Atherosclerosis: evidence for impairment of resolution of vascular inflammation governed by specific lipid mediators
- PMID: 18559988
- PMCID: PMC2537438
- DOI: 10.1096/fj.08-112201
Atherosclerosis: evidence for impairment of resolution of vascular inflammation governed by specific lipid mediators
Abstract
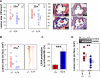
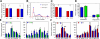
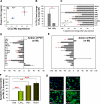
Atherosclerosis is now recognized as an inflammatory disease involving the vascular wall. Recent results indicate that acute inflammation does not simply passively resolve as previously assumed but is actively terminated by a homeostatic process that is governed by specific lipid-derived mediators initiated by lipoxygenases. Experiments with animals and humans support a proinflammatory role for the 5-lipoxygenase system. In contrast, results from animal experiments show a range of responses with the 12/15-lipoxygenase pathways in atherosclerosis. To date, the only two clinical epidemiology human studies both support an antiatherogenic role for 12/15-lipoxygenase downstream actions. We tested the hypothesis that atherosclerosis results from a failure in the resolution of local inflammation by analyzing apolipoprotein E-deficient mice with 1) global leukocyte 12/15-lipoxygenase deficiency, 2) normal enzyme expression, or 3) macrophage-specific 12/15-lipoxygenase overexpression. Results from these indicate that 12/15-lipoxygenase expression protects mice against atherosclerosis via its role in the local biosynthesis of lipid mediators, including lipoxin A(4), resolvin D1, and protectin D1. These mediators exert potent agonist actions on macrophages and vascular endothelial cells that can control the magnitude of the local inflammatory response. Taken together, these findings suggest that a failure of local endogenous resolution mechanisms may underlie the unremitting inflammation that fuels atherosclerosis.
Figures

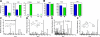


Similar articles
-
A role for 12/15-lipoxygenase-derived proresolving mediators in postoperative ileus: protectin DX-regulated neutrophil extravasation.J Leukoc Biol. 2016 Feb;99(2):231-9. doi: 10.1189/jlb.3HI0515-189R. Epub 2015 Aug 20. J Leukoc Biol. 2016. PMID: 26292977
-
Protective activities of distinct omega-3 enriched oils are linked to their ability to upregulate specialized pro-resolving mediators.PLoS One. 2020 Dec 16;15(12):e0242543. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0242543. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 33326419 Free PMC article.
-
Critical role of macrophage 12/15-lipoxygenase for atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice.Circulation. 2004 Oct 5;110(14):2024-31. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000143628.37680.F6. Epub 2004 Sep 27. Circulation. 2004. PMID: 15451785
-
Potential role of the lipoxygenase derived lipid mediators in atherosclerosis: leukotrienes, lipoxins and resolvins.Clin Chem Lab Med. 2010 Aug;48(8):1063-73. doi: 10.1515/CCLM.2010.212. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2010. PMID: 20441482 Review.
-
Inflammation and immune regulation by 12/15-lipoxygenases.Prog Lipid Res. 2006 Jul;45(4):334-56. doi: 10.1016/j.plipres.2006.02.003. Epub 2006 Mar 31. Prog Lipid Res. 2006. PMID: 16678271 Review.
Cited by
-
LXA4 actions direct fibroblast function and wound closure.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015 Sep 4;464(4):1072-1077. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.07.076. Epub 2015 Jul 17. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015. PMID: 26188508 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment With a Marine Oil Supplement Alters Lipid Mediators and Leukocyte Phenotype in Healthy Patients and Those With Peripheral Artery Disease.J Am Heart Assoc. 2020 Aug 4;9(15):e016113. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.120.016113. Epub 2020 Jul 22. J Am Heart Assoc. 2020. PMID: 32696697 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Itaconate suppresses atherosclerosis by activating a Nrf2-dependent antiinflammatory response in macrophages in mice.J Clin Invest. 2023 Dec 12;134(3):e173034. doi: 10.1172/JCI173034. J Clin Invest. 2023. PMID: 38085578 Free PMC article.
-
Lipoxin A4 inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced production of inflammatory cytokines in keratinocytes by up-regulating SOCS2 and down-regulating TRAF6.J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2015 Jun;35(3):426-431. doi: 10.1007/s11596-015-1448-8. Epub 2015 Jun 14. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2015. PMID: 26072084
-
Defective phagocytosis of apoptotic cells by macrophages in atherosclerotic lesions of ob/ob mice and reversal by a fish oil diet.Circ Res. 2009 Nov 20;105(11):1072-82. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.109.199570. Epub 2009 Oct 15. Circ Res. 2009. PMID: 19834009 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hansson G K. Mechanisms of disease-Inflammation, atherosclerosis, and coronary artery disease. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:1685–1695. - PubMed
-
- Libby P. Inflammation in atherosclerosis. Nature. 2002;420:868–874. - PubMed
-
- Stary H C, Chandler A B, Glagov S, Guyton J R, Insull W, Rosenfeld M E, Schaffer S A, Schwartz C J, Wagner W D, Wissler R W. A definition of initial, fatty streak, and intermediate lesions of atherosclerosis—a report from the committee on vascular-lesions of the Council on Arteriosclerosis, American-Heart-Association. Circulation. 1994;89:2462–2478. - PubMed
-
- Stary H C. Evolution and progression of atherosclerotic lesions in coronary-arteries of children and young-adults. Arteriosclerosis. 1989;9:I19–I32. - PubMed
-
- Serhan C N. Resolution phase of inflammation: novel endogenous anti-inflammatory and proresolving lipid mediators and pathways. Ann Rev Immunol. 2007;25:101–137. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

