Internal deletions of IE2 86 and loss of the late IE2 60 and IE2 40 proteins encoded by human cytomegalovirus affect the levels of UL84 protein but not the amount of UL84 mRNA or the loading and distribution of the mRNA on polysomes
- PMID: 18787008
- PMCID: PMC2573290
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01293-08
Internal deletions of IE2 86 and loss of the late IE2 60 and IE2 40 proteins encoded by human cytomegalovirus affect the levels of UL84 protein but not the amount of UL84 mRNA or the loading and distribution of the mRNA on polysomes
Abstract
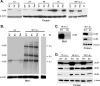
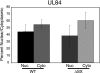
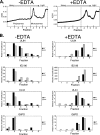
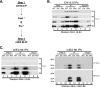
The major immediate-early (IE) region of human cytomegalovirus encodes two IE proteins, IE1 72 and IE2 86, that are translated from alternatively spliced transcripts that differ in their 3' ends. Two other proteins that correspond to the C-terminal region of IE2 86, IE2 60 and IE2 40, are expressed at late times. In this study, we used IE2 mutant viruses to examine the mechanism by which IE2 86, IE2 60, and IE2 40 affect the expression of a viral DNA replication factor, UL84. Deletion of amino acids (aa) 136 to 290 of IE2 86 results in a significant decrease in UL84 protein during the infection. This loss of UL84 is both proteasome and calpain independent, and the stability of the protein in the context of infection with the mutant remains unaffected. The RNA for UL84 is expressed to normal levels in the mutant virus-infected cells, as are the RNAs for two other proteins encoded by this region, UL85 and UL86. Moreover, nuclear-to-cytoplasmic transport and the distribution of the UL84 mRNA on polysomes are unaffected. A region between aa 290 and 369 of IE2 86 contributes to the UL84-IE2 86 interaction in vivo and in vitro. IE2 86, IE2 60, and IE2 40 are each able to interact with UL84 in the mutant-infected cells, suggesting that these interactions may be important for the roles of UL84 and the IE2 proteins. Thus, these data have defined the contribution of IE2 86, IE2 60, and IE2 40 to the efficient expression of UL84 throughout the infection.
Figures

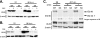

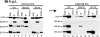

Similar articles
-
Human cytomegalovirus IE2 86 and IE2 40 proteins differentially regulate UL84 protein expression posttranscriptionally in the absence of other viral gene products.J Virol. 2010 May;84(10):5158-70. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00090-10. Epub 2010 Mar 3. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 20200242 Free PMC article.
-
Characteristics of Immediate-Early 2 (IE2) and UL84 Proteins in UL84-Independent Strains of Human Cytomegalovirus (HCMV).Microbiol Spectr. 2021 Oct 31;9(2):e0053921. doi: 10.1128/Spectrum.00539-21. Epub 2021 Sep 22. Microbiol Spectr. 2021. PMID: 34550009 Free PMC article.
-
Human cytomegalovirus UL84 oligomerization and heterodimerization domains act as transdominant inhibitors of oriLyt-dependent DNA replication: evidence that IE2-UL84 and UL84-UL84 interactions are required for lytic DNA replication.J Virol. 2004 Sep;78(17):9203-14. doi: 10.1128/JVI.78.17.9203-9214.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 15308715 Free PMC article.
-
Human cytomegalovirus late protein encoded by ie2: a trans-activator as well as a repressor of gene expression.J Gen Virol. 1994 Sep;75 ( Pt 9):2337-48. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-75-9-2337. J Gen Virol. 1994. PMID: 8077932
-
The IE2 60-kilodalton and 40-kilodalton proteins are dispensable for human cytomegalovirus replication but are required for efficient delayed early and late gene expression and production of infectious virus.J Virol. 2007 Mar;81(6):2573-83. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02454-06. Epub 2007 Jan 3. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17202222 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Inhibition of IKKα by BAY61-3606 Reveals IKKα-Dependent Histone H3 Phosphorylation in Human Cytomegalovirus Infected Cells.PLoS One. 2016 Mar 1;11(3):e0150339. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0150339. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26930276 Free PMC article.
-
A mutation deleting sequences encoding the amino terminus of human cytomegalovirus UL84 impairs interaction with UL44 and capsid localization.J Virol. 2012 Oct;86(20):11066-77. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01379-12. Epub 2012 Aug 1. J Virol. 2012. PMID: 22855486 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple Transcripts Encode Full-Length Human Cytomegalovirus IE1 and IE2 Proteins during Lytic Infection.J Virol. 2016 Sep 12;90(19):8855-65. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00741-16. Print 2016 Oct 1. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 27466417 Free PMC article.
-
Human cytomegalovirus IE2 86 and IE2 40 proteins differentially regulate UL84 protein expression posttranscriptionally in the absence of other viral gene products.J Virol. 2010 May;84(10):5158-70. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00090-10. Epub 2010 Mar 3. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 20200242 Free PMC article.
-
Human MicroRNAs Attenuate the Expression of Immediate Early Proteins and HCMV Replication during Lytic and Latent Infection in Connection with Enhancement of Phosphorylated RelA/p65 (Serine 536) That Binds to MIEP.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 2;23(5):2769. doi: 10.3390/ijms23052769. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35269913 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahn, J. H., C. J. Chiou, and G. S. Hayward. 1998. Evaluation and mapping of the DNA binding and oligomerization domains of the IE2 regulatory protein of human cytomegalovirus using yeast one and two hybrid interaction assays. Gene 21025-36. - PubMed
-
- Andreoni, K. A., X. Wang, S. M. Huang, and E. S. Huang. 2002. Human cytomegalovirus hyperimmune globulin not only neutralizes HCMV infectivity, but also inhibits HCMV-induced intracellular NF-κB, Sp1, and PI3-K signaling pathways. J. Med. Virol. 6733-40. - PubMed
-
- Barrasa, M. I., N. Harel, Y. Yu, and J. C. Alwine. 2003. Strain variations in single amino acids of the 86-kilodalton human cytomegalovirus major immediate-early protein (IE2) affect its functional and biochemical properties: implications of dynamic protein conformation. J. Virol. 774760-4772. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

