Munc18c is not rate-limiting for glucose and long-chain fatty acid uptake in the heart
- PMID: 19009238
- PMCID: PMC3580071
- DOI: 10.1007/s11010-008-9942-y
Munc18c is not rate-limiting for glucose and long-chain fatty acid uptake in the heart
Abstract
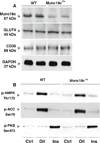
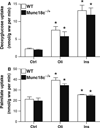
The role of soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor attachment protein receptor (SNARE)- and SNARE-associated proteins have not yet been assessed in regulation of cardiac glucose uptake, nor in the regulation of long-chain fatty acid (LCFA) uptake in any tissue. Munc18c is a SNARE-associated protein that regulates GLUT4 translocation in skeletal muscle and adipose tissue. Using cardiomyocytes from Munc18c(-/+) mice (with 56% reduction of Munc18c protein expression), we investigated whether this syntaxin4-associated protein is involved in regulation of cardiac substrate uptake. Basal, insulin- and oligomycin (a 5' AMP-activated protein kinase-activating agent)-stimulated glucose and LCFA uptake were not altered significantly in Munc18c(-/+) cardiomyocytes compared to wild-type cells. We conclude, therefore, that Munc18c is not rate-limiting for cardiac substrate uptake, neither under basal conditions nor when maximally stimulated metabolically.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Munc18c provides stimulus-selective regulation of GLUT4 but not fatty acid transporter trafficking in skeletal muscle.FEBS Lett. 2012 Jul 30;586(16):2428-35. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2012.05.061. Epub 2012 Jun 8. FEBS Lett. 2012. PMID: 22687245 Free PMC article.
-
Differential regulation of cardiac glucose and fatty acid uptake by endosomal pH and actin filaments.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2010 Jun;298(6):C1549-59. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00334.2009. Epub 2010 Apr 7. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20375272
-
Adipocytes from Munc18c-null mice show increased sensitivity to insulin-stimulated GLUT4 externalization.J Clin Invest. 2005 Feb;115(2):291-301. doi: 10.1172/JCI22681. J Clin Invest. 2005. PMID: 15690082 Free PMC article.
-
Munc18c: a controversial regulator of peripheral insulin action.Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2014 Nov;25(11):601-8. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2014.06.010. Epub 2014 Jul 12. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2014. PMID: 25028245 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Signalling components involved in contraction-inducible substrate uptake into cardiac myocytes.Proc Nutr Soc. 2004 May;63(2):251-8. doi: 10.1079/PNS2004333. Proc Nutr Soc. 2004. PMID: 15294039 Review.
Cited by
-
Munc18c provides stimulus-selective regulation of GLUT4 but not fatty acid transporter trafficking in skeletal muscle.FEBS Lett. 2012 Jul 30;586(16):2428-35. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2012.05.061. Epub 2012 Jun 8. FEBS Lett. 2012. PMID: 22687245 Free PMC article.
-
Insulin signaling in the heart.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2021 Jul 1;321(1):E130-E145. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00158.2021. Epub 2021 May 31. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2021. PMID: 34056923 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Glatz JF, Bonen A, Ouwens DM, et al. Regulation of sarcolemmal transport of substrates in the healthy and diseased heart. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2006;20:471–476. - PubMed
-
- Luiken JJ, Koonen DP, Willems J, et al. Insulin stimulates long-chain fatty acid utilization by rat cardiac myocytes through cellular redistribution of FAT/CD36. Diabetes. 2002;51:3113–3119. - PubMed
-
- Luiken JJ, Coort SL, Willems J, et al. Contraction-induced fatty acid translocase/CD36 translocation in rat cardiac myocytes is mediated through AMP-activated protein kinase signaling. Diabetes. 2003;52:1627–1634. - PubMed
-
- Watson RT, Pessin JE. GLUT4 translocation: the last 200 nanometers. Cell Signal. 2007;19:2209–2217. - PubMed
-
- Rudich A, Klip A. Push/pull mechanisms of GLUT4 traffic in muscle cells. Acta Physiol Scand. 2003;178:297–308. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

