Cell cycle-independent expression of immediate-early gene 3 results in G1 and G2 arrest in murine cytomegalovirus-infected cells
- PMID: 18667506
- PMCID: PMC2566281
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01212-08
Cell cycle-independent expression of immediate-early gene 3 results in G1 and G2 arrest in murine cytomegalovirus-infected cells
Abstract
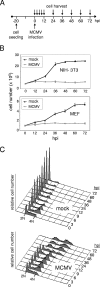
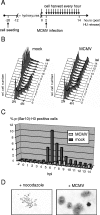
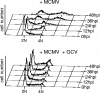
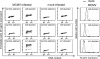
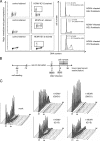
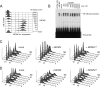
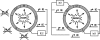
The infectious cycle of human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) is intricately linked to the host's cell cycle. Viral gene expression can be initiated only in G(0)/G(1) phase. Once expressed, the immediate-early gene product IE2 prevents cellular DNA synthesis, arresting infected cells with a G(1) DNA content. This function is required for efficient viral replication in vitro. A prerequisite for addressing its in vivo relevance is the characterization of cell cycle-regulatory activities of CMV species for which animal models have been established. Here, we show that murine CMV (MCMV), like HCMV, has a strong antiproliferative capacity and arrests cells in G(1). Unexpectedly, and in contrast to HCMV, MCMV can also block cells that have passed through S phase by arresting them in G(2). Moreover, MCMV can also replicate in G(2) cells. This is made possible by the cell cycle-independent expression of MCMV immediate-early genes. Transfection experiments show that of several MCMV candidate genes, only immediate-early gene 3 (ie3), the homologue of HCMV IE2, exhibits cell cycle arrest activity. Accordingly, an MCMV ie3 deletion mutant has lost the ability to arrest cells in either G(1) or G(2). Thus, despite interspecies variations in the cell cycle dependence of viral gene expression, the central theme of HCMV IE2-induced cell cycle arrest is conserved in the murine counterpart, raising the possibility of studying its physiological relevance at the level of the whole organism.
Figures

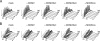
Similar articles
-
The major immediate-early gene ie3 of mouse cytomegalovirus is essential for viral growth.J Virol. 2000 Dec;74(23):11129-36. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.23.11129-11136.2000. J Virol. 2000. PMID: 11070009 Free PMC article.
-
Differential expression of the immediate-early 2 and 3 proteins in developing mouse brains infected with murine cytomegalovirus.Arch Virol. 2006 Nov;151(11):2181-96. doi: 10.1007/s00705-006-0793-0. Epub 2006 Jun 8. Arch Virol. 2006. PMID: 16755372
-
CTCF binding to the first intron of the major immediate early (MIE) gene of human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) negatively regulates MIE gene expression and HCMV replication.J Virol. 2014 Jul;88(13):7389-401. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00845-14. Epub 2014 Apr 16. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 24741094 Free PMC article.
-
Differences between mouse and human cytomegalovirus interactions with their respective hosts at immediate early times of the replication cycle.Med Microbiol Immunol. 2008 Jun;197(2):241-9. doi: 10.1007/s00430-008-0078-1. Epub 2008 Feb 9. Med Microbiol Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18264718 Review.
-
Mouse models of cytomegalovirus latency: overview.J Clin Virol. 2002 Aug;25 Suppl 2:S23-36. doi: 10.1016/s1386-6532(02)00087-2. J Clin Virol. 2002. PMID: 12361754 Review.
Cited by
-
Real-time transcriptional profiling of cellular and viral gene expression during lytic cytomegalovirus infection.PLoS Pathog. 2012 Sep;8(9):e1002908. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002908. Epub 2012 Sep 6. PLoS Pathog. 2012. PMID: 22969428 Free PMC article.
-
Synthetic lethal mutations in the cyclin A interface of human cytomegalovirus.PLoS Pathog. 2017 Jan 27;13(1):e1006193. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006193. eCollection 2017 Jan. PLoS Pathog. 2017. PMID: 28129404 Free PMC article.
-
Human cytomegalovirus riding the cell cycle.Med Microbiol Immunol. 2015 Jun;204(3):409-19. doi: 10.1007/s00430-015-0396-z. Epub 2015 Mar 17. Med Microbiol Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25776080 Review.
-
The mouse cytomegalovirus immediate-early 1 gene is not required for establishment of latency or for reactivation in the lungs.J Virol. 2009 May;83(9):4030-8. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02520-08. Epub 2009 Feb 11. J Virol. 2009. PMID: 19211741 Free PMC article.
-
Adenovirus E1A/E1B Transformed Amniotic Fluid Cells Support Human Cytomegalovirus Replication.Viruses. 2016 Feb 2;8(2):37. doi: 10.3390/v8020037. Viruses. 2016. PMID: 26848680 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bain, M., and J. Sinclair. 2007. The S phase of the cell cycle and its perturbation by human cytomegalovirus. Rev. Med. Virol. 17423-434. - PubMed
-
- Barrasa, M. I., N. Harel, Y. Yu, and J. C. Alwine. 2003. Strain variations in single amino acids of the 86-kilodalton human cytomegalovirus major immediate-early protein (IE2) affect its functional and biochemical properties: implications of dynamic protein conformation. J. Virol. 774760-4772. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

