Differential functions of the Apoer2 intracellular domain in selenium uptake and cell signaling
- PMID: 19007311
- PMCID: PMC2642607
- DOI: 10.1515/BC.2009.011
Differential functions of the Apoer2 intracellular domain in selenium uptake and cell signaling
Abstract
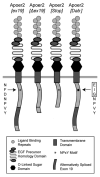
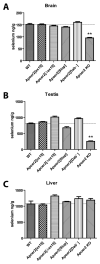
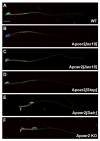
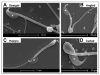
Apolipoprotein E receptor 2 (Apoer2) is a multifunctional transport and signaling receptor that regulates the uptake of selenium into the mouse brain and testis through endocytosis of selenoprotein P (Sepp1). Mice deficient in Apoer2 or Sepp1 are infertile, with kinked and hypomotile spermatozoa. They also develop severe neurological defects on a low selenium diet, due to a profound impairment of selenium uptake. Little is known about the function of Apoer2 in the testis beyond its role as a Sepp1 receptor. By contrast, in the brain, Apoer2 is an essential component of the Reelin signaling pathway, which is required for proper neuronal organization and synapse function. Using knock-in mice, we have functionally dissociated the signaling motifs in the Apoer2 cytoplasmic domain from Sepp1 uptake. Selenium concentration of brain and testis was normal in the knock-in mutants, in contrast to Apoer2 knock-outs. Thus, the neurological defects in the signaling impaired knock-in mice are not caused by a selenium uptake defect, but instead are a direct consequence of a disruption of the Reelin signal. Reduced sperm motility was observed in some of the knock-in mice, indicating a novel signaling role for Apoer2 in sperm development and function that is independent of selenium uptake.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Selenoprotein P-expression, functions, and roles in mammals.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009 Nov;1790(11):1441-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2009.03.026. Epub 2009 Apr 1. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009. PMID: 19345254 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Apolipoprotein E receptor-2 (ApoER2) mediates selenium uptake from selenoprotein P by the mouse testis.J Biol Chem. 2007 Apr 20;282(16):12290-7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M611403200. Epub 2007 Feb 21. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17314095
-
Deletion of apolipoprotein E receptor-2 in mice lowers brain selenium and causes severe neurological dysfunction and death when a low-selenium diet is fed.J Neurosci. 2007 Jun 6;27(23):6207-11. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1153-07.2007. J Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 17553992 Free PMC article.
-
Selenoprotein P and apolipoprotein E receptor-2 interact at the blood-brain barrier and also within the brain to maintain an essential selenium pool that protects against neurodegeneration.FASEB J. 2014 Aug;28(8):3579-88. doi: 10.1096/fj.14-252874. Epub 2014 Apr 23. FASEB J. 2014. PMID: 24760755 Free PMC article.
-
SeP, ApoER2 and megalin as necessary factors to maintain Se homeostasis in mammals.J Trace Elem Med Biol. 2012 Oct;26(4):262-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jtemb.2012.03.003. Epub 2012 Jun 8. J Trace Elem Med Biol. 2012. PMID: 22683052 Review.
Cited by
-
Transcriptomics of maternal and fetal membranes can discriminate between gestational-age matched preterm neonates with and without cognitive impairment diagnosed at 18-24 months.PLoS One. 2015 Mar 30;10(3):e0118573. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0118573. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25822971 Free PMC article.
-
Antiphospholipid antibodies induce thrombosis by PP2A activation via apoER2-Dab2-SHC1 complex formation in endothelium.Blood. 2018 May 10;131(19):2097-2110. doi: 10.1182/blood-2017-11-814681. Epub 2018 Mar 2. Blood. 2018. PMID: 29500169 Free PMC article.
-
Isoform-specific binding of selenoprotein P to the β-propeller domain of apolipoprotein E receptor 2 mediates selenium supply.J Biol Chem. 2014 Mar 28;289(13):9195-207. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.549014. Epub 2014 Feb 13. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24532792 Free PMC article.
-
Canonical and Non-canonical Reelin Signaling.Front Cell Neurosci. 2016 Jun 30;10:166. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2016.00166. eCollection 2016. Front Cell Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27445693 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Selenoprotein P-expression, functions, and roles in mammals.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009 Nov;1790(11):1441-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2009.03.026. Epub 2009 Apr 1. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009. PMID: 19345254 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Andersen OM, Yeung CH, Vorum H, Wellner M, Andreassen TK, et al. Essential role of the apolipoprotein E receptor-2 in sperm development. J Biol Chem. 2003;278(26):23989–23995. - PubMed
-
- Beffert U, Nematollah Farsian F, Masiulis I, Hammer RE, Yoon SO, et al. ApoE receptor 2 controls neuronal survival in the adult brain. Curr Biol. 2006a;16(24):2446–2452. - PubMed
-
- Beffert U, Weeber EJ, Durudas A, Qiu S, Masiulis I, et al. Modulation of synaptic plasticity and memory by Reelin involves differential splicing of the lipoprotein receptor Apoer2. Neuron. 2005;47(4):567–579. - PubMed
-
- Burk RF, Hill KE. Selenoprotein P: an extracellular protein with unique physical characteristics and a role in selenium homeostasis. Annu Rev Nutr. 2005;25:215–235. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P01 HL020948-210015/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL20948/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 ES002497/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL063762/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL020948-320005/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL020948-250015/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL020948-310005/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL020948-240015/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL063762-09/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL020948-220015/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 HL063762/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL020948/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL63762/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 ES002497/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- ES02497/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL020948-230015/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
