Physiological involvement in pH signaling of Vps24-mediated recruitment of Aspergillus PalB cysteine protease to ESCRT-III
- PMID: 19056728
- PMCID: PMC2640967
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M808645200
Physiological involvement in pH signaling of Vps24-mediated recruitment of Aspergillus PalB cysteine protease to ESCRT-III
Abstract
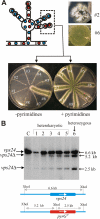
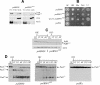
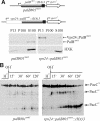
Activation of the Aspergillus nidulans transcription factor PacC, which mediates ambient pH regulation of gene expression and is recruited to ESCRT-III by the Vps32-interacting scaffold PalA, involves its ambient pH-dependent C-terminal proteolysis. This reaction is almost certainly catalyzed by the PalB calpain-like protease. Here we show that PalB associates with membranes and interacts specifically and directly with ESCRT-III Vps24. The PalB N-terminal MIT domain and the Vps24 C-terminal MIM motif are necessary and sufficient for this interaction. PalB(DeltaMIT), a mutant PalB lacking the MIT domain is inefficiently recruited to membranes and impaired in PacC proteolytic processing. Notably, membrane recruitment is promoted and PacC processing largely restored by covalent attachment of Vps24 to mutant PalB(DeltaMIT). This is the first reported evidence that calpain-like recruitment to ESCRT-III lattices plays a physiological role. It unambiguously positions the calpain-like protease PalB within the ESCRT-III-associated pH signaling complex, underlines the positive role of ESCRT-III in ambient pH signal transduction, and suggests a possible mechanism for PalB activation.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Aspergillus nidulans Ambient pH Signaling Does Not Require Endocytosis.Eukaryot Cell. 2015 Jun;14(6):545-53. doi: 10.1128/EC.00031-15. Epub 2015 Apr 3. Eukaryot Cell. 2015. PMID: 25841020 Free PMC article.
-
Further characterization of the signaling proteolysis step in the Aspergillus nidulans pH signal transduction pathway.Eukaryot Cell. 2007 Jun;6(6):960-70. doi: 10.1128/EC.00047-07. Epub 2007 Apr 6. Eukaryot Cell. 2007. PMID: 17416893 Free PMC article.
-
Signaling of ambient pH in Aspergillus involves a cysteine protease.J Biol Chem. 1995 Dec 1;270(48):28519-22. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.48.28519. J Biol Chem. 1995. PMID: 7499363
-
Liaison alcaline: Pals entice non-endosomal ESCRTs to the plasma membrane for pH signaling.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2014 Dec;22:49-59. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2014.09.005. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 25460796 Review.
-
Ambient pH gene regulation in fungi: making connections.Trends Microbiol. 2008 Jun;16(6):291-300. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2008.03.006. Epub 2008 May 3. Trends Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18457952 Review.
Cited by
-
Receptor-mediated signaling in Aspergillus fumigatus.Front Microbiol. 2013 Feb 20;4:26. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2013.00026. eCollection 2013. Front Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23430083 Free PMC article.
-
Aspergillus nidulans Ambient pH Signaling Does Not Require Endocytosis.Eukaryot Cell. 2015 Jun;14(6):545-53. doi: 10.1128/EC.00031-15. Epub 2015 Apr 3. Eukaryot Cell. 2015. PMID: 25841020 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive analysis of the human ESCRT-III-MIT domain interactome reveals new cofactors for cytokinetic abscission.Elife. 2022 Sep 15;11:e77779. doi: 10.7554/eLife.77779. Elife. 2022. PMID: 36107470 Free PMC article.
-
Eisosome organization in the filamentous ascomycete Aspergillus nidulans.Eukaryot Cell. 2010 Oct;9(10):1441-54. doi: 10.1128/EC.00087-10. Epub 2010 Aug 6. Eukaryot Cell. 2010. PMID: 20693301 Free PMC article.
-
Mutational analysis of Candida albicans SNF7 reveals genetically separable Rim101 and ESCRT functions and demonstrates divergence in bro1-domain protein interactions.Genetics. 2010 Mar;184(3):673-94. doi: 10.1534/genetics.109.112029. Epub 2009 Dec 21. Genetics. 2010. PMID: 20026677 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

