Competitive repair pathways in immunoglobulin gene hypermutation
- PMID: 19010770
- PMCID: PMC2660922
- DOI: 10.1098/rstb.2008.0206
Competitive repair pathways in immunoglobulin gene hypermutation
Abstract
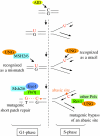
This review focuses on the contribution of translesion DNA polymerases to immunoglobulin gene hypermutation, in particular on the roles of DNA polymerase eta (Poleta) in the generation of mutations at A/T bases from the initial cytosine-targeted activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID)-mediated deamination event, and of Polkappa, an enzyme of the same polymerase family, used as a substitute when Poleta is absent. The proposition that the UNG uracil glycosylase and the MSH2-MSH6 mismatch recognition complex are two competitive rather than alternative pathways in the processing of uracils generated by AID is further discussed.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Antibody diversification caused by disrupted mismatch repair and promiscuous DNA polymerases.DNA Repair (Amst). 2016 Feb;38:110-116. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2015.11.011. Epub 2015 Dec 2. DNA Repair (Amst). 2016. PMID: 26719140 Free PMC article. Review.
-
AID-associated DNA repair pathways regulate malignant transformation in a murine model of BCL6-driven diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.Blood. 2016 Jan 7;127(1):102-12. doi: 10.1182/blood-2015-02-628164. Epub 2015 Sep 18. Blood. 2016. PMID: 26385350 Free PMC article.
-
The concerted action of Msh2 and UNG stimulates somatic hypermutation at A . T base pairs.Mol Cell Biol. 2009 Sep;29(18):5148-57. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00647-09. Epub 2009 Jul 13. Mol Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19596785 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanisms of antibody somatic hypermutation.Annu Rev Biochem. 2007;76:1-22. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.76.061705.090740. Annu Rev Biochem. 2007. PMID: 17328676 Review.
-
Hijacked DNA repair proteins and unchained DNA polymerases.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2009 Mar 12;364(1517):605-11. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2008.0188. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2009. PMID: 19008198 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A broad atlas of somatic hypermutation allows prediction of activation-induced deaminase targets.J Exp Med. 2018 Mar 5;215(3):761-771. doi: 10.1084/jem.20171738. Epub 2018 Jan 26. J Exp Med. 2018. PMID: 29374026 Free PMC article.
-
AID and Apobec3G haphazard deamination and mutational diversity.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013 Sep;70(17):3089-108. doi: 10.1007/s00018-012-1212-1. Epub 2012 Nov 22. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013. PMID: 23178850 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biochemical basis of immunological and retroviral responses to DNA-targeted cytosine deamination by activation-induced cytidine deaminase and APOBEC3G.J Biol Chem. 2009 Oct 9;284(41):27761-27765. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R109.052449. Epub 2009 Aug 13. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19684020 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Translesion synthesis polymerases in the prevention and promotion of carcinogenesis.J Nucleic Acids. 2010 Sep 22;2010:643857. doi: 10.4061/2010/643857. J Nucleic Acids. 2010. PMID: 20936171 Free PMC article.
-
Antibody diversification caused by disrupted mismatch repair and promiscuous DNA polymerases.DNA Repair (Amst). 2016 Feb;38:110-116. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2015.11.011. Epub 2015 Dec 2. DNA Repair (Amst). 2016. PMID: 26719140 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aoufouchi S., Faili A., Zober C., D'Orlando O., Weller S., Weill J.C., Reynaud C.A. Proteasomal degradation restricts the nuclear lifespan of AID. J. Exp. Med. 2008;205:1357–1368. doi:10.1084/jem.20070950 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bardwell P.D., Woo C.J., Wei K., Li Z., Martin A., Sack S.Z., Parris T., Edelmann W., Scharff M.D. Altered somatic hypermutation and reduced class-switch recombination in exonuclease 1-mutant mice. Nat. Immunol. 2004;5:224–229. doi:10.1038/ni1031 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Delbos F., De Smet A., Faili A., Aoufouchi S., Weill J.C., Reynaud C.A. Contribution of DNA polymerase eta to immunoglobulin gene hypermutation in the mouse. J. Exp. Med. 2005;201:1191–1196. doi:10.1084/jem.20050292 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Delbos F., Aoufouchi S., Faili A., Weill J.C., Reynaud C.A. DNA polymerase eta is the sole contributor of A/T modifications during immunoglobulin gene hypermutation in the mouse. J. Exp. Med. 2007;204:17–23. doi:10.1084/jem.20062131 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Di Noia J.M., Rada C., Neuberger M.S. SMUG1 is able to excise uracil from immunoglobulin genes: insight into mutation versus repair. EMBO J. 2006;25:585–595. doi:10.1038/sj.emboj.7600939 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

