The Janus-faced nature of the C(2)B domain is fundamental for synaptotagmin-1 function
- PMID: 18953334
- PMCID: PMC2587052
- DOI: 10.1038/nsmb.1508
The Janus-faced nature of the C(2)B domain is fundamental for synaptotagmin-1 function
Abstract
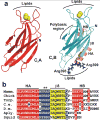
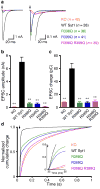
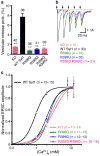
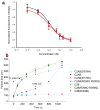
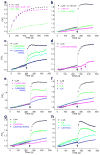
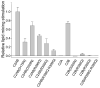
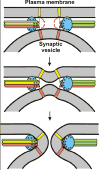
Synaptotagmin-1 functions as a Ca2+ sensor in neurotransmitter release and was proposed to act on both the synaptic vesicle and plasma membranes through interactions involving the Ca2+ binding top loops of its C(2) domains and the Ca2+-independent bottom face of the C(2)B domain. However, the functional importance of the C(2)B domain bottom face is unclear. We now show that mutating two conserved arginine residues at the C(2)B domain bottom face practically abolishes synchronous release in hippocampal neurons. Reconstitution experiments reveal that Ca2+-synaptotagmin-1 can dramatically stimulate the rate of SNARE-dependent lipid mixing, and that the two-arginine mutation strongly impairs this activity. These results demonstrate that synaptotagmin-1 function depends crucially on the bottom face of the C(2)B domain and strongly support the notion that synaptotagmin-1 triggers membrane fusion and neurotransmitter release by bringing the vesicle and plasma membranes together, much like the SNAREs do but in a Ca2+-dependent manner.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A quaternary SNARE-synaptotagmin-Ca2+-phospholipid complex in neurotransmitter release.J Mol Biol. 2007 Mar 30;367(3):848-63. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2007.01.040. Epub 2007 Jan 23. J Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17320903 Free PMC article.
-
Synaptotagmin-1 C2B domain interacts simultaneously with SNAREs and membranes to promote membrane fusion.Elife. 2016 Apr 15;5:e14211. doi: 10.7554/eLife.14211. Elife. 2016. PMID: 27083046 Free PMC article.
-
A Post-Docking Role of Synaptotagmin 1-C2B Domain Bottom Residues R398/399 in Mouse Chromaffin Cells.J Neurosci. 2015 Oct 21;35(42):14172-82. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1911-15.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26490858 Free PMC article.
-
Conserved arginine residues in synaptotagmin 1 regulate fusion pore expansion through membrane contact.Nat Commun. 2021 Feb 3;12(1):761. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-21090-x. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 33536412 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling the mechanisms of synaptotagmin and SNARE function in neurotransmitter release.Trends Cell Biol. 2006 Jul;16(7):339-50. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2006.04.006. Epub 2006 May 12. Trends Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16698267 Review.
Cited by
-
Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate clusters act as molecular beacons for vesicle recruitment.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2013 Jun;20(6):679-86. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2570. Epub 2013 May 12. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23665582 Free PMC article.
-
Reconstitution of the vital functions of Munc18 and Munc13 in neurotransmitter release.Science. 2013 Jan 25;339(6118):421-5. doi: 10.1126/science.1230473. Epub 2012 Dec 20. Science. 2013. PMID: 23258414 Free PMC article.
-
Tilting the balance between facilitatory and inhibitory functions of mammalian and Drosophila Complexins orchestrates synaptic vesicle exocytosis.Neuron. 2009 Nov 12;64(3):367-80. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2009.09.043. Neuron. 2009. PMID: 19914185 Free PMC article.
-
Tomosyn inhibits synaptotagmin-1-mediated step of Ca2+-dependent neurotransmitter release through its N-terminal WD40 repeats.J Biol Chem. 2010 Dec 24;285(52):40943-55. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.156893. Epub 2010 Oct 26. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20978127 Free PMC article.
-
Membrane-Binding Cooperativity and Coinsertion by C2AB Tandem Domains of Synaptotagmins 1 and 7.Biophys J. 2019 Mar 19;116(6):1025-1036. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2019.01.035. Epub 2019 Feb 5. Biophys J. 2019. PMID: 30795874 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sudhof TC. The synaptic vesicle cycle. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2004;27:509–547. - PubMed
-
- Rizo J, Chen X, Arac D. Unraveling the mechanisms of synaptotagmin and SNARE function in neurotransmitter release. Trends Cell Biol. 2006;16:339–350. - PubMed
-
- Chapman ER. How Does Synaptotagmin Trigger Neurotransmitter Release? Annu Rev Biochem. 2008 - PubMed
-
- Sutton RB, Davletov BA, Berghuis AM, Sudhof TC, Sprang SR. Structure of the first C2 domain of synaptotagmin I: a novel Ca2+/phospholipid-binding fold. Cell. 1995;80:929–938. - PubMed
-
- Shao X, Davletov BA, Sutton RB, Sudhof TC, Rizo J. Bipartite Ca2+-binding motif in C2 domains of synaptotagmin and protein kinase C. Science. 1996;273:248–251. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

