Pulmonary hypertension: therapeutic targets within the serotonin system
- PMID: 18536742
- PMCID: PMC2579665
- DOI: 10.1038/bjp.2008.241
Pulmonary hypertension: therapeutic targets within the serotonin system
Abstract
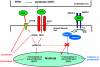
Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) is characterized by a sustained and progressive elevation in pulmonary arterial pressure and pulmonary vascular remodelling leading to right heart failure and death. Prognosis is poor and novel therapeutic approaches are needed. The serotonin hypothesis of PAH originated in the 1960s after an outbreak of the disease was reported among patients taking the anorexigenic drugs aminorex and fenfluramine. These are indirect serotonergic agonists and serotonin transporter substrates. Since then many advances have been made in our understanding of the role of serotonin in the pathobiology of PAH. The rate-limiting enzyme in the synthesis of serotonin is tryptophan hydroxylase (Tph). Serotonin is synthesized, through Tph1, in the endothelial cells of the pulmonary artery and can then act on underlying pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells and pulmonary arterial fibroblasts in a paracrine fashion causing constriction and remodelling. These effects of serotonin can be mediated through both the serotonin transporter and serotonin receptors. This review will discuss our current understanding of 'the serotonin hypothesis' of PAH and highlight possible therapeutic targets within the serotonin system.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Serotonin and pulmonary hypertension--from bench to bedside?Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2009 Jun;9(3):281-6. doi: 10.1016/j.coph.2009.02.005. Epub 2009 Mar 13. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19286424 Review.
-
The serotonin hypothesis of pulmonary hypertension revisited.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2010;661:309-22. doi: 10.1007/978-1-60761-500-2_20. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2010. PMID: 20204739 Review.
-
[Serotonin hypothesis and pulmonary artery hypertension].Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2014 Jun 6;68:738-48. doi: 10.5604/17322693.1107860. Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2014. PMID: 24934532 Review. Polish.
-
Serotonin and Pulmonary Hypertension; Sex and Drugs and ROCK and Rho.Compr Physiol. 2022 Aug 29;12(4):4103-4118. doi: 10.1002/cphy.c220004. Compr Physiol. 2022. PMID: 36036567 Review.
-
Pulmonary hypertension and the serotonin hypothesis: where are we now?Int J Clin Pract Suppl. 2007 Sep;(156):27-31. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-1241.2007.01497.x. Int J Clin Pract Suppl. 2007. PMID: 17663674 Review.
Cited by
-
The Xanthine Derivative KMUP-1 Attenuates Serotonin-Induced Vasoconstriction and K⁺-Channel Inhibitory Activity via the PKC Pathway in Pulmonary Arteries.Int J Biol Sci. 2015 Apr 25;11(6):633-42. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.11127. eCollection 2015. Int J Biol Sci. 2015. PMID: 25999786 Free PMC article.
-
Reduction of the serotonin 5-HT1B and 5-HT2A receptor-mediated contraction of human pulmonary artery by the combined 5-HT1B receptor antagonist and serotonin transporter inhibitor LY393558.Pharmacol Rep. 2020 Jun;72(3):756-762. doi: 10.1007/s43440-020-00105-2. Epub 2020 Apr 24. Pharmacol Rep. 2020. PMID: 32333296 Free PMC article.
-
Pulmonary hypertension: the science behind the disease spectrum.Eur Respir Rev. 2012 Mar 1;21(123):19-26. doi: 10.1183/09059180.00008411. Eur Respir Rev. 2012. PMID: 22379170 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serotonin transporter interacts with the PDGFβ receptor in PDGF-BB-induced signaling and mitogenesis in pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2011 Mar;300(3):L486-97. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00237.2010. Epub 2010 Dec 24. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21186266 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of Genes and Proteins Expression Associating Serotonin Signaling Pathway in Lung and Pulmonary Artery Tissues of Dogs with Pulmonary Hypertension Secondary to Degenerative Mitral Valve Disease: The Preliminary Study.Vet Sci. 2022 Sep 28;9(10):530. doi: 10.3390/vetsci9100530. Vet Sci. 2022. PMID: 36288144 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abe K, Morikawa K, Hizume T, Uwatoku T, Oi K, Seto M, et al. Prostacyclin does not inhibit rho-kinase: an implication for the treatment of pulmonary hypertension. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2005;45:120–124. - PubMed
-
- Abe K, Shimokawa H, Morikawa K, Uwatoku T, Oi K, Matsumoto Y, et al. Long-term treatment with a Rho-kinase inhibitor improves monocrotaline-induced fatal pulmonary hypertension in rats. Circ Res. 2004;94:385–393. - PubMed
-
- Abenhaim L, Moride Y, Brenot F, Rich S, Benichou J, Kurz X, et al. Appetite-suppressant drugs and the risk of primary pulmonary hypertension. International Primary Pulmonary Hypertension Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1996;335:609–616. - PubMed
-
- Baloira A, Vilarino C, Leiro V, Valverde D. Mutations in the gene encoding bone morphogenetic protein receptor 2 in patients with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension. Arch Bronconeumol. 2008;44:29–34. - PubMed
-
- Blanpain C, Le Poul E, Parma J, Knoop C, Detheux M, Parmentier M, et al. Serotonin 5-HT2B receptor loss of function mutation in a patient with fenfluramine-associated primary pulmonary hypertension. Cardiovasc Res. 2003;60:518–528. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

