Amplified transmission of HIV-1: missing link in the HIV pandemic
- PMID: 18528475
- PMCID: PMC1500941
Amplified transmission of HIV-1: missing link in the HIV pandemic
Abstract
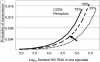
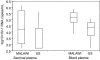
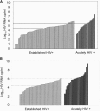
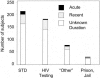
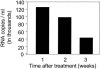
Sexual transmission of HIV most closely reflects the concentration of HIV in the genital tract; HIV in the genital tract of subjects with acute HIV and some "classical" STDS is 8-10 times greater than in control subjects. It seems likely that these latter subjects lead to spread of HIV. Accordingly, the state of North Carolina committed to HIV testing that detects subjects with acute, recent, and established infection. We tested 109,500 samples over 9 months. We found 563 people with undiagnosed HIV infection. The majority of subjects were in STD clinics. This included 23 subjects with (pre-seroconversion) acute HIV infection (HIV RNA positive, antibody negative). The median blood HIV was 209,000 copies/ml, more than 10 times higher than in subjects with established HIV infection. Recognizing the increased number of subjects with unrecognized acute HIV infection in STD clinics, we conducted similar studies in STD Clinics in Malawi and South Africa. Between 1 and 2% of subjects had undetected acute HIV infection. The median viral burden in blood of subjects in Malawi was greater than 1,000,000 copies/ml. STDS and HIV are often co-transmitted, and STDS set the stage for subsequent HIV transmission. Prevention of sexual transmission of HIV likely requires maximal suppression of genital tract HIV viral burden, either through treatment of STDS or use of antiretroviral agents.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prevalence of genital infections in medical inpatients in Blantyre, Malawi.J Infect. 1995 Jul;31(1):77-8. doi: 10.1016/s0163-4453(95)91674-1. J Infect. 1995. PMID: 8522842
-
Non-ulcerative sexually transmitted diseases as risk factors for HIV-1 transmission in women: results from a cohort study.AIDS. 1993 Jan;7(1):95-102. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199301000-00015. AIDS. 1993. PMID: 8442924
-
Trends of HIV-1 and sexually transmitted diseases among pregnant and postpartum women in urban Malawi.AIDS. 1998 Jan 22;12(2):197-203. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199802000-00010. AIDS. 1998. PMID: 9468369
-
HIV and sexually transmitted diseases: lethal synergy.Top HIV Med. 2004 Oct-Nov;12(4):104-7. Top HIV Med. 2004. PMID: 15516707 Review.
-
Effect of coinfection with STDs and of STD treatment on HIV shedding in genital-tract secretions: systematic review and data synthesis.Sex Transm Dis. 2000 May;27(5):243-8. doi: 10.1097/00007435-200005000-00001. Sex Transm Dis. 2000. PMID: 10821594 Review.
Cited by
-
The Impact of Genital Ulcers on HIV Transmission Has Been Underestimated-A Critical Review.Viruses. 2022 Mar 5;14(3):538. doi: 10.3390/v14030538. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 35336945 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sexually transmitted infections and HIV in the era of antiretroviral treatment and prevention: the biologic basis for epidemiologic synergy.J Int AIDS Soc. 2019 Aug;22 Suppl 6(Suppl Suppl 6):e25355. doi: 10.1002/jia2.25355. J Int AIDS Soc. 2019. PMID: 31468737 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic clustering analysis for HIV infection among MSM in Nigeria: implications for intervention.AIDS. 2020 Feb 1;34(2):227-236. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0000000000002409. AIDS. 2020. PMID: 31634185 Free PMC article.
-
Condom access: Associations with consistent condom use among female sex workers in two northern border cities of Mexico.AIDS Educ Prev. 2010 Oct;22(5):455-65. doi: 10.1521/aeap.2010.22.5.455. AIDS Educ Prev. 2010. PMID: 20973665 Free PMC article.
References
-
- UNAIDS. 2004 Report on the Global AIDS Epidemic ( http://www.unaids.org/bangkok2004/report.html)
-
- Royce AR, Seña A, Cates W, Cohen MS. Sexual transmission of HIV. N Engl J Med. 1997;336(15):1072–1078. - PubMed
-
- Galvin SR, Cohen MS. Sexual transmission of HIV. Nature Reviews Microbiology. 2004:33–42. - PubMed
-
- Gisselquist D, Rothenber R, Potterat JJ, Drucker E. HIV infections in sub-Saharan Africa not explained by sexual or vertical transmission. Int J STD AIDS. 2002;13:657–666. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
