Saccharomyces cerevisiae linker histone Hho1p functionally interacts with core histone H4 and negatively regulates the establishment of transcriptionally silent chromatin
- PMID: 19017647
- PMCID: PMC2613606
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M806274200
Saccharomyces cerevisiae linker histone Hho1p functionally interacts with core histone H4 and negatively regulates the establishment of transcriptionally silent chromatin
Abstract
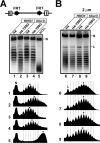
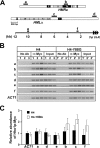
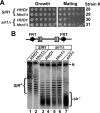
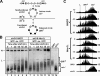
Saccharomyces cerevisiae linker histone Hho1p is not essential for cell viability, and very little is known about its function in vivo. We show that deletion of HHO1 (hho1Delta) suppresses the defect in transcriptional silencing caused by a mutation in the globular domain of histone H4. hho1Delta also suppresses the reduction in HML silencing by the deletion of SIR1 that is involved in the establishment of silent chromatin at HML. We further show that hho1Delta suppresses changes in silent chromatin structure caused by the histone H4 mutation and sir1Delta. These results suggest that HHO1 plays a negative role in transcriptionally silent chromatin. We also provide evidence that Hho1p hinders the de novo establishment of silent chromatin but does not affect the stability of preexistent silent chromatin. Unlike canonical linker histones in higher eukaryotes that have a single conserved globular domain, Hho1p possesses two globular domains. We show that the carboxyl-terminal globular domain of Hho1p is dispensable for its function, suggesting that the mode of Hho1p action is similar to that of canonical linker histones.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Yeast HMO1: Linker Histone Reinvented.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2016 Nov 30;81(1):e00037-16. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00037-16. Print 2017 Mar. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2016. PMID: 27903656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Histone H1 of Saccharomyces cerevisiae inhibits transcriptional silencing.Genetics. 2006 Jun;173(2):579-87. doi: 10.1534/genetics.105.050195. Epub 2006 Apr 2. Genetics. 2006. PMID: 16582449 Free PMC article.
-
The Saccharomyces cerevisiae linker histone Hho1p is essential for chromatin compaction in stationary phase and is displaced by transcription.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Sep 30;105(39):14838-43. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0806337105. Epub 2008 Sep 17. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 18799740 Free PMC article.
-
Yeast linker histone Hho1p is required for efficient RNA polymerase I processivity and transcriptional silencing at the ribosomal DNA.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Aug 19;105(33):11703-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0709403105. Epub 2008 Aug 7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 18687885 Free PMC article.
-
The Nuts and Bolts of Transcriptionally Silent Chromatin in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Genetics. 2016 Aug;203(4):1563-99. doi: 10.1534/genetics.112.145243. Genetics. 2016. PMID: 27516616 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Epigenome manipulation as a pathway to new natural product scaffolds and their congeners.Nat Prod Rep. 2010 Jan;27(1):11-22. doi: 10.1039/b920860g. Epub 2009 Oct 27. Nat Prod Rep. 2010. PMID: 20024091 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Yeast HMO1: Linker Histone Reinvented.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2016 Nov 30;81(1):e00037-16. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00037-16. Print 2017 Mar. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2016. PMID: 27903656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeted 2'-O methylation at a nucleotide within the pseudoknot of telomerase RNA reduces telomerase activity in vivo.Mol Cell Biol. 2010 Sep;30(18):4368-78. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00384-10. Epub 2010 Jul 20. Mol Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20647541 Free PMC article.
-
Functions of protosilencers in the formation and maintenance of heterochromatin in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.PLoS One. 2012;7(5):e37092. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0037092. Epub 2012 May 17. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22615905 Free PMC article.
-
Chromatin and transcription in yeast.Genetics. 2012 Feb;190(2):351-87. doi: 10.1534/genetics.111.132266. Genetics. 2012. PMID: 22345607 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Luger, K., Mader, A. W., Richmond, R. K., Sargent, D. F., and Richmond, T. J. (1997) Nature 389 251–260 - PubMed
-
- Woodcock, C. L., Skoultchi, A. I., and Fan, Y. (2006) Chromosome Res. 14 17–25 - PubMed
-
- Robinson, P. J., and Rhodes, D. (2006) Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 16 336–343 - PubMed
-
- Hannon, R., Bateman, E., Allan, J., Harborne, N., and Gould, H. (1984) J. Mol. Biol. 180 131–149 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

