Analysis of the differential host cell nuclear proteome induced by attenuated and virulent hemorrhagic arenavirus infection
- PMID: 19004951
- PMCID: PMC2612403
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01281-08
Analysis of the differential host cell nuclear proteome induced by attenuated and virulent hemorrhagic arenavirus infection
Abstract
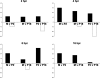
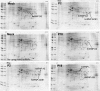
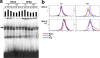
Arenaviruses are important emerging pathogens and include a number of hemorrhagic fever viruses classified as NIAID category A priority pathogens and CDC potential biothreat agents. Infection of guinea pigs with the New World arenavirus Pichindé virus (PICV) has been used as a biosafety level 2 model for the Lassa virus. Despite continuing research, little is known about the molecular basis of pathogenesis, and this has hindered the design of novel antiviral therapeutics. Modulation of the host response is a potential strategy for the treatment of infectious diseases. We have previously investigated the global host response to attenuated and lethal arenavirus infections by using high-throughput immunoblotting and kinomics approaches. In this report, we describe the differential nuclear proteomes of a murine cell line induced by mock infection and infection with attenuated and lethal variants of PICV, investigated by using two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. Spot identification using tandem mass spectrometry revealed the involvement of a number of proteins that regulate inflammation via potential modulation of NF-kappaB activity and of several heterogeneous nuclear ribonuclear proteins. Pathway analysis revealed a potential role for transcription factor XBP-1, a transcription factor involved in major histocompatibility complex II (MHC-II) expression; differential DNA-binding activity was revealed by electrophoretic mobility shift assay, and differences in surface MHC-II expression were seen following PICV infection. These data are consistent with the results of several previous studies and highlight potential differences between transcriptional and translational regulation. This study provides a number of differentially expressed targets for further research and suggests that key events in pathogenesis may be established early in infection.
Figures
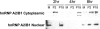
Similar articles
-
Host cell factors as antiviral targets in arenavirus infection.Viruses. 2012 Sep;4(9):1569-91. doi: 10.3390/v4091569. Epub 2012 Sep 13. Viruses. 2012. PMID: 23170173 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differential signaling networks induced by mild and lethal hemorrhagic fever virus infections.J Virol. 2006 Oct;80(20):10248-52. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01384-06. J Virol. 2006. PMID: 17005702 Free PMC article.
-
Alterations in NF-kappaB and RBP-Jkappa by arenavirus infection of macrophages in vitro and in vivo.J Virol. 2002 Feb;76(3):1154-62. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.3.1154-1162.2002. J Virol. 2002. PMID: 11773391 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro and in vivo characterizations of pichinde viral nucleoprotein exoribonuclease functions.J Virol. 2015 Jul;89(13):6595-607. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00009-15. Epub 2015 Apr 15. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 25878103 Free PMC article.
-
Current progress towards vaccines for arenavirus-caused diseases.Vaccine. 1992;10(2):89-95. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(92)90022-c. Vaccine. 1992. PMID: 1311492 Review.
Cited by
-
Quantitative Proteomics Reveal Peroxiredoxin Perturbation Upon Persistent Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis Virus Infection in Human Cells.Front Microbiol. 2019 Oct 25;10:2438. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.02438. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31708904 Free PMC article.
-
Vaccine and adjuvant design for emerging viruses: mutations, deletions, segments and signaling.Bioeng Bugs. 2011 May-Jun;2(3):129-35. doi: 10.4161/bbug.2.3.15367. Epub 2011 May 1. Bioeng Bugs. 2011. PMID: 21637006 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Host cell factors as antiviral targets in arenavirus infection.Viruses. 2012 Sep;4(9):1569-91. doi: 10.3390/v4091569. Epub 2012 Sep 13. Viruses. 2012. PMID: 23170173 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A systems biology starter kit for arenaviruses.Viruses. 2012 Dec;4(12):3625-46. doi: 10.3390/v4123625. Viruses. 2012. PMID: 23342371 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative pathogenesis and systems biology for biodefense virus vaccine development.J Biomed Biotechnol. 2010;2010:236528. doi: 10.1155/2010/236528. Epub 2010 Jun 6. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2010. PMID: 20617142 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Althage, A., B. Odermatt, D. Moskophidis, T. Kundig, U. Hoffman-Rohrer, H. Hengartner, and R. M. Zinkernagel. 1992. Immunosuppression by lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus infection: competent effector T and B cells but impaired antigen presentation. Eur. J. Immunol. 221803-1812. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

