A polymorphism in CALHM1 influences Ca2+ homeostasis, Abeta levels, and Alzheimer's disease risk
- PMID: 18585350
- PMCID: PMC2577842
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.05.048
A polymorphism in CALHM1 influences Ca2+ homeostasis, Abeta levels, and Alzheimer's disease risk
Abstract
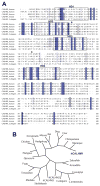
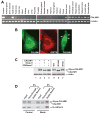
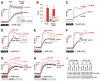
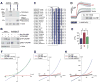
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a genetically heterogeneous disorder characterized by early hippocampal atrophy and cerebral amyloid-beta (Abeta) peptide deposition. Using TissueInfo to screen for genes preferentially expressed in the hippocampus and located in AD linkage regions, we identified a gene on 10q24.33 that we call CALHM1. We show that CALHM1 encodes a multipass transmembrane glycoprotein that controls cytosolic Ca(2+) concentrations and Abeta levels. CALHM1 homomultimerizes, shares strong sequence similarities with the selectivity filter of the NMDA receptor, and generates a large Ca(2+) conductance across the plasma membrane. Importantly, we determined that the CALHM1 P86L polymorphism (rs2986017) is significantly associated with AD in independent case-control studies of 3404 participants (allele-specific OR = 1.44, p = 2 x 10(-10)). We further found that the P86L polymorphism increases Abeta levels by interfering with CALHM1-mediated Ca(2+) permeability. We propose that CALHM1 encodes an essential component of a previously uncharacterized cerebral Ca(2+) channel that controls Abeta levels and susceptibility to late-onset AD.
Figures
Comment in
-
No association between CALHM1 and Alzheimer's disease risk.Cell. 2008 Dec 12;135(6):993-4; author reply 994-6. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.11.030. Cell. 2008. PMID: 19070563 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
CALHM1 and its polymorphism P86L differentially control Ca²⁺homeostasis, mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling, and cell vulnerability upon exposure to amyloid β.Aging Cell. 2015 Dec;14(6):1094-102. doi: 10.1111/acel.12403. Epub 2015 Sep 29. Aging Cell. 2015. PMID: 26416646 Free PMC article.
-
CALHM1 P86L polymorphism modulates CSF Aβ levels in cognitively healthy individuals at risk for Alzheimer's disease.Mol Med. 2011 Sep-Oct;17(9-10):974-9. doi: 10.2119/molmed.2011.00154. Epub 2011 May 24. Mol Med. 2011. PMID: 21629967 Free PMC article.
-
Rare variants in calcium homeostasis modulator 1 (CALHM1) found in early onset Alzheimer's disease patients alter calcium homeostasis.PLoS One. 2013 Sep 17;8(9):e74203. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0074203. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24069280 Free PMC article.
-
Linking calcium to Abeta and Alzheimer's disease.Neuron. 2008 Jul 31;59(2):190-4. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2008.07.013. Neuron. 2008. PMID: 18667147 Review.
-
Calcium homeostasis modulator (CALHM) ion channels.Pflugers Arch. 2016 Mar;468(3):395-403. doi: 10.1007/s00424-015-1757-6. Epub 2015 Nov 25. Pflugers Arch. 2016. PMID: 26603282 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Extracellular CIRP Activates the IL-6Rα/STAT3/Cdk5 Pathway in Neurons.Mol Neurobiol. 2021 Aug;58(8):3628-3640. doi: 10.1007/s12035-021-02368-z. Epub 2021 Mar 30. Mol Neurobiol. 2021. PMID: 33783711 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium homeostasis modulator 1 (CALHM1) is the pore-forming subunit of an ion channel that mediates extracellular Ca2+ regulation of neuronal excitability.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Jul 10;109(28):E1963-71. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1204023109. Epub 2012 Jun 18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 22711817 Free PMC article.
-
Cryo-electron microscopy structure of CLHM1 ion channel from Caenorhabditis elegans.Protein Sci. 2020 Aug;29(8):1803-1815. doi: 10.1002/pro.3904. Epub 2020 Jun 30. Protein Sci. 2020. PMID: 32557855 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic variability of the gene cluster CALHM 1-3 in sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease.Prion. 2012 Sep-Oct;6(4):407-12. doi: 10.4161/pri.20785. Epub 2012 Aug 9. Prion. 2012. PMID: 22874670 Free PMC article.
-
CALHM1 controls the Ca²⁺-dependent MEK, ERK, RSK and MSK signaling cascade in neurons.J Cell Sci. 2013 Mar 1;126(Pt 5):1199-206. doi: 10.1242/jcs.117135. Epub 2013 Jan 23. J Cell Sci. 2013. PMID: 23345406 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Berridge MJ, Bootman MD, Roderick HL. Calcium signalling: dynamics, homeostasis and remodelling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2003;4:517–529. - PubMed
-
- Bertram L, Blacker D, Mullin K, Keeney D, Jones J, Basu S, Yhu S, McInnis MG, Go RC, Vekrellis K, et al. Evidence for genetic linkage of Alzheimer’s disease to chromosome 10q. Science. 2000;290:2302–2303. - PubMed
-
- Bertram L, McQueen MB, Mullin K, Blacker D, Tanzi RE. Systematic meta-analyses of Alzheimer disease genetic association studies: the AlzGene database. Nat Genet. 2007;39:17–23. - PubMed
-
- Blacker D, Bertram L, Saunders AJ, Moscarillo TJ, Albert MS, Wiener H, Perry RT, Collins JS, Harrell LE, Go RC, et al. Results of a high-resolution genome screen of 437 Alzheimer’s disease families. Hum Mol Genet. 2003;12:23–32. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

