Acute alcohol intake induces SOCS1 and SOCS3 and inhibits cytokine-induced STAT1 and STAT3 signaling in human monocytes
- PMID: 18616672
- PMCID: PMC4116614
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.2008.00726.x
Acute alcohol intake induces SOCS1 and SOCS3 and inhibits cytokine-induced STAT1 and STAT3 signaling in human monocytes
Abstract
Background: Acute alcohol consumption is associated with induction of immuno-inhibitory cytokines and down-regulation of pro-inflammatory responses to various pathogens. We previously reported that alcohol activates janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription (JAK/STAT) signaling leading to IL-10 induction. The JAK-STAT pathway also activates its own negative regulators, suppressors of cytokine signaling (SOCS) 1 and SOCS3. SOCS proteins are inducible inhibitors that negatively regulate STAT3/STAT1 signaling pathways induced by cytokines, IL-6 or IFNs. Here we aimed to explore the effect of acute alcohol on induction of SOCS1/SOCS3 and regulation of STAT3/STAT1 pathways induced by IL-6 or IFNs in human monocytes.
Methods: Blood samples from normal volunteers were collected before and 24 hours after consumption of 2 ml vodka/kg body weight. For in vitro experiments human monocytes were pretreated with ethanol (EtOH) followed by stimulation with cytokines; proteins were analyzed by Western blot, nuclear protein binding to DNA by EMSA, and RNA by real time PCR.
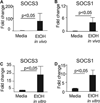
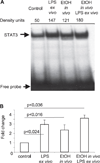
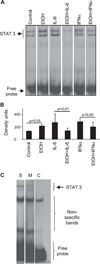
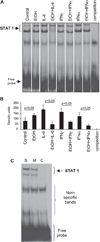
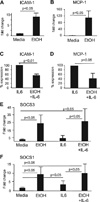
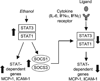
Results: Acute in vivo or in vitro alcohol treatment increased both SOCS1 and SOCS3 RNA expression in monocytes. Alcohol treatment resulted in increased STAT3 and STAT1 DNA binding capacity. Activation of both STAT1 and STAT3 has been shown to induce SOCS1/3. We hypothesized that induction of SOCS proteins by alcohol in turn may lead to modulation of cytokine signaling through STAT1 and STAT3. Indeed, we observed significant down-regulation of IL-6-, IFNalpha- and IFNgamma-induced STAT1 DNA binding as well as inhibition of IL-6- and IFNgamma-induced STAT3 when alcohol was added to monocytes 3 hours prior to the cytokine stimulation. Consistent with inhibition of IL-6-induced STAT3 DNA binding in alcohol-pretreated cells, the levels of IL-6-dependent genes, MCP-1 and ICAM-1, was reduced after IL-6 stimulation. Similar to EtOH alone, combined EtOH+IL-6 simulation resulted in increased expression of both SOCS3 and SOCS1 genes.
Conclusion: While acute alcohol treatment alone activates STAT1/3 signaling pathways and induces SOCS3 and SOCS1 levels in monocytes, alcohol also leads to down-regulation of IL-6-, IFNalpha-, and IFNgamma-induced signaling via STAT1/STAT3 pathways, likely through excessive SOCS activation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The suppressor of cytokine signaling (SOCS) 1 and SOCS3 but not SOCS2 proteins inhibit interferon-mediated antiviral and antiproliferative activities.J Biol Chem. 1998 Dec 25;273(52):35056-62. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.52.35056. J Biol Chem. 1998. PMID: 9857039
-
The comparative roles of suppressor of cytokine signaling-1 and -3 in the inhibition and desensitization of cytokine signaling.J Biol Chem. 2006 Apr 21;281(16):11135-43. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M509595200. Epub 2006 Feb 10. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16473883
-
Impaired IFN-gamma-dependent inflammatory responses in human keratinocytes overexpressing the suppressor of cytokine signaling 1.J Immunol. 2002 Jul 1;169(1):434-42. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.169.1.434. J Immunol. 2002. PMID: 12077274
-
Can the protective actions of JAK-STAT in the heart be exploited therapeutically? Parsing the regulation of interleukin-6-type cytokine signaling.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2007 Aug;50(2):126-41. doi: 10.1097/FJC.0b013e318068dd49. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17703129 Review.
-
SOCS3: A novel therapeutic target for cardioprotection.JAKSTAT. 2012 Oct 1;1(4):234-40. doi: 10.4161/jkst.22435. JAKSTAT. 2012. PMID: 24058778 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Modulation of intracellular restriction factors contributes to methamphetamine-mediated enhancement of acquired immune deficiency syndrome virus infection of macrophages.Curr HIV Res. 2012 Jul;10(5):407-14. doi: 10.2174/157016212802138797. Curr HIV Res. 2012. PMID: 22591364 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SIRT2-PFKP interaction dysregulates phagocytosis in macrophages with acute ethanol-exposure.Front Immunol. 2023 Jan 27;13:1079962. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1079962. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36865524 Free PMC article.
-
Elevated inflammatory response in caveolin-1-deficient mice with Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection is mediated by STAT3 protein and nuclear factor kappaB (NF-kappaB).J Biol Chem. 2011 Jun 17;286(24):21814-25. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.237628. Epub 2011 Apr 22. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21515682 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of TLR8- and TLR4-induced Type I IFN induction by alcohol is different from its effects on inflammatory cytokine production in monocytes.BMC Immunol. 2011 Sep 30;12:55. doi: 10.1186/1471-2172-12-55. BMC Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21962237 Free PMC article.
-
Alcohol suppresses the granulopoietic response to pulmonary Streptococcus pneumoniae infection with enhancement of STAT3 signaling.J Immunol. 2011 Apr 1;186(7):4306-13. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1002885. Epub 2011 Feb 28. J Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21357267 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alexander WS, Hilton DJ. The role of suppressors of cytokine signaling (SOCS) proteins in regulation of the immune response. Annu Rev Immunol. 2004;22:503–529. - PubMed
-
- Boe DM, Nelson S, Zhang P, Quinton L, Bagby GJ. Alcohol-induced suppression of lung chemokine production and the host defense response to Streptococcus pneumoniae. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2003;27:1838–1845. - PubMed
-
- van Boxel-Dezaire AH, Rani MR, Stark GR. Complex modulation of cell type-specific signaling in response to type I interferons. Immunity. 2006;25:361–372. - PubMed
-
- Burysek L, Syrovets T, Simmet T. The serine protease plasmin triggers expression of MCP-1 and CD40 in human primary monocytes via activation of p38 MAPK and janus kinase (JAK)/STAT signaling pathways. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:33509–33517. - PubMed
-
- Chen J, Clemens DL, Cederbaum AI, Gao B. Ethanol inhibits the JAK-STAT signaling pathway in freshly isolated rat hepatocytes but not in cultured hepatocytes or HepG2 cells: evidence for a lack of involvement of ethanol metabolism. Clin Biochem. 2001;34:203–209. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

