Forward and robust selection of the most potent and noncellular toxic siRNAs from RNAi libraries
- PMID: 19043072
- PMCID: PMC2615601
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkn953
Forward and robust selection of the most potent and noncellular toxic siRNAs from RNAi libraries
Abstract
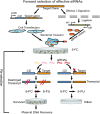
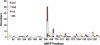
Use of highly potent small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) can substantially reduce dose-dependent cytotoxic and off-target effects. We developed a genetic forward approach by fusing the cytosine deaminase gene with targets for the robust identification of highly potent siRNAs from RNA interference (RNAi) libraries that were directly delivered into cells via bacterial invasion. We demonstrated that two simple drug selection cycles performed conveniently in a single container predominately enriched two siRNAs targets the MVP gene (siMVP) and one siRNA targets the egfp gene (siEGFP) in surviving cells and these proved to be the most effective siRNAs reported. Furthermore, the potent siRNAs isolated from the surviving cells possessed noncellular toxic characteristics. Interestingly, the length of highly potent siMVPs identified could be as short as 16-mer, and increasing the length of their native sequences dramatically reduced RNAi potency. These results suggest that the current approach can robustly discover the most potent and nontoxic siRNAs in the surviving cells, and thus has great potential in facilitating RNAi applications by minimizing the dose-dependent and sequence nonspecific side effects of siRNAs.
Figures
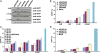
Similar articles
-
High-throughput screening of effective siRNAs from RNAi libraries delivered via bacterial invasion.Nat Methods. 2005 Dec;2(12):967-73. doi: 10.1038/nmeth812. Epub 2005 Nov 18. Nat Methods. 2005. PMID: 16299483
-
Selection of hyperfunctional siRNAs with improved potency and specificity.Nucleic Acids Res. 2009 Dec;37(22):e152. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkp864. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009. PMID: 19846596 Free PMC article.
-
L-Type Calcium Channel Blocker Enhances Cellular Delivery and Gene Silencing Potency of Cell-Penetrating Asymmetric siRNAs.Mol Pharm. 2020 Mar 2;17(3):777-786. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.9b00942. Epub 2020 Feb 10. Mol Pharm. 2020. PMID: 31976668
-
Gene silencing through RNA interference (RNAi) in vivo: strategies based on the direct application of siRNAs.J Biotechnol. 2006 Jun 25;124(1):12-25. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2005.12.003. Epub 2006 Jan 18. J Biotechnol. 2006. PMID: 16413079 Review.
-
On the art of identifying effective and specific siRNAs.Nat Methods. 2006 Sep;3(9):670-6. doi: 10.1038/nmeth911. Nat Methods. 2006. PMID: 16929310 Review.
Cited by
-
Recent advances in RNAi-based strategies for therapy and prevention of HIV-1/AIDS.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2016 Aug 1;103:174-186. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2016.03.005. Epub 2016 Mar 21. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2016. PMID: 27013255 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Production of highly potent recombinant siRNAs in Escherichia coli.Nat Protoc. 2013 Dec;8(12):2325-36. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2013.149. Epub 2013 Oct 31. Nat Protoc. 2013. PMID: 24177290
-
Structural diversity repertoire of gene silencing small interfering RNAs.Nucleic Acid Ther. 2011 Jun;21(3):125-31. doi: 10.1089/nat.2011.0286. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2011. PMID: 21749289 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The dose can make the poison: lessons learned from adverse in vivo toxicities caused by RNAi overexpression.Silence. 2011 Oct 26;2:8. doi: 10.1186/1758-907X-2-8. Silence. 2011. PMID: 22029761 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular characteristics and efficacy of 16D10 siRNAs in inhibiting root-knot nematode infection in transgenic grape hairy roots.PLoS One. 2013 Jul 16;8(7):e69463. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0069463. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23874962 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Birmingham A, Anderson E, Sullivan K, Reynolds A, Boese Q, Leake D, Karpilow J, Khvorova A. A protocol for designing siRNAs with high functionality and specificity. Nat. Protoc. 2007;2:2068–2078. - PubMed
-
- Grimm D, Streetz KL, Jopling CL, Storm TA, Pandey K, Davis CR, Marion P, Salazar F, Kay MA. Fatality in mice due to oversaturation of cellular microRNA/short hairpin RNA pathways. Nature. 2006;441:537–541. - PubMed
-
- Patzel V, Rutz S, Dietrich I, Koberle C, Scheffold A, Kaufmann SH. Design of siRNAs producing unstructured guide-RNAs results in improved RNA interference efficiency. Nat. Biotechnol. 2005;23:1440–1444. - PubMed
-
- Zhao HF, L’Abbe D, Jolicoeur N, Wu M, Li Z, Yu Z, Shen SH. High-throughput screening of effective siRNAs from RNAi libraries delivered via bacterial invasion. Nat. methods. 2005;2:967–973. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

