Non-P450 aldehyde oxidizing enzymes: the aldehyde dehydrogenase superfamily
- PMID: 18611112
- PMCID: PMC2658643
- DOI: 10.1517/17425255.4.6.697
Non-P450 aldehyde oxidizing enzymes: the aldehyde dehydrogenase superfamily
Abstract
Background: Aldehydes are highly reactive molecules. While several non-P450 enzyme systems participate in their metabolism, one of the most important is the aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH) superfamily, composed of NAD(P)+-dependent enzymes that catalyze aldehyde oxidation.
Objective: This article presents a review of what is currently known about each member of the human ALDH superfamily including the pathophysiological significance of these enzymes.
Methods: Relevant literature involving all members of the human ALDH family was extensively reviewed, with the primary focus on recent and novel findings.
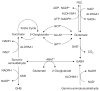
Conclusion: To date, 19 ALDH genes have been identified in the human genome and mutations in these genes and subsequent inborn errors in aldehyde metabolism are the molecular basis of several diseases, including Sjögren-Larsson syndrome, type II hyperprolinemia, gamma-hydroxybutyric aciduria and pyridoxine-dependent seizures. ALDH enzymes also play important roles in embryogenesis and development, neurotransmission, oxidative stress and cancer. Finally, ALDH enzymes display multiple catalytic and non-catalytic functions including ester hydrolysis, antioxidant properties, xenobiotic bioactivation and UV light absorption.
Figures
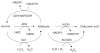




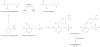
Similar articles
-
Analysis and update of the human aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH) gene family.Hum Genomics. 2005 Jun;2(2):138-43. doi: 10.1186/1479-7364-2-2-138. Hum Genomics. 2005. PMID: 16004729 Free PMC article.
-
Neurotoxicity and metabolism of the catecholamine-derived 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetaldehyde and 3,4-dihydroxyphenylglycolaldehyde: the role of aldehyde dehydrogenase.Pharmacol Rev. 2007 Jun;59(2):125-50. doi: 10.1124/pr.59.2.1. Epub 2007 Mar 22. Pharmacol Rev. 2007. PMID: 17379813 Review.
-
Aldehyde dehydrogenases: from eye crystallins to metabolic disease and cancer stem cells.Chem Biol Interact. 2013 Feb 25;202(1-3):2-10. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2012.10.026. Epub 2012 Nov 16. Chem Biol Interact. 2013. PMID: 23159885 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Update on the aldehyde dehydrogenase gene (ALDH) superfamily.Hum Genomics. 2011 May;5(4):283-303. doi: 10.1186/1479-7364-5-4-283. Hum Genomics. 2011. PMID: 21712190 Free PMC article.
-
Single amino acid polymorphism in aldehyde dehydrogenase gene superfamily.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2015 Jan 1;20(2):335-76. doi: 10.2741/4313. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2015. PMID: 25553455 Review.
Cited by
-
Characterization of aldehyde dehydrogenase isozymes in ovarian cancer tissues and sphere cultures.BMC Cancer. 2012 Aug 1;12:329. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-12-329. BMC Cancer. 2012. PMID: 22852552 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting cancer stem cell-specific markers and/or associated signaling pathways for overcoming cancer drug resistance.Tumour Biol. 2016 Oct;37(10):13059-13075. doi: 10.1007/s13277-016-5294-5. Epub 2016 Aug 26. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 27561758 Review.
-
Aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH) superfamily in plants: gene nomenclature and comparative genomics.Planta. 2013 Jan;237(1):189-210. doi: 10.1007/s00425-012-1749-0. Epub 2012 Sep 25. Planta. 2013. PMID: 23007552 Free PMC article.
-
Mitigation of radiation-induced dermatitis by activation of aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 using topical alda-1 in mice.Radiat Res. 2012 Jul;178(1):69-74. doi: 10.1667/rr2861.1. Epub 2012 Mar 9. Radiat Res. 2012. PMID: 22404739 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative Stress-Part of the Solution or Part of the Problem in the Hypoxic Environment of a Brain Tumor.Antioxidants (Basel). 2020 Aug 14;9(8):747. doi: 10.3390/antiox9080747. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32823815 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vasiliou V, Pappa A, Petersen DR. Role of aldehyde dehydrogenases in endogenous and xenobiotic metabolism. Chem Biol Interact. 2000;129:1–19. - PubMed
-
- Vasiliou V, Pappa A, Estey T. Role of human aldehyde dehydrogenases in endobiotic and xenobiotic metabolism. Drug Metab Rev. 2004;36:279–99. - PubMed
-
- O’Brien PJ, Siraki AG, Shangari N. Aldehyde sources, metabolism, molecular toxicity mechanisms, and possible effects on human health. Crit Rev Toxicol. 2005;35:609–62. - PubMed
-
- Esterbauer H, Schaur RJ, Zollner H. Chemistry and biochemistry of 4-hydroxynonenal, malonaldehyde and related aldehydes. Free Radic Biol Med. 1991;11:81–128. A landmark paper concerning the chemical properties and reactivity of aldehydes. - PubMed
-
- Marchitti SA, Deitrich RA, Vasiliou V. Neurotoxicity and metabolism of the catecholamine-derived 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetaldehyde and 3,4-dihydroxyphenylglycolaldehyde: the role of aldehyde dehydrogenase. Pharmacol Rev. 2007:59125–50. A comprehensive recent review paper. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
