Distinct flippases translocate glycerophospholipids and oligosaccharide diphosphate dolichols across the endoplasmic reticulum
- PMID: 18597486
- PMCID: PMC2646664
- DOI: 10.1021/bi800723n
Distinct flippases translocate glycerophospholipids and oligosaccharide diphosphate dolichols across the endoplasmic reticulum
Abstract
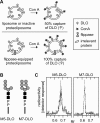
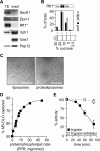
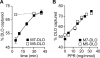
Transbilayer movement, or flip-flop, of lipids across the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is required for membrane biogenesis, protein glycosylation, and GPI anchoring. Specific ER membrane proteins, flippases, are proposed to facilitate lipid flip-flop, but no ER flippase has been biochemically identified. The glycolipid Glc 3Man 9GlcNAc 2-PP-dolichol is the oligosaccharide donor for protein N-glycosylation reactions in the ER lumen. Synthesis of Glc 3Man 9GlcNAc 2-PP-dolichol is initiated on the cytoplasmic side of the ER and completed on the lumenal side, requiring flipping of the intermediate Man 5GlcNAc 2-PP-dolichol (M5-DLO) across the ER. Here we report the reconstitution of M5-DLO flipping in proteoliposomes generated from Triton X-100-extracted Saccharomyces cerevisiae microsomal proteins. Flipping was assayed by using the lectin Concanavalin A to capture M5-DLOs that had been translocated from the inner to the outer leaflet of the vesicles. M5-DLO flipping in the reconstituted system was ATP-independent and trypsin-sensitive and required a membrane protein(s) that sedimented at approximately 4 S. Man 7GlcNAc 2-PP-dolichol, a higher-order lipid intermediate, was flipped >10-fold more slowly than M5-DLO at 25 degrees C. Chromatography on Cibacron Blue dye resin enriched M5-DLO flippase activity approximately 5-fold and resolved it from both the ER glycerophospholipid flippase activity and the genetically identified flippase candidate Rft1 [Helenius, J., et al. (2002) Nature 415, 447-450]. The latter result indicates that Rft1 is not the M5-DLO flippase. Our data (i) demonstrate that the ER has at least two distinct flippase proteins, each specifically capable of translocating a class of phospholipid, and (ii) provide, for the first time, a biochemical means of identifying the M5-DLO flippase.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Specific transbilayer translocation of dolichol-linked oligosaccharides by an endoplasmic reticulum flippase.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Jan 20;106(3):767-72. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0810225106. Epub 2009 Jan 7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. PMID: 19129492 Free PMC article.
-
Stereoselective transbilayer translocation of mannosyl phosphoryl dolichol by an endoplasmic reticulum flippase.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Jun 22;107(25):11289-94. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1002408107. Epub 2010 Jun 7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20534553 Free PMC article.
-
Flip-flop of fluorescently labeled phospholipids in proteoliposomes reconstituted with Saccharomyces cerevisiae microsomal proteins.Eukaryot Cell. 2007 Sep;6(9):1625-34. doi: 10.1128/EC.00198-07. Epub 2007 Jul 6. Eukaryot Cell. 2007. PMID: 17616631 Free PMC article.
-
The ins(ide) and out(side) of dolichyl phosphate biosynthesis and recycling in the endoplasmic reticulum.Glycobiology. 2001 May;11(5):61R-70R. doi: 10.1093/glycob/11.5.61r. Glycobiology. 2001. PMID: 11425794 Review.
-
Transmembrane movement of dolichol linked carbohydrates during N-glycoprotein biosynthesis in the endoplasmic reticulum.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2002 Jun;13(3):171-8. doi: 10.1016/s1084-9521(02)00045-9. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2002. PMID: 12137737 Review.
Cited by
-
AglR is required for addition of the final mannose residue of the N-linked glycan decorating the Haloferax volcanii S-layer glycoprotein.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012 Oct;1820(10):1664-70. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2012.06.014. Epub 2012 Jun 27. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012. PMID: 22750201 Free PMC article.
-
A Fluorescence-based Assay for Measuring Phospholipid Scramblase Activity in Giant Unilamellar Vesicles.Bio Protoc. 2022 Mar 20;12(6):e4366. doi: 10.21769/BioProtoc.4366. eCollection 2022 Mar 20. Bio Protoc. 2022. PMID: 35434199 Free PMC article.
-
Biochemical characterization and membrane topology of Alg2 from Saccharomyces cerevisiae as a bifunctional alpha1,3- and 1,6-mannosyltransferase involved in lipid-linked oligosaccharide biosynthesis.J Biol Chem. 2009 May 1;284(18):11900-12. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M806416200. Epub 2009 Mar 12. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19282279 Free PMC article.
-
Suppression of Rft1 expression does not impair the transbilayer movement of Man5GlcNAc2-P-P-dolichol in sealed microsomes from yeast.J Biol Chem. 2009 Jul 24;284(30):19835-42. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.000893. Epub 2009 Jun 3. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19494107 Free PMC article.
-
Role of flippases, scramblases and transfer proteins in phosphatidylserine subcellular distribution.Traffic. 2015 Jan;16(1):35-47. doi: 10.1111/tra.12233. Epub 2014 Nov 5. Traffic. 2015. PMID: 25284293 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hanover J. A.; Lennarz W. J. (1980) N-Linked glycoprotein assembly. Evidence that oligosaccharide attachment occurs within the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum. J. Biol. Chem. 255, 3600–3604. - PubMed
-
- Snider M. D.; Robbins P. W. (1982) Transmembrane organization of protein glycosylation: Mature oligosaccharide-lipid is located on the luminal side of microsomes from Chinese hamster ovary cells. J. Biol. Chem. 257, 6796–6801. - PubMed
-
- Hirschberg C. B.; Snider M. D. (1987) Topography of glycosylation in the rough endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 56, 63–87. - PubMed
-
- Lennarz W. J. (1987) Protein glycosylation in the endoplasmic reticulum: Current topological issues. Biochemistry 26, 7205–7210. - PubMed
-
- Helenius J.; Aebi M. (2002) Transmembrane movement of dolichol-linked carbohydrates during N-glycoprotein biosynthesis in the endoplasmic reticulum. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 13, 171–178. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

