Inflammatory and coagulation biomarkers and mortality in patients with HIV infection
- PMID: 18942885
- PMCID: PMC2570418
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pmed.0050203
Inflammatory and coagulation biomarkers and mortality in patients with HIV infection
Abstract
Background: In the Strategies for Management of Anti-Retroviral Therapy trial, all-cause mortality was higher for participants randomized to intermittent, CD4-guided antiretroviral treatment (ART) (drug conservation [DC]) than continuous ART (viral suppression [VS]).We hypothesized that increased HIV-RNA levels following ART interruption induced activation of tissue factor pathways, thrombosis, and fibrinolysis.
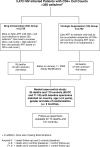
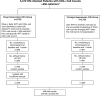
Methods and findings: Stored samples were used to measure six biomarkers: high sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP), interleukin-6 (IL-6), amyloid A, amyloid P, D-dimer, and prothrombin fragment 1+2. Two studies were conducted: (1) a nested case-control study for studying biomarker associations with mortality, and (2) a study to compare DC and VS participants for biomarker changes. For (1), markers were determined at study entry and before death (latest level) for 85 deaths and for two controls (n = 170) matched on country, age, sex, and date of randomization. Odds ratios (ORs) were estimated with logistic regression. For each biomarker, each of the three upper quartiles was compared to the lowest quartile. For (2), the biomarkers were assessed for 249 DC and 250 VS participants at study entry and 1 mo following randomization. Higher levels of hsCRP, IL-6, and D-dimer at study entry were significantly associated with an increased risk of all-cause mortality. Unadjusted ORs (highest versus lowest quartile) were 2.0 (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.0-4.1; p = 0.05), 8.3 (95% CI, 3.3-20.8; p < 0.0001), and 12.4 (95% CI, 4.2-37.0; p < 0.0001), respectively. Associations were significant after adjustment, when the DC and VS groups were analyzed separately, and when latest levels were assessed. IL-6 and D-dimer increased at 1 mo by 30% and 16% in the DC group and by 0% and 5% in the VS group (p < 0.0001 for treatment difference for both biomarkers); increases in the DC group were related to HIV-RNA levels at 1 mo (p < 0.0001). In an expanded case-control analysis (four controls per case), the OR (DC/VS) for mortality was reduced from 1.8 (95% CI, 1.1-3.1; p = 0.02) to 1.5 (95% CI, 0.8-2.8) and 1.4 (95% CI, 0.8-2.5) after adjustment for latest levels of IL-6 and D-dimer, respectively.
Conclusions: IL-6 and D-dimer were strongly related to all-cause mortality. Interrupting ART may further increase the risk of death by raising IL-6 and D-dimer levels. Therapies that reduce the inflammatory response to HIV and decrease IL-6 and D-dimer levels may warrant investigation.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00027352.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Pre-ART levels of inflammation and coagulation markers are strong predictors of death in a South African cohort with advanced HIV disease.PLoS One. 2012;7(3):e24243. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0024243. Epub 2012 Mar 20. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22448211 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Changes in inflammatory and coagulation biomarkers: a randomized comparison of immediate versus deferred antiretroviral therapy in patients with HIV infection.J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2011 Jan 1;56(1):36-43. doi: 10.1097/QAI.0b013e3181f7f61a. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2011. PMID: 20930640 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Severity of cardiovascular disease outcomes among patients with HIV is related to markers of inflammation and coagulation.J Am Heart Assoc. 2014 May 28;3(3):e000844. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.114.000844. J Am Heart Assoc. 2014. PMID: 24870935 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma concentrations of IL-6, MIP-1β, IP-10, and PTX-3 as predictors of the immunological response to antiretroviral treatment in people with HIV.Front Immunol. 2024 Aug 29;15:1447926. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1447926. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39267754 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inflammatory markers and poor outcome after stroke: a prospective cohort study and systematic review of interleukin-6.PLoS Med. 2009 Sep;6(9):e1000145. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1000145. Epub 2009 Sep 8. PLoS Med. 2009. PMID: 19901973 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Acupuncture to Reduce HIV-Associated Inflammation.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015;2015:908538. doi: 10.1155/2015/908538. Epub 2015 Apr 2. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015. PMID: 25922615 Free PMC article.
-
IL-8 Alterations in HIV-1 Infected Children With Disease Progression.Medicine (Baltimore). 2016 May;95(21):e3734. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000003734. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016. PMID: 27227934 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidized LDL Levels Are Increased in HIV Infection and May Drive Monocyte Activation.J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2015 Jun 1;69(2):154-60. doi: 10.1097/QAI.0000000000000566. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2015. PMID: 25647528 Free PMC article.
-
Sudden cardiac death in patients with human immunodeficiency virus infection.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012 May 22;59(21):1891-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2012.02.024. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012. PMID: 22595409 Free PMC article.
-
Making a Monkey out of Human Immunodeficiency Virus/Simian Immunodeficiency Virus Pathogenesis: Immune Cell Depletion Experiments as a Tool to Understand the Immune Correlates of Protection and Pathogenicity in HIV Infection.Viruses. 2024 Jun 17;16(6):972. doi: 10.3390/v16060972. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 38932264 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- The Strategies for Management of Antiretroviral Therapy (SMART) Study Group. CD4+ count - guided interruption of antiretroviral treatment. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:2283–2296. - PubMed
-
- De Larrangas GF, Petroni A, Deluchi G, Alonso BS, Benetucci JA. Viral load and disease progression as responsible for endothelial activation and/or injury in human immunodeficiency virus-1-infected patients. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 2003;14:15–18. - PubMed
-
- Lekakis J, Ikonomidis I, Palios I, Rollidis L, Tsiodras S, et al. Arterial wall properties and endothelial function in HIV infected patients. Euro Heart J (Suppl 1) 2007;28:P2870.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

