Postrecruitment regulation of RNA polymerase II directs rapid signaling responses at the promoters of estrogen target genes
- PMID: 19103744
- PMCID: PMC2643830
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00841-08
Postrecruitment regulation of RNA polymerase II directs rapid signaling responses at the promoters of estrogen target genes
Abstract
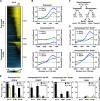
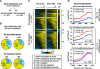
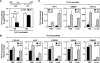
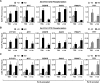
Under classical models for signal-dependent transcription in eukaryotes, DNA-binding activator proteins regulate the recruitment of RNA polymerase II (Pol II) to a set of target promoters. However, recent studies, as well as our results herein, show that Pol II is widely distributed (i.e., "preloaded") at the promoters of many genes prior to specific signaling events. How Pol II recruitment and Pol II preloading fit within a unified model of gene regulation is unclear. In addition, the mechanisms through which cellular signals activate preloaded Pol II across mammalian genomes remain largely unknown. We show here that the predominant genomic outcome of estrogen signaling is the postrecruitment regulation of Pol II activity at target gene promoters, likely through specific changes in Pol II phosphorylation rather than through recruitment of Pol II to the promoters. Furthermore, we show that negative elongation factor binds to estrogen target promoters in conjunction with preloaded Pol II and represses gene expression until the appropriate signal is received. Finally, our studies reveal that the estrogen-dependent activation of preloaded Pol II facilitates rapid gene regulatory responses which play important physiological roles in regulating estrogen signaling itself. Our results reveal a broad use of postrecruitment Pol II regulation by the estrogen signaling pathway, a mode of regulation that is likely to apply to a wide variety of signal-regulated pathways.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Genomic analyses of transcription factor binding, histone acetylation, and gene expression reveal mechanistically distinct classes of estrogen-regulated promoters.Mol Cell Biol. 2007 Jul;27(14):5090-104. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00083-07. Epub 2007 May 21. Mol Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17515612 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of RNA polymerase I-dependent promoters by the hepatitis B virus X protein via activated Ras and TATA-binding protein.Mol Cell Biol. 1998 Dec;18(12):7086-94. doi: 10.1128/MCB.18.12.7086. Mol Cell Biol. 1998. PMID: 9819395 Free PMC article.
-
Osmostress-induced transcription by Hot1 depends on a Hog1-mediated recruitment of the RNA Pol II.EMBO J. 2003 May 15;22(10):2433-42. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdg243. EMBO J. 2003. PMID: 12743037 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of snRNA gene expression by the Drosophila melanogaster small nuclear RNA activating protein complex (DmSNAPc).Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2011 Feb;46(1):11-26. doi: 10.3109/10409238.2010.518136. Epub 2010 Oct 6. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 20925482 Review.
-
Poised RNA polymerase II gives pause for thought.Cell. 2008 May 16;133(4):581-4. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.04.027. Cell. 2008. PMID: 18485867 Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibition of BET proteins impairs estrogen-mediated growth and transcription in breast cancers by pausing RNA polymerase advancement.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2015 Apr;150(2):265-78. doi: 10.1007/s10549-015-3319-1. Epub 2015 Feb 27. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2015. PMID: 25721606 Free PMC article.
-
Cohesin is required for expression of the estrogen receptor-alpha (ESR1) gene.Epigenetics Chromatin. 2012 Aug 22;5(1):13. doi: 10.1186/1756-8935-5-13. Epigenetics Chromatin. 2012. PMID: 22913342 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclin dependent kinase-9 mediated transcriptional de-regulation of cMYC as a critical determinant of endocrine-therapy resistance in breast cancers.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2014 Jan;143(1):113-24. doi: 10.1007/s10549-013-2789-2. Epub 2013 Dec 6. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2014. PMID: 24309997 Free PMC article.
-
Histone demethylase JMJD2B functions as a co-factor of estrogen receptor in breast cancer proliferation and mammary gland development.PLoS One. 2011 Mar 18;6(3):e17830. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0017830. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21445275 Free PMC article.
-
Ready, pause, go: regulation of RNA polymerase II pausing and release by cellular signaling pathways.Trends Biochem Sci. 2015 Sep;40(9):516-25. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2015.07.003. Epub 2015 Aug 4. Trends Biochem Sci. 2015. PMID: 26254229 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Acevedo, M. L., K. C. Lee, J. D. Stender, B. S. Katzenellenbogen, and W. L. Kraus. 2004. Selective recognition of distinct classes of coactivators by a ligand-inducible activation domain. Mol. Cell 13725-738. - PubMed
-
- Agalioti, T., S. Lomvardas, B. Parekh, J. Yie, T. Maniatis, and D. Thanos. 2000. Ordered recruitment of chromatin modifying and general transcription factors to the IFN-beta promoter. Cell 103667-678. - PubMed
-
- Aiyar, S. E., A. L. Blair, D. A. Hopkinson, S. Bekiranov, and R. Li. 2007. Regulation of clustered gene expression by cofactor of BRCA1 (COBRA1) in breast cancer cells. Oncogene 262543-2553. - PubMed
-
- Aiyar, S. E., J. L. Sun, A. L. Blair, C. A. Moskaluk, Y. Z. Lu, Q. N. Ye, Y. Yamaguchi, A. Mukherjee, D. M. Ren, H. Handa, and R. Li. 2004. Attenuation of estrogen receptor alpha-mediated transcription through estrogen-stimulated recruitment of a negative elongation factor. Genes Dev. 182134-2146. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
