Anticonvulsant treatments of dysphoric mania: a trial of gabapentin, lamotrigine and carbamazepine in Iran
- PMID: 18728802
- PMCID: PMC2515896
- DOI: 10.2147/ndt.s2316
Anticonvulsant treatments of dysphoric mania: a trial of gabapentin, lamotrigine and carbamazepine in Iran
Abstract
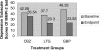
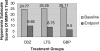
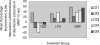
The treatment of dysphoric mania is challenging given the need to treat symptoms of both depression and mania simultaneously without provoking any clinical exacerbation. The newer antiepileptic drugs such as gabapentin, lamotrogine, and carbamazepine are often used as adjuncts to either lithium or valproic acid in the treatment of bipolar disorder. We decided to undertake a monotherapy trial because previous evidence suggested mixed states may be more responsive to anticonvulsants than more traditional antimanic agents. 51 patients with a DSM IV diagnosis of dysphoric mania were randomized to three groups comprising gapbapentin, lamotrogine or carbamazepine and followed for 8 weeks. Psychiatric diagnosis was verified by the structural clinical interview for the DSM-IV (SCID). The MMPI-2 in full was used to assess symptoms at baseline and 8 weeks. All three groups showed significant changes in MMPI-2 scores for depression and mania subscales. Gabapentin showed the greatest change in depression symptom improvement relative to lamotrogine and carbamazepine, respectively. Although manic symptoms improved overall, here were no differences between groups in the degree of manic symptom improvement.
Keywords: anticonvulsant; depression; dysphoric mania; manic-depression; mood stabilizer.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Antipsychotics in bipolar disorders].Encephale. 2004 Sep-Oct;30(5):417-24. doi: 10.1016/s0013-7006(04)95456-5. Encephale. 2004. PMID: 15627046 Review. French.
-
Rational polypharmacy in the bipolar affective disorders.Epilepsy Res Suppl. 1996;11:153-80. Epilepsy Res Suppl. 1996. PMID: 9294735 Review.
-
Efficacy of newer anticonvulsant medications in bipolar spectrum mood disorders.J Clin Psychiatry. 2003;64 Suppl 8:9-14. J Clin Psychiatry. 2003. PMID: 12892536 Review.
-
Rapid titration of mood stabilizers predicts remission from mixed or pure mania in bipolar patients.J Clin Psychiatry. 1998 Apr;59(4):151-8. doi: 10.4088/jcp.v59n0402. J Clin Psychiatry. 1998. PMID: 9590664
-
The place of anticonvulsant therapy in bipolar illness.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 1996 Nov;128(2):115-29. doi: 10.1007/s002130050117. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 1996. PMID: 8956373 Review.
Cited by
-
Is anticonvulsant treatment of mania a class effect? Data from randomized clinical trials.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2011 Jun;17(3):167-77. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-5949.2009.00089.x. Epub 2009 Dec 15. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2011. PMID: 20015083 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gabapentin and pregabalin in bipolar disorder, anxiety states, and insomnia: Systematic review, meta-analysis, and rationale.Mol Psychiatry. 2022 Mar;27(3):1339-1349. doi: 10.1038/s41380-021-01386-6. Epub 2021 Nov 24. Mol Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 34819636 Free PMC article.
-
Risk factors and the outcome of therapy in patients with seizure after Carbamazepine poisoning: A two-year cross-sectional study.J Res Pharm Pract. 2015 Jan-Mar;4(1):18-23. doi: 10.4103/2279-042X.150046. J Res Pharm Pract. 2015. PMID: 25710046 Free PMC article.
-
A critical review of the recent literature and selected therapy guidelines since 2006 on the use of lamotrigine in bipolar disorder.Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2013;9:101-11. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S37126. Epub 2013 Jan 18. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2013. PMID: 23378766 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Valproic acid Clearance between Epileptic Patients and Patients with Acute Mania.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2011 Nov;14(6):546-50. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2011. PMID: 23493631 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Altshuler LL, Keck PE, McElroy SL, et al. Gabapentin in the acute treatment of refractory bipolar disorder. Bipolar Disord. 1999;1:61–5. - PubMed
-
- Akiskal HS. Mood Disorders: Clinical Features. In: Sadock BJ, Sadock VA, editors. Comprehensive Text Book of Psychiatry. 8. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins; 2005. p. 1636.
-
- Akiskal HS, Hantouche EG, Bourgeois ML, et al. Gender, temperament, and the clinical picture in dysphoric mixed mania: findings from a French national study (EPIMAN) J Affect Disord. 1998;50(2–3):175–86. - PubMed
-
- Baker RW, Tohen M, Fawcett J, et al. Acute dysphoric mania: treatment response to olanzapine versus placebo. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2003;23:132–7. - PubMed
-
- Berk M. Lamotrigine and the treatment of mania in bipolar disorder. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 1999;9(Suppl 4):S119–23. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

