5-HT inhibition of rat insulin 2 promoter Cre recombinase transgene and proopiomelanocortin neuron excitability in the mouse arcuate nucleus
- PMID: 19135134
- PMCID: PMC2661429
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.12.003
5-HT inhibition of rat insulin 2 promoter Cre recombinase transgene and proopiomelanocortin neuron excitability in the mouse arcuate nucleus
Abstract
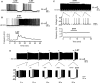
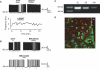
A number of anti-obesity agents have been developed that enhance hypothalamic 5-HT transmission. Various studies have demonstrated that arcuate neurons, which express proopiomelanocortin peptides (POMC neurons), and neuropeptide Y with agouti-related protein (NPY/AgRP) neurons, are components of the hypothalamic circuits responsible for energy homeostasis. An additional arcuate neuron population, rat insulin 2 promoter Cre recombinase transgene (RIPCre) neurons, has recently been implicated in hypothalamic melanocortin circuits involved in energy balance. It is currently unclear how 5-HT modifies neuron excitability in these local arcuate neuronal circuits. We show that 5-HT alters the excitability of the majority of mouse arcuate RIPCre neurons, by either hyperpolarization and inhibition or depolarization and excitation. RIPCre neurons sensitive to 5-HT, predominantly exhibit hyperpolarization and pharmacological studies indicate that inhibition of neuronal firing is likely to be through 5-HT(1F) receptors increasing current through a voltage-dependent potassium conductance. Indeed, 5-HT(1F) receptor immunoreactivity co-localizes with RIPCre green fluorescent protein expression. A minority population of POMC neurons also respond to 5-HT by hyperpolarization, and this appears to be mediated by the same receptor-channel mechanism. As neither POMC nor RIPCre neuronal populations display a common electrical response to 5-HT, this may indicate that sub-divisions of POMC and RIPCre neurons exist, perhaps serving different outputs.
Figures

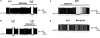

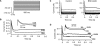

Similar articles
-
Melanocortins and agouti-related protein modulate the excitability of two arcuate nucleus neuron populations by alteration of resting potassium conductances.J Physiol. 2007 Jan 15;578(Pt 2):425-38. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2006.119479. Epub 2006 Oct 26. J Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17068101 Free PMC article.
-
Leptin modulates the intrinsic excitability of AgRP/NPY neurons in the arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus.J Neurosci. 2014 Apr 16;34(16):5486-96. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4861-12.2014. J Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24741039 Free PMC article.
-
Peptide YY(3-36) inhibits both anorexigenic proopiomelanocortin and orexigenic neuropeptide Y neurons: implications for hypothalamic regulation of energy homeostasis.J Neurosci. 2005 Nov 9;25(45):10510-9. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2552-05.2005. J Neurosci. 2005. PMID: 16280589 Free PMC article.
-
AgRP/NPY and POMC neurons in the arcuate nucleus and their potential role in treatment of obesity.Eur J Pharmacol. 2022 Jan 15;915:174611. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.174611. Epub 2021 Nov 17. Eur J Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34798121 Review.
-
Electrophysiological actions of peripheral hormones on melanocortin neurons.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2003 Jun;994:175-86. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2003.tb03178.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2003. PMID: 12851314 Review.
Cited by
-
International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. CX. Classification of Receptors for 5-hydroxytryptamine; Pharmacology and Function.Pharmacol Rev. 2021 Jan;73(1):310-520. doi: 10.1124/pr.118.015552. Pharmacol Rev. 2021. PMID: 33370241 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deletion of Lkb1 in pro-opiomelanocortin neurons impairs peripheral glucose homeostasis in mice.Diabetes. 2011 Mar;60(3):735-45. doi: 10.2337/db10-1055. Epub 2011 Jan 24. Diabetes. 2011. PMID: 21266325 Free PMC article.
-
The 5-HT1F receptor as the target of ditans in migraine - from bench to bedside.Nat Rev Neurol. 2023 Aug;19(8):489-505. doi: 10.1038/s41582-023-00842-x. Epub 2023 Jul 12. Nat Rev Neurol. 2023. PMID: 37438431 Review.
-
Oleate induces KATP channel-dependent hyperpolarization in mouse hypothalamic glucose-excited neurons without altering cellular energy charge.Neuroscience. 2017 Mar 27;346:29-42. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2016.12.053. Epub 2017 Jan 9. Neuroscience. 2017. PMID: 28087336 Free PMC article.
-
Animal models of GWAS-identified type 2 diabetes genes.J Diabetes Res. 2013;2013:906590. doi: 10.1155/2013/906590. Epub 2013 Apr 11. J Diabetes Res. 2013. PMID: 23710470 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adham N., Borden L.A., Schechter L.E., Gustafson E.L., Cochran T.L., Vaysse P.J., Weinshank R.L., Branchek T.A. Cell-specific coupling of the cloned human 5-HT1F receptor to multiple signal transduction pathways. Arch Pharmacol. 1993;348:566–575. - PubMed
-
- Bai F., Yin T., Johnstone E.M., Su C., Varga G., Little S.P., Nelson D.L. Molecular cloning and pharmacological characterization of the guinea pig 5-HT1E receptor. Eur J Pharmacol. 2004;484:127–139. - PubMed
-
- Baxter G., Kennett G., Blaney F., Blackburn T. 5-HT2 receptor subtypes: a family re-united? Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1995;16:105–110. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

