A HAUSDORFF-BASED NOE ASSIGNMENT ALGORITHM USING PROTEIN BACKBONE DETERMINED FROM RESIDUAL DIPOLAR COUPLINGS AND ROTAMER PATTERNS
- PMID: 19122773
- PMCID: PMC2613371
A HAUSDORFF-BASED NOE ASSIGNMENT ALGORITHM USING PROTEIN BACKBONE DETERMINED FROM RESIDUAL DIPOLAR COUPLINGS AND ROTAMER PATTERNS
Abstract
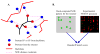
High-throughput structure determination based on solution Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) spectroscopy plays an important role in structural genomics. One of the main bottlenecks in NMR structure determination is the interpretation of NMR data to obtain a sufficient number of accurate distance restraints by assigning nuclear Overhauser effect (NOE) spectral peaks to pairs of protons. The difficulty in automated NOE assignment mainly lies in the ambiguities arising both from the resonance degeneracy of chemical shifts and from the uncertainty due to experimental errors in NOE peak positions. In this paper we present a novel NOE assignment algorithm, called HAusdorff-based NOE Assignment (HANA), that starts with a high-resolution protein backbone computed using only two residual dipolar couplings (RDCs) per residue37, 39, employs a Hausdorff-based pattern matching technique to deduce similarity between experimental and back-computed NOE spectra for each rotamer from a statistically diverse library, and drives the selection of optimal position-specific rotamers for filtering ambiguous NOE assignments. Our algorithm runs in time O(tn(3) +tn log t), where t is the maximum number of rotamers per residue and n is the size of the protein. Application of our algorithm on biological NMR data for three proteins, namely, human ubiquitin, the zinc finger domain of the human DNA Y-polymerase Eta (pol η) and the human Set2-Rpb1 interacting domain (hSRI) demonstrates that our algorithm overcomes spectral noise to achieve more than 90% assignment accuracy. Additionally, the final structures calculated using our automated NOE assignments have backbone RMSD < 1.7 Å and all-heavy-atom RMSD < 2.5 Å from reference structures that were determined either by X-ray crystallography or traditional NMR approaches. These results show that our NOE assignment algorithm can be successfully applied to protein NMR spectra to obtain high-quality structures.
Figures
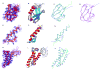
Similar articles
-
A Hausdorff-based NOE assignment algorithm using protein backbone determined from residual dipolar couplings and rotamer patterns.Comput Syst Bioinformatics Conf. 2008;7:169-81. Comput Syst Bioinformatics Conf. 2008. PMID: 19642278
-
High-resolution protein structure determination starting with a global fold calculated from exact solutions to the RDC equations.J Biomol NMR. 2009 Nov;45(3):265-81. doi: 10.1007/s10858-009-9366-3. Epub 2009 Aug 27. J Biomol NMR. 2009. PMID: 19711185 Free PMC article.
-
An efficient and accurate algorithm for assigning nuclear overhauser effect restraints using a rotamer library ensemble and residual dipolar couplings.Proc IEEE Comput Syst Bioinform Conf. 2005:189-202. doi: 10.1109/csb.2005.13. Proc IEEE Comput Syst Bioinform Conf. 2005. PMID: 16447976
-
Automated structure determination from NMR spectra.Eur Biophys J. 2009 Feb;38(2):129-43. doi: 10.1007/s00249-008-0367-z. Epub 2008 Sep 20. Eur Biophys J. 2009. PMID: 18807026 Review.
-
NMR-based automated protein structure determination.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2017 Aug 15;628:24-32. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2017.02.011. Epub 2017 Mar 2. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2017. PMID: 28263718 Review.
Cited by
-
NVR-BIP: Nuclear Vector Replacement using Binary Integer Programming for NMR Structure-Based Assignments.Comput J. 2011 May 1;54(5):708-716. doi: 10.1093/comjnl/bxp120. Comput J. 2011. PMID: 25580019 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bailey-Kellogg C, Chainraj S, Pandurangan G. A random graph approach to nmr sequential assignment. Journal of Computational Biology. 2005;12(6):569–583. - PubMed
-
- Brünger AT. X-PLOR, Version 3.1: a system for X-ray crystallography and NMR. Journal of the American Chemical Society. 1992
-
- Clore GM, Omichinski JG, Sakaguchi K, Zambrano N, Sakamoto H, Appella E, Gronenborn AM. Interhelical angles in the solution structure of the oligomerization domain of the tumour suppressor p53. Science. 1995;267:1515–1516. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

