High prevalence of human Parechovirus (HPeV) genotypes in the Amsterdam region and identification of specific HPeV variants by direct genotyping of stool samples
- PMID: 18945833
- PMCID: PMC2593270
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.01379-08
High prevalence of human Parechovirus (HPeV) genotypes in the Amsterdam region and identification of specific HPeV variants by direct genotyping of stool samples
Abstract
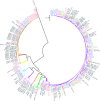
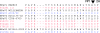
Human parechoviruses (HPeV) are widespread pathogens belonging to the Picornavirus family. Six genotypes, which have predominantly been isolated from children, are known. Data on prevalence of HPeV genotypes are generally based on cell culture, which may underestimate the prevalence of certain HPeV strains that are difficult to grow. We studied 1,824 stool samples from 1,379 children (<5 years old) sent to the Academic Medical Center, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, between 2004 and 2006. Samples were screened using specific human enterovirus (HEV) and HPeV real-time PCRs based on the 5' untranslated region. A high percentage of HPeV infections (16.3%), comparable to the percentage of HEV infections (18.4%), were found by PCR in stool samples. HPeV-positive stool samples were directly genotyped based on the VP1 region for the first time to avoid a culture bias. HPeV1 was found to be the most prevalent type. The majority of the HPeV1 strains clustered separately from the prototype strain, Harris, which has not been reported to circulate lately. However, we could identify three strains as HPeV1 Harris. HPeV3 was identified as the second most predominant type during 2004 and 2006 but was not found in 2005. HPeV4 to -6 were found in smaller numbers. One strain could not be associated with a known HPeV type (VP1 gene nucleotide similarity: 71%), possibly indicating a new genotype. Also, we report the first identification of three HPeV5 strains and one HPeV1 strain with a different motif at the C-terminal end of VP1, where the arginine-glycine-aspartic acid (RGD) motif is normally located.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Diversity of human parechoviruses isolated from stool samples collected from Thai children with acute gastroenteritis.J Clin Microbiol. 2010 Jan;48(1):115-9. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01015-09. Epub 2009 Oct 28. J Clin Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 19864477 Free PMC article.
-
[Human parechovirus associated sepsis and central nervous system infections in hospitalized children].Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2014 Jun;52(6):444-8. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2014. PMID: 25190165 Chinese.
-
Detection of human parechovirus in stool samples collected from children with acute gastroenteritis in Japan during 2007-2008.J Med Virol. 2011 Feb;83(2):331-6. doi: 10.1002/jmv.21740. J Med Virol. 2011. PMID: 21181931
-
Pediatric parechovirus infections.J Clin Virol. 2014 Jun;60(2):84-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2014.03.003. Epub 2014 Mar 13. J Clin Virol. 2014. PMID: 24690382 Review.
-
Presence of human non-polio enterovirus and parechovirus genotypes in an Amsterdam hospital in 2007 to 2011 compared to national and international published surveillance data: a comprehensive review.Euro Surveill. 2014 Nov 20;19(46):20964. doi: 10.2807/1560-7917.es2014.19.46.20964. Euro Surveill. 2014. PMID: 25425513 Review.
Cited by
-
Diversity of human parechoviruses isolated from stool samples collected from Thai children with acute gastroenteritis.J Clin Microbiol. 2010 Jan;48(1):115-9. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01015-09. Epub 2009 Oct 28. J Clin Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 19864477 Free PMC article.
-
Characteristics and outcomes of human parechovirus infection in infants (2008-2012).Eur J Pediatr. 2015 Jul;174(7):919-24. doi: 10.1007/s00431-014-2483-3. Epub 2015 Jan 10. Eur J Pediatr. 2015. PMID: 25573462
-
Parechovirus A Pathogenesis and the Enigma of Genotype A-3.Viruses. 2019 Nov 14;11(11):1062. doi: 10.3390/v11111062. Viruses. 2019. PMID: 31739613 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification and molecular characterization of the first complete genome sequence of Human Parechovirus type 15.Sci Rep. 2020 Apr 21;10(1):6759. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-63467-w. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32317760 Free PMC article.
-
Nearly constant shedding of diverse enteric viruses by two healthy infants.J Clin Microbiol. 2012 Nov;50(11):3427-34. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01589-12. Epub 2012 Aug 8. J Clin Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22875894 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baumgarte, S., L. K. de Souza Luna, K. Grywna, M. Panning, J. F. Drexler, C. Karsten, H. I. Huppertz, and C. Drosten. 2008. Prevalence, types, and RNA concentrations of human parechoviruses, including a sixth parechovirus type, in stool samples from patients with acute enteritis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 46242-248. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Beld, M., R. Minnaar, J. Weel, C. Sol, M. Damen, H. van der Avoort, P. M. Wertheim-Van Dillen, A. van Breda, and R. Boom. 2004. Highly sensitive assay for detection of enterovirus in clinical specimens by reverse transcription-PCR with an armored RNA internal control. J. Clin. Microbiol. 423059-3064. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Benschop, K., R. Molenkamp, A. van der Ham, K. Wolthers, and M. Beld. 2008. Rapid detection of human parechoviruses in clinical samples by real-time PCR. J. Clin. Virol. 4169-74. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

