The Yin and Yang of interleukin-21 in allergy, autoimmunity and cancer
- PMID: 18554883
- PMCID: PMC2546604
- DOI: 10.1016/j.coi.2008.02.004
The Yin and Yang of interleukin-21 in allergy, autoimmunity and cancer
Abstract
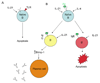
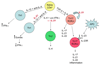
IL-21 is a type I cytokine that like IL-2, IL-4, IL-7, IL-9, and IL-15 shares the common cytokine receptor gamma chain, gamma(c). IL-21 is produced by activated CD4(+) T cells, NKT cells, and Th17 cells and has pleiotropic actions on a range of lymphoid lineages. IL-21 regulates immunoglobulin production and drives B cell terminal differentiation into plasma cells, cooperatively expands CD8(+) T cells and drives Th17 differentiation, has inhibitory effects on antigen presentation by dendritic cells, and can be pro-apoptotic for B and NK cells. Moreover, IL-21 has potent anti-tumor effects and is implicated in the development of autoimmune diseases. Regulating IL-21 actions in vivo therefore has clinical potential for a range of diseases and is an area of active investigation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Interleukin-21: basic biology and implications for cancer and autoimmunity.Annu Rev Immunol. 2008;26:57-79. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.26.021607.090316. Annu Rev Immunol. 2008. PMID: 17953510 Review.
-
IL-21: roles in immunopathology and cancer therapy.Tissue Antigens. 2009 Dec;74(6):467-79. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.2009.01382.x. Epub 2009 Oct 21. Tissue Antigens. 2009. PMID: 19845910 Review.
-
The role of interleukin-21 in HIV infection.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2012 Aug-Oct;23(4-5):173-80. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2012.05.004. Epub 2012 Jul 2. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2012. PMID: 22763176 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Il-21 enhances NK cell activation and cytolytic activity and induces Th17 cell differentiation in inflammatory bowel disease.Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2009 Aug;15(8):1133-44. doi: 10.1002/ibd.20923. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2009. PMID: 19322899
-
Interleukin 21: a cytokine/cytokine receptor system that has come of age.J Leukoc Biol. 2008 Aug;84(2):348-56. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0308149. Epub 2008 May 8. J Leukoc Biol. 2008. PMID: 18467657 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Plasma cells negatively regulate the follicular helper T cell program.Nat Immunol. 2010 Dec;11(12):1110-8. doi: 10.1038/ni.1954. Epub 2010 Oct 31. Nat Immunol. 2010. PMID: 21037578 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of interleukin-21 in the regulation of colitis-associated colon cancer.J Exp Med. 2011 Oct 24;208(11):2279-90. doi: 10.1084/jem.20111106. Epub 2011 Oct 10. J Exp Med. 2011. PMID: 21987656 Free PMC article.
-
[Roles of interleukin-21 and its receptor in autoimmune diseases].Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2016 May;18(5):466-71. doi: 10.7499/j.issn.1008-8830.2016.05.017. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2016. PMID: 27165599 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
Signalling and putative therapeutic molecules on the regulation of synoviocyte signalling in rheumatoid arthritis.Bone Joint Res. 2021 Apr;10(4):285-297. doi: 10.1302/2046-3758.104.BJR-2020-0331.R1. Bone Joint Res. 2021. PMID: 33890482 Free PMC article.
-
IL-21/IL-21R Regulates the Neutrophil-Mediated Pathologic Immune Response during Chlamydial Respiratory Infection.Mediators Inflamm. 2022 Jun 1;2022:4322092. doi: 10.1155/2022/4322092. eCollection 2022. Mediators Inflamm. 2022. PMID: 35693111 Free PMC article.
References
-
-
Spolski R, Leonard WJ. Interleukin-21: Basic Biology and Implications for Cancer and Autoimmunity. Annu Rev Immunol. 2007 This review offers the most comprehensive review of the regulation, signaling, and biology of IL-21, including actions within both lymphoid and myeloid cell lineages.
-
-
- Noguchi M, Yi H, Rosenblatt HM, Filipovich AH, Adelstein S, Modi WS, McBride OW, Leonard WJ. Interleukin-2 receptor gamma chain mutation results in X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency in humans. Cell. 1993;73:147–157. - PubMed
-
- Ozaki K, Spolski R, Feng CG, Qi CF, Cheng J, Sher A, Morse HC, 3rd, Liu C, Schwartzberg PL, Leonard WJ. A critical role for IL-21 in regulating immunoglobulin production. Science. 2002;298:1630–1634. - PubMed
-
- Kim HP, Korn LL, Gamero AM, Leonard WJ. Calcium-dependent activation of interleukin-21 gene expression in T cells. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:25291–25297. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

