Effects of triglycerides, obesity, and starvation on ghrelin transport across the blood-brain barrier
- PMID: 18682266
- PMCID: PMC2586070
- DOI: 10.1016/j.peptides.2008.07.001
Effects of triglycerides, obesity, and starvation on ghrelin transport across the blood-brain barrier
Abstract
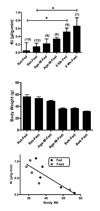
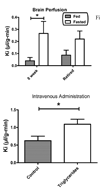
Human ghrelin is transported across the blood-brain barrier (BBB) of normal mice. Here, we studied the effects of triglycerides, obesity, and starvation in retired breeder mice maintained on a high fat diet, mice age-matched to the retired breeders but maintained on normal chow, and 8-week-old mice maintained on breeder chow. The rate of ghrelin transport across the BBB was studied by both the intravenous administration method of multiple-time regression analysis and by the brain perfusion method. We found that (1) obese, aged mice lost the ability to transport intravenously administered ghrelin across the BBB, resulting in an inverse relation between body weight and ghrelin BBB permeability; (2) serum triglycerides promoted transport of intravenously administered ghrelin across the BBB, whereas epinephrine had no effect; (3) fasting tended to promote ghrelin transport across the BBB as most readily shown in brain perfusion studies; (4) evidence suggested that a serum factor promoted ghrelin transport in 8-week-old mice. Overall, these results show that serum factors and physiological states influence the rate at which ghrelin is transported across the blood-brain barrier.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Starvation and triglycerides reverse the obesity-induced impairment of insulin transport at the blood-brain barrier.Endocrinology. 2008 Jul;149(7):3592-7. doi: 10.1210/en.2008-0008. Epub 2008 Apr 10. Endocrinology. 2008. PMID: 18403490 Free PMC article.
-
Triglycerides induce leptin resistance at the blood-brain barrier.Diabetes. 2004 May;53(5):1253-60. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.53.5.1253. Diabetes. 2004. PMID: 15111494
-
Effects of lipopolysaccharide on leptin transport across the blood-brain barrier.Brain Res. 2004 Jul 30;1016(1):58-65. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2004.04.066. Brain Res. 2004. PMID: 15234252
-
The blood-brain barrier as a cause of obesity.Curr Pharm Des. 2008;14(16):1606-14. doi: 10.2174/138161208784705496. Curr Pharm Des. 2008. PMID: 18673202 Review.
-
The blood-brain barrier as a regulatory interface in the gut-brain axes.Physiol Behav. 2006 Nov 30;89(4):472-6. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2006.07.004. Epub 2006 Aug 10. Physiol Behav. 2006. PMID: 16904139 Review.
Cited by
-
Ghrelin reverses ductular reaction and hepatic fibrosis in a rodent model of cholestasis.Sci Rep. 2020 Sep 29;10(1):16024. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-72681-5. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32994489 Free PMC article.
-
Ghrelin forms in the modulation of energy balance and metabolism.Eat Weight Disord. 2019 Dec;24(6):997-1013. doi: 10.1007/s40519-018-0599-6. Epub 2018 Oct 24. Eat Weight Disord. 2019. PMID: 30353455 Review.
-
Taking two to tango: a role for ghrelin receptor heterodimerization in stress and reward.Front Neurosci. 2013 Aug 30;7:148. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2013.00148. Front Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 24009547 Free PMC article. Review.
-
From blood-brain barrier to blood-brain interface: new opportunities for CNS drug delivery.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2016 Apr;15(4):275-92. doi: 10.1038/nrd.2015.21. Epub 2016 Jan 22. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2016. PMID: 26794270 Review.
-
Molecular Ghrelin System in the Pancreatic Acinar Cells: The Role of the Polypeptide, Caerulein and Sensory Nerves.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 May 2;18(5):929. doi: 10.3390/ijms18050929. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28468316 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Banks WA. Enhanced leptin transport across the blood-brain barrier by a1-adrenergic agents. Brain Res. 2001;899:209–217. - PubMed
-
- Banks WA, Coon AB, Robinson SM, Moinuddin A, Shultz JM, Nakaoke R, Morley JE. Triglycerides induce leptin resistance at the blood-brain barrier. Diabetes. 2004;53:1253–1260. - PubMed
-
- Banks WA, Farr SA, Morley JE. The effects of high fat diets on blood-brain barrier transport of leptin: Failure or Adaptation? Physiol Behav. 2006;88:244–248. - PubMed
-
- Banks WA, Jaspan JB, Kastin AJ. Effect of diabetes mellitus on the permeability of the blood-brain barrier to insulin. Peptides. 1997;18:1577–1584. - PubMed
-
- Banks WA, Jaspan JB, Kastin AJ. Selective, physiological transport of insulin across the blood-brain barrier: Novel demonstration by species-specific enzyme immunoassays. Peptides. 1997;18:1257–1262. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

