F-Seq: a feature density estimator for high-throughput sequence tags
- PMID: 18784119
- PMCID: PMC2732284
- DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btn480
F-Seq: a feature density estimator for high-throughput sequence tags
Abstract
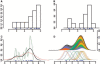
Tag sequencing using high-throughput sequencing technologies are now regularly employed to identify specific sequence features, such as transcription factor binding sites (ChIP-seq) or regions of open chromatin (DNase-seq). To intuitively summarize and display individual sequence data as an accurate and interpretable signal, we developed F-Seq, a software package that generates a continuous tag sequence density estimation allowing identification of biologically meaningful sites whose output can be displayed directly in the UCSC Genome Browser.
Availability: The software is written in the Java language and is available on all major computing platforms for download at http://www.genome.duke.edu/labs/furey/software/fseq.
Figures
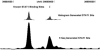
Similar articles
-
BinDNase: a discriminatory approach for transcription factor binding prediction using DNase I hypersensitivity data.Bioinformatics. 2015 Sep 1;31(17):2852-9. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btv294. Epub 2015 May 7. Bioinformatics. 2015. PMID: 25957350
-
A Gibbs sampling strategy applied to the mapping of ambiguous short-sequence tags.Bioinformatics. 2010 Oct 15;26(20):2501-8. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btq460. Epub 2010 Sep 24. Bioinformatics. 2010. PMID: 20871106 Free PMC article.
-
CistromeFinder for ChIP-seq and DNase-seq data reuse.Bioinformatics. 2013 May 15;29(10):1352-4. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btt135. Epub 2013 Mar 18. Bioinformatics. 2013. PMID: 23508969 Free PMC article.
-
Role of ChIP-seq in the discovery of transcription factor binding sites, differential gene regulation mechanism, epigenetic marks and beyond.Cell Cycle. 2014;13(18):2847-52. doi: 10.4161/15384101.2014.949201. Cell Cycle. 2014. PMID: 25486472 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DNA sequence motif: a jack of all trades for ChIP-Seq data.Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol. 2013;91:135-71. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-411637-5.00005-6. Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol. 2013. PMID: 23790213 Review.
Cited by
-
The transcription start site landscape of C. elegans.Genome Res. 2013 Aug;23(8):1348-61. doi: 10.1101/gr.151571.112. Epub 2013 May 1. Genome Res. 2013. PMID: 23636945 Free PMC article.
-
A genome scale transcriptional regulatory model of the human placenta.Sci Adv. 2024 Jun 28;10(26):eadf3411. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adf3411. Epub 2024 Jun 28. Sci Adv. 2024. PMID: 38941464 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide identification of regulatory DNA elements and protein-binding footprints using signatures of open chromatin in Arabidopsis.Plant Cell. 2012 Jul;24(7):2719-31. doi: 10.1105/tpc.112.098061. Epub 2012 Jul 5. Plant Cell. 2012. PMID: 22773751 Free PMC article.
-
Functional evaluation of transposable elements as enhancers in mouse embryonic and trophoblast stem cells.Elife. 2019 Apr 23;8:e44344. doi: 10.7554/eLife.44344. Elife. 2019. PMID: 31012843 Free PMC article.
-
HMGA2 directly mediates chromatin condensation in association with neuronal fate regulation.Nat Commun. 2023 Oct 12;14(1):6420. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-42094-9. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37828010 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Johnson DS, et al. Genome-wide mapping of in vivo protein-DNA interactions. Science. 2007;316:1497–1502. - PubMed
-
- Parzen E. On the estimation of a probability density function and mode. Ann. Math. Stat. 1962;33:1065–1076.
-
- Robertson G, et al. Genome-wide profiles of STAT1 DNA association using chromatin immunoprecipitation and massively parallel sequencing. Nat. Methods. 2007;4:651–657. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

