Sae2, Exo1 and Sgs1 collaborate in DNA double-strand break processing
- PMID: 18806779
- PMCID: PMC3818707
- DOI: 10.1038/nature07312
Sae2, Exo1 and Sgs1 collaborate in DNA double-strand break processing
Abstract
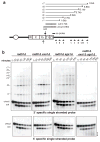
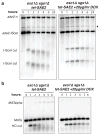
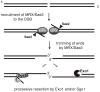
DNA ends exposed after introduction of double-strand breaks (DSBs) undergo 5'-3' nucleolytic degradation to generate single-stranded DNA, the substrate for binding by the Rad51 protein to initiate homologous recombination. This process is poorly understood in eukaryotes, but several factors have been implicated, including the Mre11 complex (Mre11-Rad50-Xrs2/NBS1), Sae2/CtIP/Ctp1 and Exo1. Here we demonstrate that yeast Exo1 nuclease and Sgs1 helicase function in alternative pathways for DSB processing. Novel, partially resected intermediates accumulate in a double mutant lacking Exo1 and Sgs1, which are poor substrates for homologous recombination. The early processing step that generates partly resected intermediates is dependent on Sae2. When Sae2 is absent, in addition to Exo1 and Sgs1, unprocessed DSBs accumulate and homology-dependent repair fails. These results suggest a two-step mechanism for DSB processing during homologous recombination. First, the Mre11 complex and Sae2 remove a small oligonucleotide(s) from the DNA ends to form an early intermediate. Second, Exo1 and/or Sgs1 rapidly process this intermediate to generate extensive tracts of single-stranded DNA that serve as substrate for Rad51.
Figures
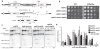

Comment in
-
Molecular biology: DNA endgames.Nature. 2008 Oct 9;455(7214):740-1. doi: 10.1038/455740a. Nature. 2008. PMID: 18843352 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Sgs1 helicase and two nucleases Dna2 and Exo1 resect DNA double-strand break ends.Cell. 2008 Sep 19;134(6):981-94. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.08.037. Cell. 2008. PMID: 18805091 Free PMC article.
-
Sae2 antagonizes Rad9 accumulation at DNA double-strand breaks to attenuate checkpoint signaling and facilitate end resection.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Dec 18;115(51):E11961-E11969. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1816539115. Epub 2018 Dec 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 30510002 Free PMC article.
-
Functional interplay between the 53BP1-ortholog Rad9 and the Mre11 complex regulates resection, end-tethering and repair of a double-strand break.PLoS Genet. 2015 Jan 8;11(1):e1004928. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004928. eCollection 2015 Jan. PLoS Genet. 2015. PMID: 25569305 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism and regulation of DNA end resection in eukaryotes.Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2016 May-Jun;51(3):195-212. doi: 10.3109/10409238.2016.1172552. Epub 2016 Apr 20. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 27098756 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DNA End Resection: Nucleases Team Up with the Right Partners to Initiate Homologous Recombination.J Biol Chem. 2015 Sep 18;290(38):22931-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R115.675942. Epub 2015 Jul 31. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 26231213 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cell biology of mitotic recombination.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2015 Mar 2;7(3):a016535. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a016535. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2015. PMID: 25731763 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Caffeine inhibits gene conversion by displacing Rad51 from ssDNA.Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Aug 18;43(14):6902-18. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv525. Epub 2015 May 27. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015. PMID: 26019181 Free PMC article.
-
Differential requirement for SUB1 in chromosomal and plasmid double-strand DNA break repair.PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e58015. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0058015. Epub 2013 Mar 12. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23554872 Free PMC article.
-
Mouse HFM1/Mer3 is required for crossover formation and complete synapsis of homologous chromosomes during meiosis.PLoS Genet. 2013 Mar;9(3):e1003383. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003383. Epub 2013 Mar 21. PLoS Genet. 2013. PMID: 23555294 Free PMC article.
-
Replication fork integrity and intra-S phase checkpoint suppress gene amplification.Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Mar 11;43(5):2678-90. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv084. Epub 2015 Feb 11. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015. PMID: 25672394 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lee SE, et al. Saccharomyces Ku70, mre11/rad50 and RPA proteins regulate adaptation to G2/M arrest after DNA damage. Cell. 1998;94:399–409. - PubMed
-
- Lisby M, Barlow JH, Burgess RC, Rothstein R. Choreography of the DNA damage response: spatiotemporal relationships among checkpoint and repair proteins. Cell. 2004;118:699–713. - PubMed
-
- Nelms BE, Maser RS, MacKay JF, Lagally MG, Petrini JH. In situ visualization of DNA double-strand break repair in human fibroblasts. Science. 1998;280:590–2. - PubMed
-
- Krogh BO, Symington LS. Recombination proteins in yeast. Annu Rev Genet. 2004;38:233–71. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

