Relationship between clinical features and gastric emptying disturbances in diabetes mellitus
- PMID: 18727706
- PMCID: PMC3899345
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.2008.03351.x
Relationship between clinical features and gastric emptying disturbances in diabetes mellitus
Abstract
Background and objectives: Gastric emptying (GE) may be delayed or rapid in diabetes mellitus. We sought to ascertain differences in risk factors or associated features (i.e. diabetic 'phenotype') among patients with diabetes who have rapid, slow or normal GE.
Methods: From a database of patients in whom gastrointestinal transit was assessed by scintigraphy, we compared the diabetic phenotype in diabetic patients with rapid, slow and normal GE.
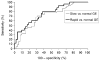
Results: Of 129 patients, 55 (42%) had normal, 46 (36%) had delayed and 28 (22%) patients had rapid GE. In each GE category, there was an approximately equal number of type 1 and type 2 diabetes. In multivariable analyses, significant weight loss (OR, 2.81; 95% CI, 1.09-7.23) and neuropathy (OR, 3.60; 95% CI, 1.007-12.89) were the risk factors for delayed and rapid GE, respectively. Insulin therapy (OR, 0.08; 95% CI, 0.01-0.53) was associated with a lower risk of rapid compared to normal GE. However, other manifestations or characteristics of the diabetes 'phenotype' (i.e. type and duration of diabetes, glycosylated haemoglobin levels, and extraintestinal complications) were not useful for discriminating normal from delayed or rapid GE. At a specificity of 60%, clinical features were 73% sensitive for discriminating between normal and delayed GE and 80% sensitive for discriminating normal from rapid GE.
Conclusions: Diabetes is associated with slow and rapid GE. Because the diabetic phenotype is of limited utility for identifying disordered GE, GE should be assessed in patients with diabetes and gastrointestinal symptoms.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clinical features and disturbances of gastrointestinal transit in patients with rapid gastric emptying.Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2020 Apr;32(4):e13779. doi: 10.1111/nmo.13779. Epub 2020 Jan 20. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2020. PMID: 31960554 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence and predictors of delayed gastric emptying among Indian patients with long-standing type 2 diabetes mellitus.Indian J Gastroenterol. 2016 Sep;35(5):385-392. doi: 10.1007/s12664-016-0694-4. Epub 2016 Sep 26. Indian J Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 27667549
-
Prevalence and determinants of delayed gastric emptying in hospitalised Type 2 diabetic patients.World J Gastroenterol. 2008 Mar 14;14(10):1564-9. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.1564. World J Gastroenterol. 2008. PMID: 18330949 Free PMC article.
-
Gastric emptying in diabetes: an overview.Diabet Med. 1996 Sep;13(9 Suppl 5):S16-22. Diabet Med. 1996. PMID: 8894465 Review.
-
Gastric emptying in type 2 diabetes: quick or slow?Diabet Med. 1996 Sep;13(9 Suppl 5):S31-3. Diabet Med. 1996. PMID: 8894468 Review.
Cited by
-
Relationships between gastric emptying, postprandial glycemia, and incretin hormones.Diabetes Care. 2013 May;36(5):1396-405. doi: 10.2337/dc12-1609. Diabetes Care. 2013. PMID: 23613599 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Nutrient Transporter Expression in the Jejunum in Relation to Body Mass Index in Patients Undergoing Bariatric Surgery.Nutrients. 2016 Oct 29;8(11):683. doi: 10.3390/nu8110683. Nutrients. 2016. PMID: 27801863 Free PMC article.
-
Gastric emptying in postural tachycardia syndrome: a preliminary report.Clin Auton Res. 2013 Aug;23(4):163-7. doi: 10.1007/s10286-013-0193-y. Epub 2013 May 25. Clin Auton Res. 2013. PMID: 23708963 Free PMC article.
-
Diabetic gastroparesis: functional/morphologic background, diagnosis, and treatment options.Curr Diab Rep. 2014;14(9):527. doi: 10.1007/s11892-014-0527-8. Curr Diab Rep. 2014. PMID: 25005121 Review.
-
Effect of Pramlintide on Postprandial Glucose Fluxes in Type 1 Diabetes.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2016 May;101(5):1954-62. doi: 10.1210/jc.2015-3952. Epub 2016 Mar 1. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2016. PMID: 26930181 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Park MI, Camilleri M. Gastroparesis: clinical update. American Journal of Gastroenterology. 2006;101:1129–1139. - PubMed
-
- Horowitz M, O’Donovan D, Jones KL, et al. Gastric emptying in diabetes: clinical significance and treatment. Diabetic Medicine. 2002;19:177–194. - PubMed
-
- Samsom M, Vermeijden JR, Smout AJ, et al. Prevalence of delayed gastric emptying in diabetic patients and relationship to dyspeptic symptoms: a prospective study in unselected diabetic patients. Diabetes Care. 2003;26:3116–3122. - PubMed
-
- Kassander P. Asymptomatic gastric retention in diabetics: gastroparesis diabeticorum. Annals of Internal Medicine. 1958;48:797–812. - PubMed
-
- Camilleri M. Clinical practice. Diabetic gastroparesis. New England Journal of Medicine. 2007;356:820–829. [Erratum appears in New England Journal of Medicine, 357, 427.] - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical