Reprogrammed FoxP3+ T regulatory cells become IL-17+ antigen-specific autoimmune effectors in vitro and in vivo
- PMID: 18713984
- PMCID: PMC2582200
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.181.5.3137
Reprogrammed FoxP3+ T regulatory cells become IL-17+ antigen-specific autoimmune effectors in vitro and in vivo
Retraction in
-
Retraction: Reprogrammed FoxP3+ T regulatory cells become IL-17+ antigen-specific autoimmune effectors in vitro and in vivo.J Immunol. 2010 Jun 1;184(11):6556. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1090035. J Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20483796 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
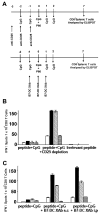
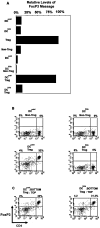
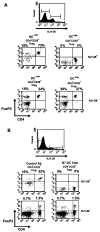
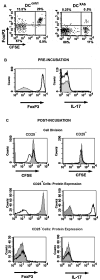
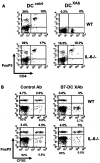
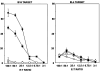
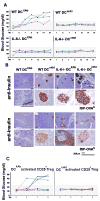
Lymphocyte differentiation from naive CD4(+) T cells into mature Th1, Th2, Th17, or T regulatory cell (Treg) phenotypes has been considered end stage in character. In this study, we demonstrate that dendritic cells (DCs) activated with a novel immune modulator B7-DC XAb (DC(XAb)) can reprogram Tregs into T effector cells. Down-regulation of FoxP3 expression after either in vitro or in vivo Treg-DC(XAb) interaction is Ag-specific, IL-6-dependent, and results in the functional reprogramming of the mature T cell phenotype. The reprogrammed Tregs cease to express IL-10 and TGFbeta, fail to suppress T cell responses, and gain the ability to produce IFN-gamma, IL-17, and TNF-alpha. The ability of IL-6(+) DC(XAb) and the inability of IL-6(-/-) DC(XAb) vaccines to protect animals from lethal melanoma suggest that exogenously modulated DC can reprogram host Tregs. In support of this hypothesis and as a test for Ag specificity, transfer of DC(XAb) into RIP-OVA mice causes a break in immune tolerance, inducing diabetes. Conversely, adoptive transfer of reprogrammed Tregs but not similarly treated CD25(-) T cells into naive RIP-OVA mice is also sufficient to cause autoimmune diabetes. Yet, treatment of normal mice with B7-DC XAb fails to elicit generalized autoimmunity. The finding that mature Tregs can be reprogrammed into competent effector cells provides new insights into the plasticity of T cell lineage, underscores the importance of DC-T cell interaction in balancing immunity with tolerance, points to Tregs as a reservoir of autoimmune effectors, and defines a new approach for breaking tolerance to self Ags as a strategy for cancer immunotherapy.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Indirect recruitment of a CD40 signaling pathway in dendritic cells by B7-DC cross-linking antibody modulates T cell functions.PLoS One. 2009;4(4):e5373. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0005373. Epub 2009 Apr 28. PLoS One. 2009. Retraction in: PLoS One. 2010 Mar 03;5(3). doi: 10.1371/annotation/36ac4b2c-cf27-41d9-90e2-e5d58d307896 PMID: 19399172 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
CD4+CD25+ T regulatory cells induced by LPS-activated bone marrow dendritic cells suppress experimental autoimmune uveoretinitis in vivo.Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2007 Feb;245(2):221-9. doi: 10.1007/s00417-006-0356-9. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2007. PMID: 16741709
-
Tolerogenic dendritic cells induce CD4+CD25hiFoxp3+ regulatory T cell differentiation from CD4+CD25-/loFoxp3- effector T cells.J Immunol. 2010 Nov 1;185(9):5003-10. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0903446. Epub 2010 Sep 24. J Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20870943
-
Dendritic cells expand antigen-specific Foxp3+ CD25+ CD4+ regulatory T cells including suppressors of alloreactivity.Immunol Rev. 2006 Aug;212:314-29. doi: 10.1111/j.0105-2896.2006.00422.x. Immunol Rev. 2006. PMID: 16903923 Review.
-
Alloantigen specific T regulatory cells in transplant tolerance.Int Immunopharmacol. 2009 May;9(5):570-4. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2009.01.016. Epub 2009 Jan 29. Int Immunopharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19539571 Review.
Cited by
-
Rapid Expansion of Virus-Specific CD4+ T Cell Types in the CNS of Susceptible Mice Infected with Theiler's Virus.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Oct 19;21(20):7719. doi: 10.3390/ijms21207719. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33086489 Free PMC article.
-
Signaling through C5a receptor and C3a receptor diminishes function of murine natural regulatory T cells.J Exp Med. 2013 Feb 11;210(2):257-68. doi: 10.1084/jem.20121525. Epub 2013 Feb 4. J Exp Med. 2013. PMID: 23382542 Free PMC article.
-
T lymphocytes and normal tissue responses to radiation.Front Oncol. 2012 Sep 19;2:119. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2012.00119. eCollection 2012. Front Oncol. 2012. PMID: 23050243 Free PMC article.
-
Sphingosine 1 phosphate receptor-1 (S1P1) promotes tumor-associated regulatory T cell expansion: leading to poor survival in bladder cancer.Cell Death Dis. 2019 Jan 18;10(2):50. doi: 10.1038/s41419-018-1298-y. Cell Death Dis. 2019. PMID: 30718502 Free PMC article.
-
Correlations between psoriasis and inflammatory bowel diseases.Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:983902. doi: 10.1155/2013/983902. Epub 2013 Jul 21. Biomed Res Int. 2013. PMID: 23971052 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sakaguchi S. Naturally arising CD4+ regulatory T cells for immunologic self-tolerance and negative control of immune responses. Annu Rev Immunol. 2004;22:531–562. - PubMed
-
- Ziegler SF. FOXP3: Of mice and men. Annu Rev Immunol. 2006;24:209–226. - PubMed
-
- Zheng Y, Rudensky AY. Foxp3 in control of the regulatory T cell lineage. Nat Immunol. 2007;8:457–462. - PubMed
-
- Miyara M, Sakaguchi S. Natural regulatory T cells: mechanisms of suppression. Trends Mol Med. 2007;13:108–116. - PubMed
-
- Bonomo A, Kehn PJ, Payer E, Rizzo L, Cheever AW, Shevach EM. Pathogenesis of post-thymectomy autoimmunity: Role of syngeneic MLR-reactive T cells. J Immunol. 1995;154:6602–6611. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

