Binding STAT2 by the acidic domain of human cytomegalovirus IE1 promotes viral growth and is negatively regulated by SUMO
- PMID: 18701593
- PMCID: PMC2573188
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00833-08
Binding STAT2 by the acidic domain of human cytomegalovirus IE1 promotes viral growth and is negatively regulated by SUMO
Abstract
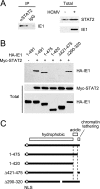
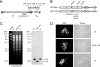
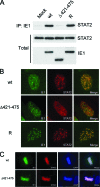
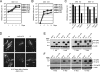
The human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) 72-kDa immediate-early 1 (IE1) protein is thought to modulate cellular antiviral functions impacting on promyelocytic leukemia (PML) nuclear bodies and signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) signaling. IE1 consists of four distinct regions: an amino-terminal region required for nuclear localization, a large central hydrophobic region responsible for PML targeting and transactivation activity, an acidic domain, and a carboxyl-terminal chromatin tethering domain. We found that the acidic domain of IE1 is required for binding to STAT2. A mutant HCMV encoding IE1(Delta421-475) with the acidic domain deleted was generated. In mutant virus-infected cells, IE1(Delta421-475) failed to bind to STAT2. The growth of mutant virus was only slightly delayed at a high multiplicity of infection (MOI) but was severely impaired at a low MOI with low-level accumulation of viral proteins. When cells were pretreated with beta interferon, the mutant virus showed an additional 1,000-fold reduction in viral growth, even at a high MOI, compared to the wild type. The inhibition of STAT2 loading on the target promoter upon infection was markedly reduced with mutant virus. Furthermore, sumoylation of IE1 at this acidic domain was found to abolish the activity of IE1 to bind to STAT2 and repress the interferon-stimulated genes. Our results provide genetic evidence that IE1 binding to STAT2 requires the 55-amino-acid acidic domain and promotes viral growth by interfering with interferon signaling and demonstrate that this viral activity is negatively regulated by a cellular sumoylation pathway.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The chromatin-tethering domain of human cytomegalovirus immediate-early (IE) 1 mediates associations of IE1, PML and STAT2 with mitotic chromosomes, but is not essential for viral replication.J Gen Virol. 2012 Apr;93(Pt 4):716-721. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.037986-0. Epub 2011 Dec 7. J Gen Virol. 2012. PMID: 22158879
-
Physical requirements and functional consequences of complex formation between the cytomegalovirus IE1 protein and human STAT2.J Virol. 2009 Dec;83(24):12854-70. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01164-09. Epub 2009 Oct 7. J Virol. 2009. PMID: 19812155 Free PMC article.
-
Ability of the human cytomegalovirus IE1 protein to modulate sumoylation of PML correlates with its functional activities in transcriptional regulation and infectivity in cultured fibroblast cells.J Virol. 2004 Jun;78(12):6527-42. doi: 10.1128/JVI.78.12.6527-6542.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 15163746 Free PMC article.
-
The Human CMV IE1 Protein: An Offender of PML Nuclear Bodies.Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol. 2017;223:77-94. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-53168-7_4. Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 28528440 Review.
-
Mechanisms of Viral Degradation of Cellular Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 2.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 1;23(1):489. doi: 10.3390/ijms23010489. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35008916 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
In vitro exposure system for study of aerosolized influenza virus.Virology. 2017 Jan;500:62-70. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2016.10.007. Epub 2016 Oct 20. Virology. 2017. PMID: 27771560 Free PMC article.
-
IE1 of Human Cytomegalovirus Inhibits Necroptotic Cell Death via Direct and Indirect Modulation of the Necrosome Complex.Viruses. 2024 Feb 13;16(2):290. doi: 10.3390/v16020290. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 38400065 Free PMC article.
-
Site-specific SUMOylation of viral polymerase processivity factor: a way of localizingtoND10 subnuclear domains for restricted and self-controlled reproduction of herpesvirus.Virulence. 2021 Dec;12(1):2883-2901. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2021.2000689. Virulence. 2021. PMID: 34747321 Free PMC article.
-
The human cytomegalovirus major immediate-early proteins as antagonists of intrinsic and innate antiviral host responses.Viruses. 2009 Dec;1(3):760-79. doi: 10.3390/v1030760. Epub 2009 Nov 5. Viruses. 2009. PMID: 21994568 Free PMC article.
-
Human pathogens and the host cell SUMOylation system.J Virol. 2012 Jan;86(2):642-54. doi: 10.1128/JVI.06227-11. Epub 2011 Nov 9. J Virol. 2012. PMID: 22072786 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ahn, J. H., E. J. Brignole III, and G. S. Hayward. 1998. Disruption of PML subnuclear domains by the acidic IE1 protein of human cytomegalovirus is mediated through interaction with PML and may modulate a RING finger-dependent cryptic transactivator function of PML. Mol. Cell. Biol. 184899-4913. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ahn, J. H., and G. S. Hayward. 2000. Disruption of PML-associated nuclear bodies by IE1 correlates with efficient early stages of viral gene expression and DNA replication in human cytomegalovirus infection. Virology 27439-55. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

