SUMO-specific protease 1 (SENP1) reverses the hormone-augmented SUMOylation of androgen receptor and modulates gene responses in prostate cancer cells
- PMID: 19116244
- PMCID: PMC5428156
- DOI: 10.1210/me.2008-0219
SUMO-specific protease 1 (SENP1) reverses the hormone-augmented SUMOylation of androgen receptor and modulates gene responses in prostate cancer cells
Abstract
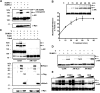
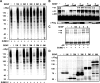
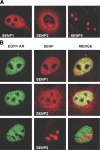
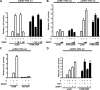
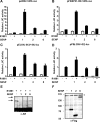
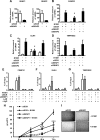
The acceptor sites for small ubiquitin-like modifier (SUMO) are conserved in the N-terminal domains of several nuclear receptors. Here, we show that androgens induce rapid and dynamic conjugation of SUMO-1 to androgen receptor (AR). Nuclear import of AR is not sufficient for SUMOylation, because constitutively nuclear apo-ARs or antagonist-bound ARs are only very weakly modified by SUMO-1 in comparison with agonist-bound ARs. Of the SUMO-specific proteases (SENP)-1, -2, -3, -5, and -6, only SENP1 and SENP2 are efficient in cleaving AR-SUMO-1 conjugates in intact cells and in vitro. Both SENP1 and -2 are nuclear and found at sites proximal to AR. Their expression promotes AR-dependent transcription, but in a promoter-selective fashion. SENP1 and -2 stimulated the activity of holo-AR on compound androgen response element-containing promoters. The effects of SENP1 and -2 on AR-dependent transcription were dependent on catalytic activity and required intact SUMO acceptor sites in AR, indicating that their coactivating effects are mainly due to their direct isopeptidase activity on holo-AR. In prostate cancer cells, ectopic expression of SENP1, but not that of SENP2, increased the transcription activity of endogenous AR. Silencing of SENP1 attenuated the expression of several AR target genes and blunted androgen-stimulated growth of LNCaP cells. Our results indicate that SENP1 reverses the ligand-induced SUMOylation of AR and helps fine tune the cellular responses to androgens in a target promoter-selective manner.
Figures

Similar articles
-
SUMO-specific protease 1 modulates cadmium-augmented transcriptional activity of androgen receptor (AR) by reversing AR SUMOylation.Toxicol Lett. 2014 Sep 2;229(2):405-13. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2014.07.003. Epub 2014 Jul 8. Toxicol Lett. 2014. PMID: 25014244
-
Induction of the SUMO-specific protease 1 transcription by the androgen receptor in prostate cancer cells.J Biol Chem. 2007 Dec 28;282(52):37341-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M706978200. Epub 2007 Oct 11. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17932034
-
Dynamic SUMOylation is linked to the activity cycles of androgen receptor in the cell nucleus.Mol Cell Biol. 2012 Oct;32(20):4195-205. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00753-12. Epub 2012 Aug 13. Mol Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22890844 Free PMC article.
-
Small ubiquitin-like modifier protein-specific protease 1 and prostate cancer.Asian J Androl. 2009 Jan;11(1):36-8. doi: 10.1038/aja.2008.45. Epub 2008 Dec 22. Asian J Androl. 2009. PMID: 19050680 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of desumoylation in the development of prostate cancer.Neoplasia. 2006 Aug;8(8):667-76. doi: 10.1593/neo.06445. Neoplasia. 2006. PMID: 16925949 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Prostaglandin 15d-PGJ(2) inhibits androgen receptor signaling in prostate cancer cells.Mol Endocrinol. 2013 Feb;27(2):212-23. doi: 10.1210/me.2012-1313. Epub 2012 Nov 28. Mol Endocrinol. 2013. PMID: 23192983 Free PMC article.
-
Outsmarting androgen receptor: creative approaches for targeting aberrant androgen signaling in advanced prostate cancer.Expert Rev Endocrinol Metab. 2011 May;6(3):483-493. doi: 10.1586/eem.11.33. Expert Rev Endocrinol Metab. 2011. PMID: 22389648 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular pathogenesis and progression of prostate cancer.Semin Oncol. 2013 Jun;40(3):244-58. doi: 10.1053/j.seminoncol.2013.04.001. Semin Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23806491 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Partners in crime: deregulation of AR activity and androgen synthesis in prostate cancer.Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2010 May;21(5):315-24. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2010.01.002. Epub 2010 Feb 6. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2010. PMID: 20138542 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathogenic mechanisms and therapeutic strategies in spinobulbar muscular atrophy.CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2013 Dec;12(8):1146-56. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2013. PMID: 24040817 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Heemers HV, Tindall DJ2007. Androgen receptor (AR) coregulators: a diversity of functions converging on and regulating the AR transcriptional complex. Endocr Rev 28:778–808 - PubMed
-
- Scher HI, Sawyers CL2005. Biology of progressive, castration-resistant prostate cancer: directed therapies targeting the androgen-receptor signaling axis. J Clin Oncol 23:8253–8261 - PubMed
-
- Simental JA, Sar M, Lane MV, French FS, Wilson EM1991. Transcriptional activation and nuclear targeting signals of the human androgen receptor. J Biol Chem 266:510–518 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

