CHD8 suppresses p53-mediated apoptosis through histone H1 recruitment during early embryogenesis
- PMID: 19151705
- PMCID: PMC3132516
- DOI: 10.1038/ncb1831
CHD8 suppresses p53-mediated apoptosis through histone H1 recruitment during early embryogenesis
Abstract
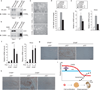
The chromodomain helicase DNA-binding (CHD) family of enzymes is thought to regulate gene expression, but their role in the regulation of specific genes has been unclear. Here we show that CHD8 is expressed at a high level during early embryogenesis and prevents apoptosis mediated by the tumour suppressor protein p53. CHD8 was found to bind to p53 and to suppress its transactivation activity. CHD8 promoted the association of p53 and histone H1, forming a trimeric complex on chromatin that was required for inhibition of p53-dependent transactivation and apoptosis. Depletion of CHD8 or histone H1 resulted in p53 activation and apoptosis. Furthermore, Chd8(-/-) mice died early during embryogenesis, manifesting widespread apoptosis, whereas deletion of p53 ameliorated this developmental arrest. These observations reveal a mode of p53 regulation mediated by CHD8, which may set a threshold for induction of apoptosis during early embryogenesis by counteracting p53 function through recruitment of histone H1.
Figures


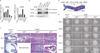
Similar articles
-
Histone H1 recruitment by CHD8 is essential for suppression of the Wnt-β-catenin signaling pathway.Mol Cell Biol. 2012 Jan;32(2):501-12. doi: 10.1128/MCB.06409-11. Epub 2011 Nov 14. Mol Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22083958 Free PMC article.
-
The autism-related protein CHD8 contributes to the stemness and differentiation of mouse hematopoietic stem cells.Cell Rep. 2021 Feb 2;34(5):108688. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.108688. Cell Rep. 2021. PMID: 33535054
-
Regulation of serum response factor activity and smooth muscle cell apoptosis by chromodomain helicase DNA-binding protein 8.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2010 Nov;299(5):C1058-67. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00080.2010. Epub 2010 Aug 25. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20739623 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct, dosage-sensitive requirements for the autism-associated factor CHD8 during cortical development.Mol Autism. 2021 Feb 24;12(1):16. doi: 10.1186/s13229-020-00409-3. Mol Autism. 2021. PMID: 33627187 Free PMC article.
-
p53 in embryonic development: maintaining a fine balance.Cell Mol Life Sci. 1999 Jan;55(1):38-47. doi: 10.1007/s000180050268. Cell Mol Life Sci. 1999. PMID: 10065150 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Genetics and genomics of autism spectrum disorder: embracing complexity.Hum Mol Genet. 2015 Oct 15;24(R1):R24-31. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddv273. Epub 2015 Jul 17. Hum Mol Genet. 2015. PMID: 26188008 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparison of the fertility of tumor suppressor gene-deficient C57BL/6 mouse strains reveals stable reproductive aging and novel pleiotropic gene.Sci Rep. 2021 Jun 11;11(1):12357. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-91342-9. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34117297 Free PMC article.
-
From neural development to cognition: unexpected roles for chromatin.Nat Rev Genet. 2013 May;14(5):347-59. doi: 10.1038/nrg3413. Epub 2013 Apr 9. Nat Rev Genet. 2013. PMID: 23568486 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The RNA interactome of human telomerase RNA reveals a coding-independent role for a histone mRNA in telomere homeostasis.Elife. 2018 Oct 25;7:e40037. doi: 10.7554/eLife.40037. Elife. 2018. PMID: 30355447 Free PMC article.
-
The ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling enzyme CHD7 regulates pro-neural gene expression and neurogenesis in the inner ear.Development. 2010 Sep;137(18):3139-50. doi: 10.1242/dev.047894. Development. 2010. PMID: 20736290 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vousden KH, Lu X. Live or let die: the cell’s response to p53. Nature Rev. Cancer. 2002;2:594–604. - PubMed
-
- Harris SL, Levine AJ. The p53 pathway: positive and negative feedback loops. Oncogene. 2005;24:2899–2908. - PubMed
-
- Vogelstein B, Lane D, Levine AJ. Surfing the p53 network. Nature. 2000;408:307–310. - PubMed
-
- Laptenko O, Prives C. Transcriptional regulation by p53: one protein, many possibilities. Cell Death Differ. 2006;13:951–961. - PubMed
-
- Aylon Y, Oren M. Living with p53, dying of p53. Cell. 2007;130:597–600. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

