Regulation of hematopoietic cell function by inhibitory immunoglobulin G receptors and their inositol lipid phosphatase effectors
- PMID: 18759919
- PMCID: PMC2968700
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2008.00663.x
Regulation of hematopoietic cell function by inhibitory immunoglobulin G receptors and their inositol lipid phosphatase effectors
Abstract
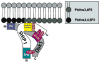
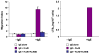
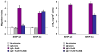
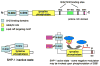
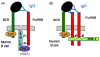
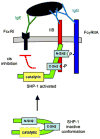
Numerous autoimmune and inflammatory disorders stem from the dysregulation of hematopoietic cell activation. The activity of inositol lipid and protein tyrosine phosphatases, and the receptors that recruit them, is critical for prevention of these disorders. Balanced signaling by inhibitory and activating receptors is now recognized to be an important factor in tuning cell function and inflammatory potential. In this review, we provide an overview of current knowledge of membrane proximal events in signaling by inhibitory/regulatory receptors focusing on structural and functional characteristics of receptors and their effectors Src homology 2 (SH2) domain-containing tyrosine phosphatase 1 and SH2 domain-containing inositol 5-phosphatase-1. We review use of new strategies to identify novel regulatory receptors and effectors. Finally, we discuss complementary actions of paired inhibitory and activating receptors, using Fc gammaRIIA and Fc gammaRIIB regulation human basophil activation as a prototype.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Effects of Src homology domain 2 (SH2)-containing inositol phosphatase (SHIP), SH2-containing phosphotyrosine phosphatase (SHP)-1, and SHP-2 SH2 decoy proteins on Fc gamma RIIB1-effector interactions and inhibitory functions.J Immunol. 2000 Jan 15;164(2):631-8. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.164.2.631. J Immunol. 2000. PMID: 10623804
-
Fc epsilon receptor I-associated lyn-dependent phosphorylation of Fc gamma receptor IIB during negative regulation of mast cell activation.J Immunol. 1998 Feb 15;160(4):1647-58. J Immunol. 1998. PMID: 9469421
-
A mouse Fcgamma-Fcepsilon protein that inhibits mast cells through activation of FcgammaRIIB, SH2 domain-containing inositol phosphatase 1, and SH2 domain-containing protein tyrosine phosphatases.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008 Feb;121(2):441-447.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2007.08.051. Epub 2007 Oct 18. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008. PMID: 17949802
-
Regulation of signal transduction by the Fc gamma receptor family members and their involvement in autoimmunity.Curr Dir Autoimmun. 2002;5:1-29. doi: 10.1159/000060554. Curr Dir Autoimmun. 2002. PMID: 11826753 Review.
-
Nonreceptor protein tyrosine and lipid phosphatases in type I fc(epsilon) receptor-mediated activation of mast cells and basophils.Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2002 Aug;128(4):253-63. doi: 10.1159/000063864. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2002. PMID: 12218363 Review.
Cited by
-
Of ITIMs, ITAMs, and ITAMis: revisiting immunoglobulin Fc receptor signaling.Immunol Rev. 2015 Nov;268(1):66-73. doi: 10.1111/imr.12336. Immunol Rev. 2015. PMID: 26497513 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Co-inhibitory molecules: Controlling the effectors or controlling the controllers?Self Nonself. 2010 Apr;1(2):77-88. doi: 10.4161/self.1.2.11548. Epub 2010 Feb 16. Self Nonself. 2010. PMID: 21487510 Free PMC article.
-
Fc receptor-targeted therapies for the treatment of inflammation, cancer and beyond.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2012 Mar 30;11(4):311-31. doi: 10.1038/nrd2909. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2012. PMID: 22460124 Review.
-
Polymorphisms and interspecies differences of the activating and inhibitory FcγRII of Macaca nemestrina influence the binding of human IgG subclasses.J Immunol. 2014 Jan 15;192(2):792-803. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1301554. Epub 2013 Dec 16. J Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24342805 Free PMC article.
-
Attenuation of HIV-associated human B cell exhaustion by siRNA downregulation of inhibitory receptors.J Clin Invest. 2011 Jul;121(7):2614-24. doi: 10.1172/JCI45685. J Clin Invest. 2011. PMID: 21633172 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

