Integrated structural model and membrane targeting mechanism of the human ESCRT-II complex
- PMID: 18539118
- PMCID: PMC2475506
- DOI: 10.1016/j.devcel.2008.04.004
Integrated structural model and membrane targeting mechanism of the human ESCRT-II complex
Abstract
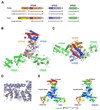
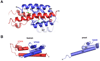
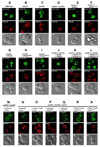
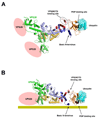
ESCRT-II plays a pivotal role in receptor downregulation and multivesicular body biogenesis and is conserved from yeast to humans. The crystal structures of two human ESCRT-II complex structures have been determined at 2.6 and 2.9 A resolution, respectively. The complex has three lobes and contains one copy each of VPS22 and VPS36 and two copies of VPS25. The structure reveals a dynamic helical domain to which both the VPS22 and VPS36 subunits contribute that connects the GLUE domain to the rest of the ESCRT-II core. Hydrodynamic analysis shows that intact ESCRT-II has a compact, closed conformation. ESCRT-II binds to the ESCRT-I VPS28 C-terminal domain subunit through a helix immediately C-terminal to the VPS36-GLUE domain. ESCRT-II is targeted to endosomal membranes by the lipid-binding activities of both the Vps36 GLUE domain and the first helix of Vps22. These data provide a unifying structural and functional framework for the ESCRT-II complex.
Figures


Similar articles
-
ESCRT-II, an endosome-associated complex required for protein sorting: crystal structure and interactions with ESCRT-III and membranes.Dev Cell. 2004 Oct;7(4):559-69. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2004.09.003. Dev Cell. 2004. PMID: 15469844
-
Crystal structure of subunit VPS25 of the endosomal trafficking complex ESCRT-II.BMC Struct Biol. 2004 Dec 4;4(1):10. doi: 10.1186/1472-6807-4-10. BMC Struct Biol. 2004. PMID: 15579210 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of the ESCRT-II endosomal trafficking complex.Nature. 2004 Sep 9;431(7005):221-5. doi: 10.1038/nature02914. Epub 2004 Aug 25. Nature. 2004. PMID: 15329733
-
Structural studies of phosphoinositide 3-kinase-dependent traffic to multivesicular bodies.Biochem Soc Symp. 2007;(74):47-57. doi: 10.1042/BSS0740047. Biochem Soc Symp. 2007. PMID: 17233579 Review.
-
Protein sorting into multivesicular endosomes.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2003 Aug;15(4):446-55. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(03)00080-2. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 12892785 Review.
Cited by
-
PI(3,4)P2-mediated cytokinetic abscission prevents early senescence and cataract formation.Science. 2021 Dec 10;374(6573):eabk0410. doi: 10.1126/science.abk0410. Epub 2021 Dec 10. Science. 2021. PMID: 34882480 Free PMC article.
-
Vesicle formation within endosomes: An ESCRT marks the spot.Commun Integr Biol. 2012 Jan 1;5(1):50-6. doi: 10.4161/cib.18208. Commun Integr Biol. 2012. PMID: 22482010 Free PMC article.
-
Membrane budding.Cell. 2010 Dec 10;143(6):875-87. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2010.11.030. Cell. 2010. PMID: 21145455 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The RNA-binding complex ESCRT-II in Xenopus laevis eggs recognizes purine-rich sequences through its subunit, Vps25.J Biol Chem. 2018 Aug 10;293(32):12593-12605. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.003718. Epub 2018 Jun 14. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29903915 Free PMC article.
-
Constitutively active ESCRT-II suppresses the MVB-sorting phenotype of ESCRT-0 and ESCRT-I mutants.Mol Biol Cell. 2015 Feb 1;26(3):554-68. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E14-10-1469. Epub 2014 Dec 10. Mol Biol Cell. 2015. PMID: 25501366 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alam SL, Langelier C, Whitby FG, Koirala S, Robinson H, Hill CP, Sundquist WI. Structural basis for ubiquitin recognition by the human ESCRT-II EAP45 GLUE domain. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2006;13:1029–1030. - PubMed
-
- Babst M. A Protein's Final ESCRT. Traffic. 2005;6:2–9. - PubMed
-
- Babst M, Katzmann DJ, Snyder WB, Wendland B, Emr SD. Endosome-associated complex, ESCRT-II, recruits transport machinery for protein sorting at the multivesicular body. Dev. Cell. 2002;3:283–289. - PubMed
-
- Bieniasz PD. Late budding domains and host proteins in enveloped virus release. Virology. 2006;344:55–63. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

