CCAR1, a key regulator of mediator complex recruitment to nuclear receptor transcription complexes
- PMID: 18722177
- PMCID: PMC2562329
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2008.08.001
CCAR1, a key regulator of mediator complex recruitment to nuclear receptor transcription complexes
Abstract
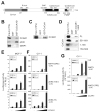
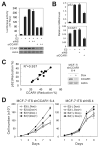
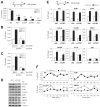
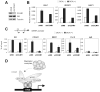
DNA-bound transcription factors recruit many coactivator proteins to remodel chromatin and activate transcription. The Mediator complex is believed to recruit RNA polymerase II to most protein-encoding genes. It is generally assumed that interaction of Mediator subunits with DNA-binding transcription factors is responsible for Mediator recruitment to promoters. However, we report here that Mediator recruitment by nuclear receptors (NR) requires a coactivator protein, CCAR1 (cell-cycle and apoptosis regulator 1). CCAR1 associates with components of the Mediator and p160 coactivator complexes and is recruited to endogenous NR target genes in response to the appropriate hormone. Reduction of endogenous CCAR1 levels inhibited hormone-induced expression of endogenous NR target genes, hormone-induced recruitment of Mediator components and RNA polymerase II to target gene promoters, and estrogen-dependent growth of breast cancer cells. Thus, CCAR1 regulates expression of key proliferation-inducing genes. CCAR1 also functions as a p53 coactivator, suggesting a broader role in transcriptional regulation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
CARP-1/CCAR1: a biphasic regulator of cancer cell growth and apoptosis.Oncotarget. 2015 Mar 30;6(9):6499-510. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3376. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 25894788 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CCAR1 promotes chromatin loading of androgen receptor (AR) transcription complex by stabilizing the association between AR and GATA2.Nucleic Acids Res. 2013 Oct;41(18):8526-36. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt644. Epub 2013 Jul 25. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013. PMID: 23887938 Free PMC article.
-
Developmentally essential protein flightless I is a nuclear receptor coactivator with actin binding activity.Mol Cell Biol. 2004 Mar;24(5):2103-17. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.5.2103-2117.2004. Mol Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 14966289 Free PMC article.
-
Cell Cycle and Apoptosis Regulator 1, CCAR1, Regulates Enhancer-Dependent Nuclear Receptor CAR Transactivation.Mol Pharmacol. 2019 Jan;95(1):120-126. doi: 10.1124/mol.118.114272. Epub 2018 Nov 5. Mol Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30397001
-
Role of the mediator complex in nuclear hormone receptor signaling.Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 2006;156:23-43. doi: 10.1007/s10254-005-0002-0. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16634145 Review.
Cited by
-
Necdin enhances myoblasts survival by facilitating the degradation of the mediator of apoptosis CCAR1/CARP1.PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e43335. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0043335. Epub 2012 Aug 14. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22905258 Free PMC article.
-
The splicing factor CCAR1 regulates the Fanconi anemia/BRCA pathway.Mol Cell. 2024 Jul 25;84(14):2618-2633.e10. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2024.06.031. Epub 2024 Jul 17. Mol Cell. 2024. PMID: 39025073 Free PMC article.
-
CARP-1/CCAR1: a biphasic regulator of cancer cell growth and apoptosis.Oncotarget. 2015 Mar 30;6(9):6499-510. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3376. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 25894788 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A novel mechanism of cell growth regulation by Cell Cycle and Apoptosis Regulatory Protein (CARP)-1.J Mol Signal. 2010 Jul 1;5:7. doi: 10.1186/1750-2187-5-7. J Mol Signal. 2010. PMID: 20594350 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating miR-1254 predicts ventricular remodeling in patients with ST-Segment-Elevation Myocardial Infarction: A cardiovascular magnetic resonance study.Sci Rep. 2018 Oct 11;8(1):15115. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-33491-y. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30310086 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aravind L, Koonin EV. SAP - a putative DNA-binding motif involved in chromosomal organization. Trends Biochem Sci. 2000;25:112–114. - PubMed
-
- Blazek E, Mittler G, Meisterernst M. The mediator of RNA polymerase II. Chromosoma. 2005;113:399–408. - PubMed
-
- Burakov D, Crofts LA, Chang CP, Freedman LP. Reciprocal recruitment of DRIP/mediator and p160 coactivator complexes in vivo by estrogen receptor. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:14359–14362. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

