The Creb1 coactivator Crtc1 is required for energy balance and fertility
- PMID: 18758446
- PMCID: PMC2667698
- DOI: 10.1038/nm.1866
The Creb1 coactivator Crtc1 is required for energy balance and fertility
Abstract
The adipocyte-derived hormone leptin maintains energy balance by acting on hypothalamic leptin receptors (Leprs) that act on the signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (Stat3). Although disruption of Lepr-Stat3 signaling promotes obesity in mice, other features of Lepr function, such as fertility, seem normal, pointing to the involvement of additional regulators. Here we show that the cyclic AMP responsive element-binding protein-1 (Creb1)-regulated transcription coactivator-1 (Crtc1) is required for energy balance and reproduction-Crtc1(-/-) mice are hyperphagic, obese and infertile. Hypothalamic Crtc1 was phosphorylated and inactive in leptin-deficient ob/ob mice, while leptin administration increased amounts of dephosphorylated nuclear Crtc1. Dephosphorylated Crtc1 stimulated expression of the Cartpt and Kiss1 genes, which encode hypothalamic neuropeptides that mediate leptin's effects on satiety and fertility. Crtc1 overexpression in hypothalamic cells increased Cartpt and Kiss1 gene expression, whereas Crtc1 depletion decreased it. Indeed, leptin enhanced Crtc1 activity over the Cartpt and Kiss1 promoters in cells overexpressing Lepr, and these effects were disrupted by expression of a dominant-negative Creb1 polypeptide. As leptin administration increased recruitment of hypothalamic Crtc1 to Cartpt and Kiss1 promoters, our results indicate that the Creb1-Crtc1 pathway mediates the central effects of hormones and nutrients on energy balance and fertility.
Figures
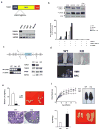

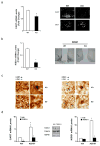
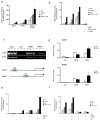
Comment in
-
Mouse fertility is not dependent on the CREB coactivator Crtc1.Nat Med. 2009 Sep;15(9):989-90; author reply 991. doi: 10.1038/nm0909-989. Nat Med. 2009. PMID: 19734865 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Leptin recruits Creb-regulated transcriptional coactivator 1 to improve hyperglycemia in insulin-deficient diabetes.Mol Metab. 2014 Dec 19;4(3):227-36. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2014.12.006. eCollection 2015 Mar. Mol Metab. 2014. PMID: 25737949 Free PMC article.
-
Leptin's effect on puberty in mice is relayed by the ventral premammillary nucleus and does not require signaling in Kiss1 neurons.J Clin Invest. 2011 Jan;121(1):355-68. doi: 10.1172/JCI45106. Epub 2010 Dec 22. J Clin Invest. 2011. PMID: 21183787 Free PMC article.
-
Kisspeptins: bridging energy homeostasis and reproduction.Brain Res. 2010 Dec 10;1364:129-38. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2010.08.057. Epub 2010 Aug 25. Brain Res. 2010. PMID: 20800054 Review.
-
Neither signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) or STAT5 signaling pathways are required for leptin's effects on fertility in mice.Endocrinology. 2013 Jul;154(7):2434-45. doi: 10.1210/en.2013-1109. Epub 2013 May 21. Endocrinology. 2013. PMID: 23696567
-
Metabolic control of puberty: roles of leptin and kisspeptins.Horm Behav. 2013 Jul;64(2):187-94. doi: 10.1016/j.yhbeh.2013.01.014. Horm Behav. 2013. PMID: 23998663 Review.
Cited by
-
Crtc1 Deficiency Causes Obesity Potentially via Regulating PPARγ Pathway in White Adipose.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Apr 12;9:602529. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.602529. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33912553 Free PMC article.
-
Leptin recruits Creb-regulated transcriptional coactivator 1 to improve hyperglycemia in insulin-deficient diabetes.Mol Metab. 2014 Dec 19;4(3):227-36. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2014.12.006. eCollection 2015 Mar. Mol Metab. 2014. PMID: 25737949 Free PMC article.
-
Deletion of Crtc1 leads to hippocampal neuroenergetic impairments associated with depressive-like behavior.Mol Psychiatry. 2022 Nov;27(11):4485-4501. doi: 10.1038/s41380-022-01791-5. Epub 2022 Oct 12. Mol Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 36224260 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of function of the melanocortin 2 receptor accessory protein 2 is associated with mammalian obesity.Science. 2013 Jul 19;341(6143):275-8. doi: 10.1126/science.1233000. Science. 2013. PMID: 23869016 Free PMC article.
-
The nutrient sensor CRTC and Sarcalumenin/thinman represent an alternate pathway in cardiac hypertrophy.Cell Rep. 2024 Aug 27;43(8):114549. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2024.114549. Epub 2024 Aug 1. Cell Rep. 2024. PMID: 39093699 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Friedman JM. The function of leptin in nutrition, weight, and physiology. Nutr Rev. 2002;60:S1–14. discussion S68–84, 85–7. - PubMed
-
- Bjorbaek C, Kahn BB. Leptin signaling in the central nervous system and the periphery. Recent Prog Horm Res. 2004;59:305–31. - PubMed
-
- Badman MK, Flier JS. The adipocyte as an active participant in energy balance and metabolism. Gastroenterology. 2007;132:2103–15. - PubMed
-
- Myers MG, Cowley MA, Munzberg H. Mechanisms of Leptin Action and Leptin Resistance. Annu Rev Physiol. 2008;70:537–556. - PubMed
-
- Lambert PD, et al. CART peptides in the central control of feeding and interactions with neuropeptide Y. Synapse. 1998;29:293–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

