TGF-beta induces apoptosis in human B cells by transcriptional regulation of BIK and BCL-XL
- PMID: 19136942
- PMCID: PMC2857326
- DOI: 10.1038/cdd.2008.183
TGF-beta induces apoptosis in human B cells by transcriptional regulation of BIK and BCL-XL
Abstract
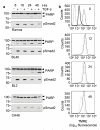
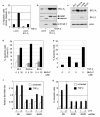
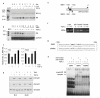
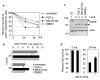
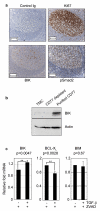
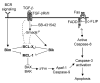
Transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) potently induces apoptosis in Burkitt's lymphoma (BL) cell lines and in explanted primary human B lymphocytes. The physiological relevance and mechanism of TGF-beta-mediated apoptosis induction in these cells remains to be determined. Here we demonstrate the requirement for TGF-beta-mediated regulation of BIK and BCL-X(L) to activate an intrinsic apoptotic pathway in centroblastic BL cells. TGF-beta directly induced transcription of BIK and a consensus Smad-binding element identified in the BIK promoter recruits TGF-beta-activated Smad transcription factor complexes in vivo. TGF-beta also transcriptionally repressed expression of the apoptosis inhibitor BCL-X(L). Inhibition of BCL-X(L) sensitised BL cells to TGF-beta-induced apoptosis whereas overexpression of BCL-X(L) or suppression of BIK by shRNA, diminished TGF-beta-induced apoptosis. BIK and BCL-X(L) were also identified as TGF-beta target genes in purified normal human centroblast B cells and immunohistochemical analyses of tonsil tissue revealed widespread TGF-beta receptor-regulated Smad activation and a focal pattern of BIK expression. Furthermore, using a selective inhibitor of the TGF-beta receptor we provide evidence that autocrine TGF-beta signalling through ALK5 contributes to the default apoptotic programme in normal human centroblasts undergoing spontaneous apoptosis. Our data suggests that TGF-beta may act as a physiological mediator of human germinal centre homoeostasis by regulation of BIK and BCL-X(L).
Figures

Similar articles
-
Transforming growth factor-β directly induces p53-up-regulated modulator of apoptosis (PUMA) during the rapid induction of apoptosis in myc-driven B-cell lymphomas.J Biol Chem. 2013 Feb 15;288(7):5198-209. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.410274. Epub 2012 Dec 14. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23243310 Free PMC article.
-
Transforming growth factor-beta-mediated apoptosis in the Ramos B-lymphoma cell line is accompanied by caspase activation and Bcl-XL downregulation.Exp Cell Res. 1998 Jul 10;242(1):244-54. doi: 10.1006/excr.1998.4096. Exp Cell Res. 1998. PMID: 9665822
-
Reversal of Mutant KRAS-Mediated Apoptosis Resistance by Concurrent Noxa/Bik Induction and Bcl-2/Bcl-xL Antagonism in Colon Cancer Cells.Mol Cancer Res. 2015 Apr;13(4):659-69. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-14-0476. Epub 2014 Dec 29. Mol Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 25548100 Free PMC article.
-
BIK, the founding member of the BH3-only family proteins: mechanisms of cell death and role in cancer and pathogenic processes.Oncogene. 2008 Dec;27 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S20-9. doi: 10.1038/onc.2009.40. Oncogene. 2008. PMID: 19641504 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting the BCL-2 family in malignancies of germinal centre origin.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2009 Dec;13(12):1459-72. doi: 10.1517/14728220903379565. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2009. PMID: 19922301 Review.
Cited by
-
Repression of the proapoptotic cellular BIK/NBK gene by Epstein-Barr virus antagonizes transforming growth factor β1-induced B-cell apoptosis.J Virol. 2014 May;88(9):5001-13. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03642-13. Epub 2014 Feb 19. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 24554662 Free PMC article.
-
FOXP1 directly represses transcription of proapoptotic genes and cooperates with NF-κB to promote survival of human B cells.Blood. 2014 Nov 27;124(23):3431-40. doi: 10.1182/blood-2014-01-553412. Epub 2014 Sep 29. Blood. 2014. PMID: 25267198 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphoinositide 3-kinase/AKT/mTORC1/2 signaling determines sensitivity of Burkitt's lymphoma cells to BH3 mimetics.Mol Cancer Res. 2012 Mar;10(3):347-59. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-11-0394. Epub 2012 Jan 12. Mol Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22241218 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory T cell-based therapies for autoimmunity.Discov Med. 2016 Aug;22(119):73-80. Discov Med. 2016. PMID: 27585233 Free PMC article. Review.
-
BIK drives an aggressive breast cancer phenotype through sublethal apoptosis and predicts poor prognosis of ER-positive breast cancer.Cell Death Dis. 2020 Jun 11;11(6):448. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-2654-2. Cell Death Dis. 2020. PMID: 32528057 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shi Y, Massague J. Mechanisms of TGF-beta signaling from cell membrane to the nucleus. Cell. 2003;113:685–700. - PubMed
-
- Schuster N, Krieglstein K. Mechanisms of TGF-beta-mediated apoptosis. Cell Tissue Res. 2002;307:1–14. - PubMed
-
- Li MO, Wan YY, Sanjabi S, Robertson AK, Flavell RA. Transforming growth factor-beta regulation of immune responses. Annu Rev Immunol. 2006;24:99–146. - PubMed
-
- Inman GJ, Allday MJ. Resistance to TGF-beta1 correlates with a reduction of TGF-beta type II receptor expression in Burkitt’s lymphoma and Epstein-Barr virus-transformed B lymphoblastoid cell lines. J Gen Virol. 2000;81:1567–78. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

