Cellular versus viral microRNAs in host-virus interaction
- PMID: 19095692
- PMCID: PMC2651794
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkn1004
Cellular versus viral microRNAs in host-virus interaction
Abstract
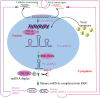
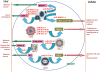
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) mark a new paradigm of RNA-directed gene expression regulation in a wide spectrum of biological systems. These small non-coding RNAs can contribute to the repertoire of host-pathogen interactions during viral infection. This interplay has important consequences, both for the virus and the host. There have been reported evidences of host-cellular miRNAs modulating the expression of various viral genes, thereby playing a pivotal role in the host-pathogen interaction network. In the hide-and-seek game between the pathogens and the infected host, viruses have evolved highly sophisticated gene-silencing mechanisms to evade host-immune response. Recent reports indicate that virus too encode miRNAs that protect them against cellular antiviral response. Furthermore, they may exploit the cellular miRNA pathway to their own advantage. Nevertheless, our increasing knowledge of the host-virus interaction at the molecular level should lead us toward possible explanations to viral tropism, latency and oncogenesis along with the development of an effective, durable and nontoxic antiviral therapy. Here, we summarize the recent updates on miRNA-induced gene-silencing mechanism, modulating host-virus interactions with a glimpse of the miRNA-based antiviral therapy for near future.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Silencing viral microRNA as a novel antiviral therapy?J Biomed Biotechnol. 2009;2009:419539. doi: 10.1155/2009/419539. Epub 2009 May 28. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2009. PMID: 19704916 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Viral and cellular microRNAs as determinants of viral pathogenesis and immunity.Cell Host Microbe. 2008 Jun 12;3(6):375-87. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2008.05.002. Cell Host Microbe. 2008. PMID: 18541214 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Host-virus interaction: a new role for microRNAs.Retrovirology. 2006 Oct 11;3:68. doi: 10.1186/1742-4690-3-68. Retrovirology. 2006. PMID: 17032463 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNAs and human retroviruses.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011 Nov-Dec;1809(11-12):686-93. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2011.05.009. Epub 2011 May 24. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011. PMID: 21640212 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNAi and cellular miRNAs in infections by mammalian viruses.Methods Mol Biol. 2011;721:23-41. doi: 10.1007/978-1-61779-037-9_2. Methods Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21431677 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Association of a single-nucleotide polymorphism within the miR-146a gene with susceptibility for acute-on-chronic hepatitis B liver failure.Immunogenetics. 2013 Apr;65(4):257-63. doi: 10.1007/s00251-012-0675-4. Epub 2013 Jan 6. Immunogenetics. 2013. PMID: 23292505
-
Two less common human microRNAs miR-875 and miR-3144 target a conserved site of E6 oncogene in most high-risk human papillomavirus subtypes.Protein Cell. 2015 Aug;6(8):575-588. doi: 10.1007/s13238-015-0142-8. Epub 2015 Apr 28. Protein Cell. 2015. PMID: 25913515 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-221 modulates RSV replication in human bronchial epithelium by targeting NGF expression.PLoS One. 2012;7(1):e30030. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0030030. Epub 2012 Jan 17. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22272270 Free PMC article.
-
Pseudorabies virus infected porcine epithelial cell line generates a diverse set of host microRNAs and a special cluster of viral microRNAs.PLoS One. 2012;7(1):e30988. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0030988. Epub 2012 Jan 23. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22292087 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA let-7f-5p Inhibits Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus by Targeting MYH9.Sci Rep. 2016 Sep 30;6:34332. doi: 10.1038/srep34332. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27686528 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lee RC, Feinbaum RL, Ambros V. The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell. 1993;75:843–854. - PubMed
-
- Lau NC, Lim LP, Weinstein EG, Bartel DP. An abundant class of tiny RNAs with probable regulatory roles in Caenorhabditis elegans. Science. 2001;294:858–862. - PubMed
-
- Cullen BR. Viruses and microRNAs. Nat. Genet. 2006;38:S25–S30. - PubMed
-
- Ghosh Z, Chakrabarti J, Mallick B. miRNomics—the bioinformatics of microRNA genes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007;363:6–11. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

