Evaluation of alpha-synuclein immunohistochemical methods used by invited experts
- PMID: 18626651
- PMCID: PMC2708176
- DOI: 10.1007/s00401-008-0409-8
Evaluation of alpha-synuclein immunohistochemical methods used by invited experts
Abstract
The use of alpha-synuclein immunohistochemistry has altered our concepts of the cellular pathology, anatomical distribution and prevalence of Lewy body disorders. However, the diversity of methodology between laboratories has led to some inconsistencies in the literature. Adoption of uniformly sensitive methods may resolve some of these differences. Eight different immunohistochemical methods for demonstrating alpha-synuclein pathology, developed in eight separate expert laboratories, were evaluated for their sensitivity for neuronal elements affected by human Lewy body disorders. Identical test sets of formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded sections from subjects diagnosed neuropathologically with or without Lewy body disorders were stained with the eight methods and graded by three observers for specific and nonspecific staining. The methods did not differ significantly in terms of Lewy body counts, but varied considerably in their ability to reveal neuropil elements such as fibers and dots. One method was clearly superior for revealing these neuropil elements and the critical factor contributing to its high sensitivity was considered to be its use of proteinase K as an epitope retrieval method. Some methods, however, achieved relatively high sensitivities with optimized formic acid protocols combined with a hydrolytic step. One method was developed that allows high sensitivity with commercially available reagents.
Figures

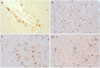
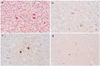
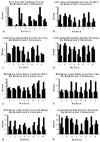

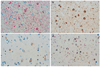
Similar articles
-
Olfactory bulb alpha-synucleinopathy has high specificity and sensitivity for Lewy body disorders.Acta Neuropathol. 2009 Feb;117(2):169-74. doi: 10.1007/s00401-008-0450-7. Epub 2008 Nov 4. Acta Neuropathol. 2009. PMID: 18982334 Free PMC article.
-
TIGAR inclusion pathology is specific for Lewy body diseases.Brain Res. 2019 Mar 1;1706:218-223. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2018.09.032. Epub 2018 Sep 26. Brain Res. 2019. PMID: 30267647
-
Fluorescence and autoradiographic evaluation of tau PET ligand PBB3 to α-synuclein pathology.Mov Disord. 2017 Jun;32(6):884-892. doi: 10.1002/mds.27013. Epub 2017 Apr 25. Mov Disord. 2017. PMID: 28440890 Free PMC article.
-
A critical evaluation of current staging of alpha-synuclein pathology in Lewy body disorders.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009 Jul;1792(7):730-40. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2008.07.006. Epub 2008 Aug 5. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009. PMID: 18718530 Review.
-
Neuropathology underlying clinical variability in patients with synucleinopathies.Acta Neuropathol. 2011 Aug;122(2):187-204. doi: 10.1007/s00401-011-0852-9. Epub 2011 Jul 1. Acta Neuropathol. 2011. PMID: 21720849 Review.
Cited by
-
Sequence variants in eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4-gamma (eIF4G1) are associated with Lewy body dementia.Acta Neuropathol. 2013 Mar;125(3):425-38. doi: 10.1007/s00401-012-1059-4. Epub 2012 Nov 4. Acta Neuropathol. 2013. PMID: 23124435 Free PMC article.
-
Corticospinal tract degeneration associated with TDP-43 type C pathology and semantic dementia.Brain. 2013 Feb;136(Pt 2):455-70. doi: 10.1093/brain/aws324. Epub 2013 Jan 28. Brain. 2013. PMID: 23358603 Free PMC article.
-
Corticobasal degeneration with olivopontocerebellar atrophy and TDP-43 pathology: an unusual clinicopathologic variant of CBD.Acta Neuropathol. 2013 May;125(5):741-52. doi: 10.1007/s00401-013-1087-8. Epub 2013 Jan 31. Acta Neuropathol. 2013. PMID: 23371366 Free PMC article.
-
Arizona Study of Aging and Neurodegenerative Disorders and Brain and Body Donation Program.Neuropathology. 2015 Aug;35(4):354-89. doi: 10.1111/neup.12189. Epub 2015 Jan 26. Neuropathology. 2015. PMID: 25619230 Free PMC article.
-
Parkinson's disease is not associated with gastrointestinal myenteric ganglion neuron loss.Acta Neuropathol. 2012 Nov;124(5):665-80. doi: 10.1007/s00401-012-1040-2. Epub 2012 Sep 2. Acta Neuropathol. 2012. PMID: 22941241 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alafuzoff I, Parkkinen L, Al-Sarraj S, Arzberger T, Bell J, Bodi I, Bogdanovic N, Budka H, Ferrer I, Gelpi E, Gentleman S, Giaccone G, Kamphorst W, King A, Korkolopoulou P, Kovacs GG, Larionov S, Meyronet D, Monoranu C, Morris J, Parchi P, Patsouris E, Roggendorf W, Seilhean D, Streichenberger N, Thal DR, Kretzschmar H. Assessment of alpha-synuclein pathology: a study of the BrainNet Europe Consortium. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2008;67:125–143. - PubMed
-
- Arai T, Ueda K, Ikeda K, Akiyama H, Haga C, Kondo H, Kuroki N, Niizato K, Iritani S, Tsuchiya K. Argyrophilic glial inclusions in the midbrain of patients with Parkinson’s disease and diffuse Lewy body disease are immunopositive for NACP/alpha-synuclein. Neurosci Lett. 1999;259:83–86. - PubMed
-
- Armstrong RA, Cairns NJ, Lantos PL. Multiple system atrophy (MSA): topographic distribution of the alpha-synuclein-associated pathological changes. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2006;12:356–362. - PubMed
-
- Arnold MM, Srivastava S, Fredenburgh J, Stockard CR, Myers RB, Grizzle WE. Effects of fixation and tissue processing on immunohistochemical demonstration of specific antigens. Biotech Histochem. 1996;71:224–230. - PubMed

