Measles virus V protein is a decoy substrate for IkappaB kinase alpha and prevents Toll-like receptor 7/9-mediated interferon induction
- PMID: 18922877
- PMCID: PMC2593327
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01321-08
Measles virus V protein is a decoy substrate for IkappaB kinase alpha and prevents Toll-like receptor 7/9-mediated interferon induction
Abstract
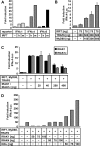
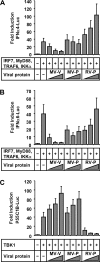
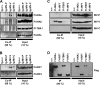
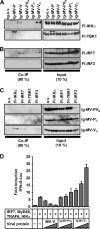
The central role of plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDC) in activating host immune responses stems from their high capacity to express alpha interferon (IFN-alpha) after stimulation of Toll-like receptors 7 and 9 (TLR7 and -9). This involves the adapter MyD88 and the kinases interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 1 (IRAK1), IRAK4, and IkappaB kinase alpha (IKKalpha), which activates IFN regulatory factor 7 (IRF7) and is independent of the canonical kinases TBK1 and IKKepsilon. We have recently shown that the immunosuppressive measles virus (MV) abolishes TLR7/9/MyD88-dependent IFN induction in human pDC (Schlender et al., J. Virol. 79:5507-5515, 2005), but the molecular mechanisms remained elusive. Here, we have reconstituted the pathway in cell lines and identified IKKalpha and IRF7 as specific targets of the MV V protein (MV-V). Binding of MV-V to IKKalpha resulted in phosphorylation of V on the expense of IRF7 phosphorylation by IKKalpha in vitro and in living cells. This corroborates the role of IKKalpha as the kinase phosphorylating IRF7. MV-V in addition bound to IRF7 and to phosphomimetic IRF7 and inhibited IRF7 transcriptional activity. Binding to both IKKalpha and IRF7 required the 68-amino-acid unique C-terminal domain of V. Inhibition of TLR/MyD88-dependent IFN induction by MV-V is unique among paramyxovirus V proteins and should contribute to the unique immunosuppressive phenotype of measles. The mechanisms employed by MV-V inspire strategies to interfere with immunopathological TLR/MyD88 signaling.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Human parainfluenza virus type 2 V protein inhibits TRAF6-mediated ubiquitination of IRF7 to prevent TLR7- and TLR9-dependent interferon induction.J Virol. 2013 Jul;87(14):7966-76. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03525-12. Epub 2013 May 15. J Virol. 2013. PMID: 23678181 Free PMC article.
-
An anti-interferon activity shared by paramyxovirus C proteins: inhibition of Toll-like receptor 7/9-dependent alpha interferon induction.FEBS Lett. 2014 Jan 3;588(1):28-34. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2013.11.015. Epub 2013 Nov 20. FEBS Lett. 2014. PMID: 24269682
-
Human Metapneumovirus M2-2 Protein Acts as a Negative Regulator of Alpha Interferon Production by Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells.J Virol. 2017 Sep 27;91(20):e00579-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00579-17. Print 2017 Oct 15. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 28768858 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation and function of IKK and IKK-related kinases.Sci STKE. 2006 Oct 17;2006(357):re13. doi: 10.1126/stke.3572006re13. Sci STKE. 2006. PMID: 17047224 Review.
-
[Nucleic acids recognition by innate immunity].Uirusu. 2012 Jun;62(1):39-45. doi: 10.2222/jsv.62.39. Uirusu. 2012. PMID: 23189823 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Toll-like receptors: key players in antiviral immunity.Curr Opin Virol. 2011 Dec;1(6):447-54. doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2011.10.006. Epub 2011 Oct 28. Curr Opin Virol. 2011. PMID: 22440908 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antagonism of the phosphatase PP1 by the measles virus V protein is required for innate immune escape of MDA5.Cell Host Microbe. 2014 Jul 9;16(1):19-30. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2014.06.007. Cell Host Microbe. 2014. PMID: 25011105 Free PMC article.
-
Human parainfluenza virus type 2 V protein inhibits TRAF6-mediated ubiquitination of IRF7 to prevent TLR7- and TLR9-dependent interferon induction.J Virol. 2013 Jul;87(14):7966-76. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03525-12. Epub 2013 May 15. J Virol. 2013. PMID: 23678181 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of interferon regulatory factor 3 activation by paramyxovirus V protein.J Virol. 2012 Jul;86(13):7136-45. doi: 10.1128/JVI.06705-11. Epub 2012 Apr 24. J Virol. 2012. PMID: 22532687 Free PMC article.
-
Measles virus-induced suppression of immune responses.Immunol Rev. 2010 Jul;236:176-89. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2010.00925.x. Immunol Rev. 2010. PMID: 20636817 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

