Deficiency of Bloom syndrome helicase activity is radiomimetic
- PMID: 18787401
- PMCID: PMC2891340
- DOI: 10.4161/cbt.7.11.6779
Deficiency of Bloom syndrome helicase activity is radiomimetic
Abstract
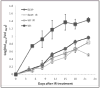
Bloom syndrome is caused by homozygous mutations in BLM, which encodes a RecQ DNA helicase. Patient-derived cells deficient in BLM helicase activity exhibit genetic instability--apparent cytogenetically as sister chromatid exchanges--and activated DNA damage signaling. In this report, we show that BLM-knockout colorectal cancer cells exhibited endogenous, ATM-dependent double-strand DNA break responses similar to those recently observed in Bloom syndrome patient-derived cells. Xenograft tumors established from BLM-deficient cancer cells were not radiosensitive, but exhibited growth impairment that was comparable to that of wild type tumors treated with a single, high dose of ionizing radiation. These results suggest that pharmacological inhibitors of BLM would have a radiomimetic effect and that transient inhibition of BLM activity might be a viable strategy for anticancer therapy.
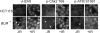
Figures

Similar articles
-
Endogenous gamma-H2AX-ATM-Chk2 checkpoint activation in Bloom's syndrome helicase deficient cells is related to DNA replication arrested forks.Mol Cancer Res. 2007 Jul;5(7):713-24. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-07-0028. Mol Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17634426
-
Functional link between BLM defective in Bloom's syndrome and the ataxia-telangiectasia-mutated protein, ATM.J Biol Chem. 2002 Aug 23;277(34):30515-23. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M203801200. Epub 2002 May 28. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 12034743
-
ATM-dependent phosphorylation and accumulation of endogenous BLM protein in response to ionizing radiation.Oncogene. 2000 Dec 7;19(52):5955-63. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1204003. Oncogene. 2000. PMID: 11146546
-
Clinical features of Bloom syndrome and function of the causative gene, BLM helicase.Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2004 May;4(3):393-401. doi: 10.1586/14737159.4.3.393. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2004. PMID: 15137905 Review.
-
Bloom syndrome and the underlying causes of genetic instability.Mol Genet Metab. 2021 May;133(1):35-48. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2021.03.003. Epub 2021 Mar 10. Mol Genet Metab. 2021. PMID: 33736941 Review.
Cited by
-
Irradiated Blm-deficient mice are a highly tumor prone model for analysis of a broad spectrum of hematologic malignancies.Leuk Res. 2010 Feb;34(2):210-20. doi: 10.1016/j.leukres.2009.06.007. Epub 2009 Aug 25. Leuk Res. 2010. PMID: 19709744 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and pharmacological inactivation of the MYCN gene network as a therapeutic strategy for neuroblastic tumor cells.J Biol Chem. 2015 Jan 23;290(4):2198-212. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.624056. Epub 2014 Dec 4. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25477524 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Traverso G, Bettegowda C, Kraus J, Speicher MR, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B, Lengauer C. Hyper-recombination and genetic instability in BLM-deficient epithelial cells. Cancer Res. 2003;63:8578–81. - PubMed
-
- Wu L, Hickson ID. The bloom’s syndrome helicase suppresses crossing over during homologous recombination. Nature. 2003;426:870–4. - PubMed
-
- Hickson ID. RecQ helicases: Caretakers of the genome. Nat Rev Cancer. 2003;3:169–78. - PubMed
-
- Ockey CH, Saffhill R. Delayed DNA maturation, a possible cause of the elevated sister-chromatid exchange in bloom’s syndrome. Carcinogenesis. 1986;7:53–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
