Effects of Wy14643 on hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury in rats
- PMID: 19058328
- PMCID: PMC2773856
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.14.6936
Effects of Wy14643 on hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury in rats
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the effects and possible mechanisms of Wy14643 on hepatic ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) injury in rats.
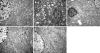
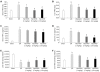
Methods: Thirty male Sprague-Dawley rats weighing 220-280 g were randomly divided into five experimental groups: sham group (G1, n=6): a sham operation was performed (except for liver I/R); I/R-untreated group (G2, n=6): rats underwent liver ischemia for 90 min followed by reperfusion for 4 h; and I/R+Wy14643 groups (G3, G4, G5; n=6): after the same surgical procedure as in group 2, animals were pretreated with Wy14643 at the dose of 1, 5 and 10 mg/kg 1 h before ischemia, respectively. Hepatic ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) was induced by clamping blood supply to the left lateral and median lobes of the liver for 90 min, and atraumatic clamp was removed for 4 h reperfusion. Blood samples and liver tissues were obtained at the end of reperfusion to assess serum and hepatic tissue homogenate aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), myeloperoxidase (MPO), serum interleukin-1beta (IL-1beta) and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha), as well as activity of superoxide dismutase (SOD) and content of malondialdehyde (MDA) in the hepatic tissue homogenate.
Results: Hepatic I/R induced a significant increase in the serum levels of ALT, AST, TNF-alpha, IL-1beta and MPO, as well as the levels of ALT, AST and MDA in the liver tissue homogenate, which were reduced by pretreatment with Wy14643 at the dose of 1, 5 and 10 mg/kg, respectively. The activity of SOD in the liver tissue homogenate was decreased after hepatic I/R, which was enhanced by Wy14643 pretreatment. In addition, serum and liver tissue homogenate ALT and AST in the Wy14643 10 mg/kg group were lower than in the Wy14643 1 mg/kg and 5 mg/kg groups, respectively.
Conclusion: Wy14643 pretreatment exerts significant protection against hepatic I/R injury in rats. The protective effects are possibly associated with enhancement of anti-oxidant and inhibition inflammation response.
Figures
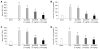
Similar articles
-
Effect of preischemic treatment with fenofibrate, a peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-α ligand, on hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats.J Mol Histol. 2011 Apr;42(2):113-22. doi: 10.1007/s10735-011-9313-y. Epub 2011 Feb 9. J Mol Histol. 2011. Retraction in: J Mol Histol. 2013 Aug;44(4):495. doi: 10.1007/s10735-013-9509-4. PMID: 21305343 Retracted.
-
Alpha-lipoic acid protects against hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats.Pharmacology. 2007;79(3):163-70. doi: 10.1159/000098953. Epub 2007 Jan 24. Pharmacology. 2007. PMID: 17259747
-
Heat Shock Protein 70 (HSP70) Reduces Hepatic Inflammatory and Oxidative Damage in a Rat Model of Liver Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury with Hyperbaric Oxygen Preconditioning.Med Sci Monit. 2018 Nov 12;24:8096-8104. doi: 10.12659/MSM.911641. Med Sci Monit. 2018. PMID: 30417859 Free PMC article.
-
Preventive effect of omega-3 fatty acids in a rat model of stress-induced liver injury.J Cell Physiol. 2019 Jul;234(7):11960-11968. doi: 10.1002/jcp.27848. Epub 2018 Dec 7. J Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30536657 Review.
-
Functional role of miR‑155 in physiological and pathological processes of liver injury (Review).Mol Med Rep. 2021 Oct;24(4):714. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2021.12353. Epub 2021 Aug 13. Mol Med Rep. 2021. PMID: 34396452 Review.
Cited by
-
The Current Knowledge of the Role of PPAR in Hepatic Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury.PPAR Res. 2012;2012:802384. doi: 10.1155/2012/802384. Epub 2012 May 16. PPAR Res. 2012. PMID: 22675337 Free PMC article.
-
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-α activation protects against endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced HepG2 cell apoptosis.Mol Cell Biochem. 2014 Jan;385(1-2):179-90. doi: 10.1007/s11010-013-1826-0. Epub 2013 Sep 26. Mol Cell Biochem. 2014. PMID: 24068329
-
The Effect of Cerium Oxide on Lung Tissue in Lower Extremity Ischemia Reperfusion Injury in Sevoflurane Administered Rats.Int J Nanomedicine. 2020 Oct 6;15:7481-7489. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S263001. eCollection 2020. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020. PMID: 33116483 Free PMC article.
-
Protective Effects of Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor-α Agonist, Wy14643, on Hypoxia/Reoxygenation Injury in Primary Rat Hepatocytes.PPAR Res. 2012;2012:547980. doi: 10.1155/2012/547980. Epub 2011 Oct 9. PPAR Res. 2012. PMID: 22007188 Free PMC article.
-
TNF-α suppression by glutathione preconditioning attenuates hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury in young and aged rats.Inflamm Res. 2015 Jan;64(1):71-81. doi: 10.1007/s00011-014-0785-6. Epub 2014 Nov 25. Inflamm Res. 2015. PMID: 25420731
References
-
- Okaya T, Lentsch AB. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha regulates postischemic liver injury. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2004;286:G606–G612. - PubMed
-
- Jaeschke H. Mechanisms of reperfusion injury after warm ischemia of the liver. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 1998;5:402–408. - PubMed
-
- Jaeschke H, Farhood A. Neutrophil and Kupffer cell-induced oxidant stress and ischemia-reperfusion injury in rat liver. Am J Physiol. 1991;260:G355–G362. - PubMed
-
- Jaeschke H, Bautista AP, Spolarics Z, Spitzer JJ. Superoxide generation by neutrophils and Kupffer cells during in vivo reperfusion after hepatic ischemia in rats. J Leukoc Biol. 1992;52:377–382. - PubMed
-
- Jaeschke H, Smith CW. Mechanisms of neutrophil-induced parenchymal cell injury. J Leukoc Biol. 1997;61:647–653. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

