction assays were used to assess the toxicity of eight suspected neurotoxicants. For several of the neurotoxicants examined, significant effects were observed at similar concentrations between assays. High-throughput reproduction and growth assays were used to estimate the toxicity of thousands of chemicals in two libraries. These assays will prove useful in evaluating the role of alternative toxicological models in tiered toxicity testing of thousands of chemicals.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures


Similar articles
-
High-Throughput Measurement for Toxic Effects of Metal Mixtures in Caenorhabditis elegans.Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2326:19-32. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1514-0_2. Methods Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 34097258
-
A high-throughput method for assessing chemical toxicity using a Caenorhabditis elegans reproduction assay.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2010 Jun 1;245(2):153-9. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2010.02.014. Epub 2010 Mar 4. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20206647 Free PMC article.
-
High-throughput COPAS assay for screening of developmental and reproductive toxicity of nanoparticles using the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans.J Appl Toxicol. 2019 Oct;39(10):1470-1479. doi: 10.1002/jat.3833. Epub 2019 Jul 9. J Appl Toxicol. 2019. PMID: 31287177
-
Utility of Caenorhabditis elegans in high throughput neurotoxicological research.Neurotoxicol Teratol. 2010 Jan-Feb;32(1):62-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ntt.2008.11.005. Epub 2008 Dec 7. Neurotoxicol Teratol. 2010. PMID: 19087888 Review.
-
Drosophotoxicology: the growing potential for Drosophila in neurotoxicology.Neurotoxicol Teratol. 2010 Jan-Feb;32(1):74-83. doi: 10.1016/j.ntt.2009.06.004. Epub 2009 Jun 24. Neurotoxicol Teratol. 2010. PMID: 19559084 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
From the Cover: Arsenite Uncouples Mitochondrial Respiration and Induces a Warburg-like Effect in Caenorhabditis elegans.Toxicol Sci. 2016 Aug;152(2):349-62. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfw093. Epub 2016 May 20. Toxicol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27208080 Free PMC article.
-
A discrete time model for the analysis of medium-throughput C. elegans growth data.PLoS One. 2009 Sep 15;4(9):e7018. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0007018. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19753303 Free PMC article.
-
Microfluidic Device to Measure the Speed of C. elegans Using the Resistance Change of the Flexible Electrode.Micromachines (Basel). 2016 Mar 19;7(3):50. doi: 10.3390/mi7030050. Micromachines (Basel). 2016. PMID: 30407423 Free PMC article.
-
Caenorhabditis elegans as a tool for environmental risk assessment: emerging and promising applications for a "nobelized worm".Crit Rev Toxicol. 2019 May;49(5):411-429. doi: 10.1080/10408444.2019.1626801. Epub 2019 Jul 3. Crit Rev Toxicol. 2019. PMID: 31268799 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mitochondria as a target of organophosphate and carbamate pesticides: Revisiting common mechanisms of action with new approach methodologies.Reprod Toxicol. 2019 Oct;89:83-92. doi: 10.1016/j.reprotox.2019.07.007. Epub 2019 Jul 14. Reprod Toxicol. 2019. PMID: 31315019 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Albertson DG, Thomson JN. The pharynx of Caenorhabditis elegans. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1976;275:299–325. - PubMed
-
- Altun ZF, Hall DH. WormAtlas. 20022006
-
- Anderson GL, Boyd WA, Williams PL. Assessment of sublethal endpoints for toxicity testing with the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Environ Toxicol Chem. 2001;20:833–8. - PubMed
-
- Anderson GL, Cole RD, Williams PL. Assessing behavioral toxicity with Caenorhabditis elegans. Environ Toxicol Chem. 2004;23:1235–40. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

