Functional regulation of MyD88-activated interferon regulatory factor 5 by K63-linked polyubiquitination
- PMID: 18824541
- PMCID: PMC2593423
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00662-08
Functional regulation of MyD88-activated interferon regulatory factor 5 by K63-linked polyubiquitination
Abstract
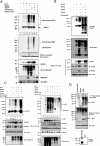
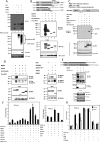
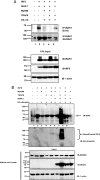
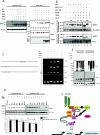
Interferon regulatory factor 5 (IRF-5) plays an important role in the innate antiviral and inflammatory response. Specific IRF-5 haplotypes are associated with dysregulated expression of type I interferons and predisposition to autoimmune disorders. IRF-5 is activated by Toll-like receptor 7 (TLR7) and TLR9 via the MyD88 pathway, where it interacts with both MyD88 and the E3 ubiquitin ligase, TRAF6. To understand the role of these interactions in the regulation of IRF-5, we examined the role of ubiquitination and showed that IRF-5 is subjected to TRAF6-mediated K63-linked ubiquitination, which is important for IRF-5 nuclear translocation and target gene regulation. We show that while the murine IRF-5 and human IRF-5 variant 4 (HuIRF-5v4) and HuIRF-5v5 are ubiquitinated, an IRF-5 bone marrow variant mutant containing an internal deletion of 288 nucleotides is not ubiquitinated. Lysine residues at positions 410 and 411 in a putative TRAF6 consensus binding domain of IRF-5 are the targets of K63-linked ubiquitination. Mutagenesis of these two lysines abolished IRF-5 ubiquitination, nuclear translocation, and the IFNA promoter-inducing activity but not the IRF-5-TRAF6 interaction. Finally, we show that IRAK1 associates with IRF-5 and that this interaction precedes and is required for IRF-5 ubiquitination and activation. Thus, our findings offer a new mechanistic insight into IRF-5 gene induction program through hitherto unknown processes of IRF-5 ubiquitination.
Figures
Similar articles
-
IKKalpha negatively regulates IRF-5 function in a MyD88-TRAF6 pathway.Cell Signal. 2010 Jan;22(1):117-27. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2009.09.021. Epub 2009 Sep 25. Cell Signal. 2010. PMID: 19786094
-
Src Family Kinases Regulate Interferon Regulatory Factor 1 K63 Ubiquitination following Activation by TLR7/8 Vaccine Adjuvant in Human Monocytes and B Cells.Front Immunol. 2018 Mar 1;9:330. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00330. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29545793 Free PMC article.
-
Endotoxin tolerance impairs IL-1 receptor-associated kinase (IRAK) 4 and TGF-beta-activated kinase 1 activation, K63-linked polyubiquitination and assembly of IRAK1, TNF receptor-associated factor 6, and IkappaB kinase gamma and increases A20 expression.J Biol Chem. 2011 Mar 11;286(10):7905-7916. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.182873. Epub 2011 Jan 10. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21220427 Free PMC article.
-
The role of hybrid ubiquitin chains in the MyD88 and other innate immune signalling pathways.Cell Death Differ. 2017 Jul;24(7):1153-1159. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2017.17. Epub 2017 May 5. Cell Death Differ. 2017. PMID: 28475177 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IRF family proteins and type I interferon induction in dendritic cells.Cell Res. 2006 Feb;16(2):134-40. doi: 10.1038/sj.cr.7310018. Cell Res. 2006. PMID: 16474425 Review.
Cited by
-
TRAF molecules in cell signaling and in human diseases.J Mol Signal. 2013 Jun 13;8(1):7. doi: 10.1186/1750-2187-8-7. J Mol Signal. 2013. PMID: 23758787 Free PMC article.
-
Reducing IRF5 expression attenuates colitis in mice, but impairs the clearance of intestinal pathogens.Mucosal Immunol. 2019 Jul;12(4):874-887. doi: 10.1038/s41385-019-0165-1. Epub 2019 May 3. Mucosal Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31053739 Free PMC article.
-
Cathepsin K Deficiency Ameliorates Systemic Lupus Erythematosus-like Manifestations in Faslpr Mice.J Immunol. 2017 Mar 1;198(5):1846-1854. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1501145. Epub 2017 Jan 16. J Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28093526 Free PMC article.
-
Increased Adipose Tissue Expression of Interferon Regulatory Factor (IRF)-5 in Obesity: Association with Metabolic Inflammation.Cells. 2019 Nov 11;8(11):1418. doi: 10.3390/cells8111418. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31718015 Free PMC article.
-
IRF5 Is Required for Bacterial Clearance in Human M1-Polarized Macrophages, and IRF5 Immune-Mediated Disease Risk Variants Modulate This Outcome.J Immunol. 2019 Feb 1;202(3):920-930. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1800226. Epub 2018 Dec 28. J Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30593537 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akira, S., and K. Takeda. 2004. Toll-like receptor signalling. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 4499-511. - PubMed
-
- Akira, S., S. Uematsu, and O. Takeuchi. 2006. Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. Cell 124783-801. - PubMed
-
- Alexopoulou, L., A. C. Holt, R. Medzhitov, and R. A. Flavell. 2001. Recognition of double-stranded RNA and activation of NF-κB by Toll-like receptor 3. Nature 413732-738. - PubMed
-
- Barnes, B., B. Lubyova, and P. M. Pitha. 2002. On the role of IRF in host defense. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2259-71. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
