Noninvasive radiofrequency ablation of cancer targeted by gold nanoparticles
- PMID: 18656617
- PMCID: PMC2596609
- DOI: 10.1016/j.surg.2008.03.036
Noninvasive radiofrequency ablation of cancer targeted by gold nanoparticles
Abstract
Introduction: Current radiofrequency ablation (RFA) techniques require invasive needle placement and are limited by accuracy of targeting. The purpose of this study was to test a novel non invasive radiowave machine that uses RF energy to thermally destroy tissue. Gold nanoparticles were designed and produced to facilitate tissue heating by the radiowaves.
Methods: A solid state radiowave machine consisting of a power generator and transmitting/receiving couplers which transmit radiowaves at 13.56 MHz was used. Gold nanoparticles were produced by citrate reduction and exposed to the RF field either in solutions testing or after incubation with HepG2 cells. A rat hepatoma model using JM-1 cells and Fisher rats was employed using direct injection of nanoparticles into the tumor to focus the radiowaves for select heating. Temperatures were measured using a fiber-optic thermometer for real-time data.
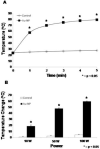
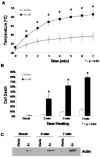
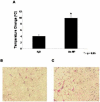
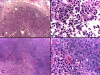
Results: Solutions containing gold nanoparticles heated in a time- and power-dependent manner. HepG2 liver cancer cells cultured in the presence of gold nanoparticles achieved adequate heating to cause cell death upon exposure to the RF field with no cytotoxicity attributable to the gold nanoparticles themselves. In vivo rat exposures at 35 W using direct gold nanoparticle injections resulted in significant temperature increases and thermal injury at subcutaneous injection sites as compared to vehicle (water) injected controls.
Discussion: These data show that non invasive radiowave thermal ablation of cancer cells is feasible when facilitated by gold nanoparticles. Future studies will focus on tumor selective targeting of nanoparticles for in vivo tumor destruction.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Theranostic Iron Oxide/Gold Ion Nanoprobes for MR Imaging and Noninvasive RF Hyperthermia.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017 Aug 30;9(34):28260-28272. doi: 10.1021/acsami.7b08939. Epub 2017 Aug 17. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017. PMID: 28789518
-
Pancreatic carcinoma cells are susceptible to noninvasive radio frequency fields after treatment with targeted gold nanoparticles.Surgery. 2010 Aug;148(2):319-24. doi: 10.1016/j.surg.2010.04.025. Epub 2010 Jun 11. Surgery. 2010. PMID: 20541785 Free PMC article.
-
"Gold nanoparticles composite-folic acid conjugated graphene oxide nanohybrids" for targeted chemo-thermal cancer ablation: In vitro screening and in vivo studies.Eur J Pharm Sci. 2017 Jan 1;96:351-361. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2016.10.011. Epub 2016 Oct 6. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2017. PMID: 27721039
-
Feasibility of a Novel In-situ Local Tumor Ablation and Recycling Machine Based on Radiofrequency Dielectric Heating: In-depth Review on Research Background and Preliminary Report of an Experimental Study.Clin Orthop Surg. 2024 Feb;16(1):157-167. doi: 10.4055/cios23186. Epub 2024 Jan 15. Clin Orthop Surg. 2024. PMID: 38304211 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeted hyperthermia using metal nanoparticles.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2010 Mar 8;62(3):339-45. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2009.11.006. Epub 2009 Nov 10. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2010. PMID: 19909777 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Non-invasive radiofrequency ablation of malignancies mediated by quantum dots, gold nanoparticles and carbon nanotubes.Ther Deliv. 2011 Oct;2(10):1325-30. doi: 10.4155/tde.11.102. Ther Deliv. 2011. PMID: 22826886 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metal nanoparticles as a potential technique for the diagnosis and treatment of gastrointestinal cancer: a comprehensive review.Cancer Cell Int. 2023 Nov 19;23(1):280. doi: 10.1186/s12935-023-03115-1. Cancer Cell Int. 2023. PMID: 37981671 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Remotely Activated Nanoparticles for Anticancer Therapy.Nanomicro Lett. 2020 Oct 27;13(1):11. doi: 10.1007/s40820-020-00537-8. Nanomicro Lett. 2020. PMID: 34138198 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TiO2 nanotube platforms for smart drug delivery: a review.Int J Nanomedicine. 2016 Sep 21;11:4819-4834. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S108847. eCollection 2016. Int J Nanomedicine. 2016. PMID: 27703349 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fiber-Optic Distributed Sensing Network for Thermal Mapping of Gold Nanoparticles-Mediated Radiofrequency Ablation.Biosensors (Basel). 2022 May 18;12(5):352. doi: 10.3390/bios12050352. Biosensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35624653 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tanabe KK, Curley SA, Dodd GD, Siperstein AE, Goldberg SN. Radiofrequency ablation: the experts weigh in. Cancer. 2004;100:641–50. - PubMed
-
- Kuvshinoff B, Fong Y. Surgical therapy of liver metastases. Semin Oncol. 2007;34:177–85. Review. - PubMed
-
- Goodman M, Geller DA. Radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma. In: Carr B, editor. Hepatocellular Cancer. Human Press; Totowa, NJ: 2005. pp. 171–183.
-
- McGahan JP, Browning PD, Brock JM, Tesluk H. Hepatic ablation using radiofrequency electrocautery. Invest Radiol. 1990;25:267–270. - PubMed
-
- Rossi S, Fornari F, Pathies C, Buscarini L. Thermal lesions induced by 480 KHz localized current field in guinea pig and pig liver. Tumori. 1990;76:54–57. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

