The relationship of left ventricular mass and geometry to incident cardiovascular events: the MESA (Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis) study
- PMID: 19095132
- PMCID: PMC2706368
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jacc.2008.09.014
The relationship of left ventricular mass and geometry to incident cardiovascular events: the MESA (Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis) study
Abstract
Objective: The purpose of this study was to evaluate the relationship of left ventricular (LV) mass and geometry measured with cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to incident cardiovascular events in the MESA (Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis) study.
Background: MRI is highly accurate for evaluation of heart size and structure and has not previously been used in a large epidemiologic study to predict cardiovascular events.
Methods: A total of 5,098 participants in the MESA study underwent cardiac MRI at the baseline examination and were followed up for a median of 4 years. Cox proportional hazard models were constructed to predict the end points of coronary heart disease (CHD), stroke, and heart failure (HF) after adjustment for cardiovascular risk factors.
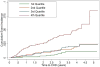
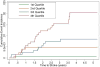
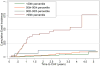
Results: A total of 216 incident events were observed during the follow-up period. In adjusted models, the end points of incident CHD and stroke were positively associated with increased LV mass-to-volume ratio (CHD, hazard ratio [HR]: 2.1 per g/ml, p = 0.02; stroke, HR: 4.2 per g/ml, p = 0.005). In contrast, LV mass showed the strongest association with incident HF events (HR: 1.4 per 10% increment, p < 0.0001). The HF events occurred primarily in participants with LV hypertrophy, that is, >or=95th percentile of LV mass (HR: 8.6, 95% confidence interval: 3.7 to 19.9, reference group <50th percentile of LV mass).
Conclusions: The LV size was related to incident HF, stroke, and CHD in this multiethnic cohort. Whereas body size-adjusted LV mass alone predicted incident HF, concentric ventricular remodeling predicted incident stroke and CHD.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Left Ventricular Mass at MRI and Long-term Risk of Cardiovascular Events: The Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA).Radiology. 2019 Oct;293(1):107-114. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2019182871. Epub 2019 Aug 27. Radiology. 2019. PMID: 31453766 Free PMC article.
-
Left ventricular dilation and incident congestive heart failure in asymptomatic adults without cardiovascular disease: multi-ethnic study of atherosclerosis (MESA).J Card Fail. 2014 Dec;20(12):905-11. doi: 10.1016/j.cardfail.2014.09.002. Epub 2014 Sep 16. J Card Fail. 2014. PMID: 25225112 Free PMC article.
-
Resting heart rate as predictor for left ventricular dysfunction and heart failure: MESA (Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis).J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014 Apr 1;63(12):1182-1189. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2013.11.027. Epub 2014 Jan 8. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014. PMID: 24412444 Free PMC article.
-
Geographic access to cardiac rehabilitation and cardiovascular disease outcomes: A study of rural United States counties.Curr Probl Cardiol. 2024 Sep;49(9):102740. doi: 10.1016/j.cpcardiol.2024.102740. Epub 2024 Jul 5. Curr Probl Cardiol. 2024. PMID: 38972468 Review.
-
New Insights from Major Prospective Cohort Studies with Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance (CMR).Curr Cardiol Rep. 2015 Jun;17(6):46. doi: 10.1007/s11886-015-0599-3. Curr Cardiol Rep. 2015. PMID: 25939757 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Alcohol consumption and myocardial remodeling in elderly women and men.Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2015 Jun;8(6):10.1161/CIRCIMAGING.115.003523 e003523. doi: 10.1161/CIRCIMAGING.115.003523. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2015. PMID: 26015268 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Left ventricular global function index by magnetic resonance imaging--a novel marker for assessment of cardiac performance for the prediction of cardiovascular events: the multi-ethnic study of atherosclerosis.Hypertension. 2013 Apr;61(4):770-8. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.111.198028. Epub 2013 Feb 19. Hypertension. 2013. PMID: 23424238 Free PMC article.
-
Relation between carotid intima-media thickness and left ventricular mass in type 1 diabetes mellitus (from the Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications [EDIC] Study).Am J Cardiol. 2012 Nov 15;110(10):1534-40. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2012.07.014. Epub 2012 Aug 9. Am J Cardiol. 2012. PMID: 22884107 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Discordance of Low-Density Lipoprotein and High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Particle Versus Cholesterol Concentration for the Prediction of Cardiovascular Disease in Patients With Metabolic Syndrome and Diabetes Mellitus (from the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis [MESA]).Am J Cardiol. 2016 Jun 15;117(12):1921-7. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2016.03.040. Epub 2016 Apr 6. Am J Cardiol. 2016. PMID: 27156827 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of empagliflozin on cardiac remodelling in South Asian and non-South Asian individuals: insights from the EMPA-HEART CardioLink-6 randomised clinical trial.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2023 Nov 15;23(1):557. doi: 10.1186/s12872-023-03549-5. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2023. PMID: 37964221 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Kannel WB, Gordon T, Castelli WP, Margolis JR. Electrocardiographic left ventricular hypertrophy and risk of coronary heart disease. The Framingham study. Ann Intern Med. 1970;72:813–22. - PubMed
-
- Levy D, Garrison RJ, Savage DD, Kannel WB, Castelli WP. Left ventricular mass and incidence of coronary heart disease in an elderly cohort. The Framingham Heart Study. Ann Intern Med. 1989;110:101–7. - PubMed
-
- Levy D, Garrison RJ, Savage DD, Kannel WB, Castelli WP. Prognostic implications of echocardiographically determined left ventricular mass in the Framingham Heart Study. N Engl J Med. 1990;322:1561–6. - PubMed
-
- Gardin JM, McClelland R, Kitzman D, et al. M-mode echocardiographic predictors of six- to seven-year incidence of coronary heart disease, stroke, congestive heart failure, and mortality in an elderly cohort (the Cardiovascular Health Study) Am J Cardiol. 2001;87:1051–7. - PubMed
-
- Gottdiener JS, Arnold AM, Aurigemma GP, et al. Predictors of congestive heart failure in the elderly: the Cardiovascular Health Study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2000;35:1628–37. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous