Circulating insulin-like growth factor peptides and prostate cancer risk: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 19142965
- PMCID: PMC2743036
- DOI: 10.1002/ijc.24202
Circulating insulin-like growth factor peptides and prostate cancer risk: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Insulin-like growth factors (IGF-I, IGF-II) and their binding proteins (IGFBP-1-6) play a key role in cell proliferation, differentiation and apoptosis, suggesting possible involvement in carcinogenesis. Several epidemiological studies show associations of IGFs with prostate cancer. We searched the published literature for all studies relating levels of IGFs or IGFBPs with prostate cancer. We performed random effects meta-analysis to calculate summary odds ratios. The number of studies (prostate cancer cases) included in each meta-analysis were 42 (7,481) IGF-I; 10 (923) IGF-II; 3 (485) IGFBP-1; 5 (577) IGFBP-2; 29 (6,541) IGFBP-3 and 11 (3,545) IGF-1:IGFBP-3 ratio. The pooled odds ratios (95% confidence intervals) per standard deviation increase in peptide were: IGF-I, OR = 1.21 (1.07, 1.36); IGF-II, OR = 1.17 (0.93, 1.47); IGFBP-1, OR = 1.21 (0.62, 2.33); IGFBP-2, OR = 1.18 (0.90, 1.54); IGFBP-3, OR = 0.88 (0.79, 0.98); IGFI:IGFBP-3 ratio, OR = 1.10 (0.97, 1.24). For all exposures, there was substantial heterogeneity (all I(2) > 75%), partly explained by study design: the magnitude of associations was smaller in prospective vs. retrospective studies, and for IGFBP-3, the inverse association with prostate cancer risk was seen in retrospective but not prospective studies. There was weak evidence that associations of IGF-I and IGFBP-3 with prostate cancer were stronger for advanced disease. Our meta-analysis confirms that raised circulating lGF-I is positively associated with prostate cancer risk. Associations between IGFBP-3 and prostate cancer were inconsistent, and there was little evidence for a role of IGF-II, IGFBP-1 or IGFBP-2 in prostate cancer risk.
(c) 2008 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures
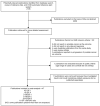
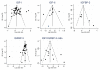
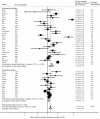
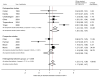
Similar articles
-
Insulin-like growth factors, their binding proteins, and prostate cancer risk: analysis of individual patient data from 12 prospective studies.Ann Intern Med. 2008 Oct 7;149(7):461-71, W83-8. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-149-7-200810070-00006. Ann Intern Med. 2008. PMID: 18838726 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating insulin-like growth factors and IGF-binding proteins in PSA-detected prostate cancer: the large case-control study ProtecT.Cancer Res. 2012 Jan 15;72(2):503-15. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-1601. Epub 2011 Nov 21. Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22106399 Free PMC article.
-
The relation between adiposity throughout the life course and variation in IGFs and IGFBPs: evidence from the ProtecT (Prostate testing for cancer and Treatment) study.Cancer Causes Control. 2010 Nov;21(11):1829-42. doi: 10.1007/s10552-010-9610-x. Epub 2010 Jul 23. Cancer Causes Control. 2010. PMID: 20652394
-
Does milk intake promote prostate cancer initiation or progression via effects on insulin-like growth factors (IGFs)? A systematic review and meta-analysis.Cancer Causes Control. 2017 Jun;28(6):497-528. doi: 10.1007/s10552-017-0883-1. Epub 2017 Mar 30. Cancer Causes Control. 2017. PMID: 28361446 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fetal growth in relation to maternal and fetal IGF-axes: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2013 Sep;92(9):997-1006. doi: 10.1111/aogs.12192. Epub 2013 Jul 16. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2013. PMID: 23745729 Review.
Cited by
-
Prediagnostic Body Mass Index Trajectories in Relation to Prostate Cancer Incidence and Mortality in the PLCO Cancer Screening Trial.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2016 Oct 20;109(3):djw225. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djw225. Print 2017 Mar. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2016. PMID: 27754927 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Inhibition of the insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor enhances effects of simvastatin on prostate cancer cells in co-culture with bone.Cancer Microenviron. 2013 Dec;6(3):231-40. doi: 10.1007/s12307-013-0129-z. Epub 2013 Jan 22. Cancer Microenviron. 2013. PMID: 23335094 Free PMC article.
-
Pooled analysis of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway variants and risk of prostate cancer.Cancer Res. 2010 Mar 15;70(6):2389-96. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-3575. Epub 2010 Mar 2. Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20197460 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of IGFBP2 in various cancers: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Cancer Med. 2022 Aug;11(16):3035-3047. doi: 10.1002/cam4.4680. Epub 2022 May 11. Cancer Med. 2022. PMID: 35546443 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Psychosocial biomarker research: integrating social, emotional and economic factors into population studies of aging and health.Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2011 Apr;6(2):226-33. doi: 10.1093/scan/nsq032. Epub 2010 Apr 1. Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 20360352 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gennigens C, Menetrier-Caux C, Droz JP. Insulin-Like Growth Factor (IGF) family and prostate cancer. Critical Reviews in Oncology-Hematology. 2006;58(2):124–145. - PubMed
-
- Roddam AW, Allen NE, Appleby P, Key TJ, Ferrucci L, Carter HB, Metter EJ, Chen C, Weiss NS, Fitzpatrick A, Hsing AW, Lacey JV, Jr., Helzlsouer K, Rinaldi S, Riboli E, Kaaks R, Janssen JAMJ, Wildhagen MF, Schroder FH, Platz EA, Pollak M, Giovannucci E, Schaefer C, Quesenberry CP, Jr., Vogelman JH, Severi G, English DR, Giles GG, Stattin P, Hallmans G, Johansson M, Chan JM, Gann P, Oliver SE, Holly JM, Donovan J, Meyer F, Bairati I, Galan P. Insulin-like Growth Factors, Their Binding Proteins, and Prostate Cancer Risk: Analysis of Individual Patient Data from 12 Prospective Studies. Ann Intern Med. 2008;149(7):461–471. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Renehan AG, Zwahlen M, Minder C, O'Dwyer ST, Shalet SM, Egger M. Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I, IGF binding protein-3, and cancer risk: systematic review and meta-regression analysis. Lancet. 2004;363(9418):1346–1353. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

